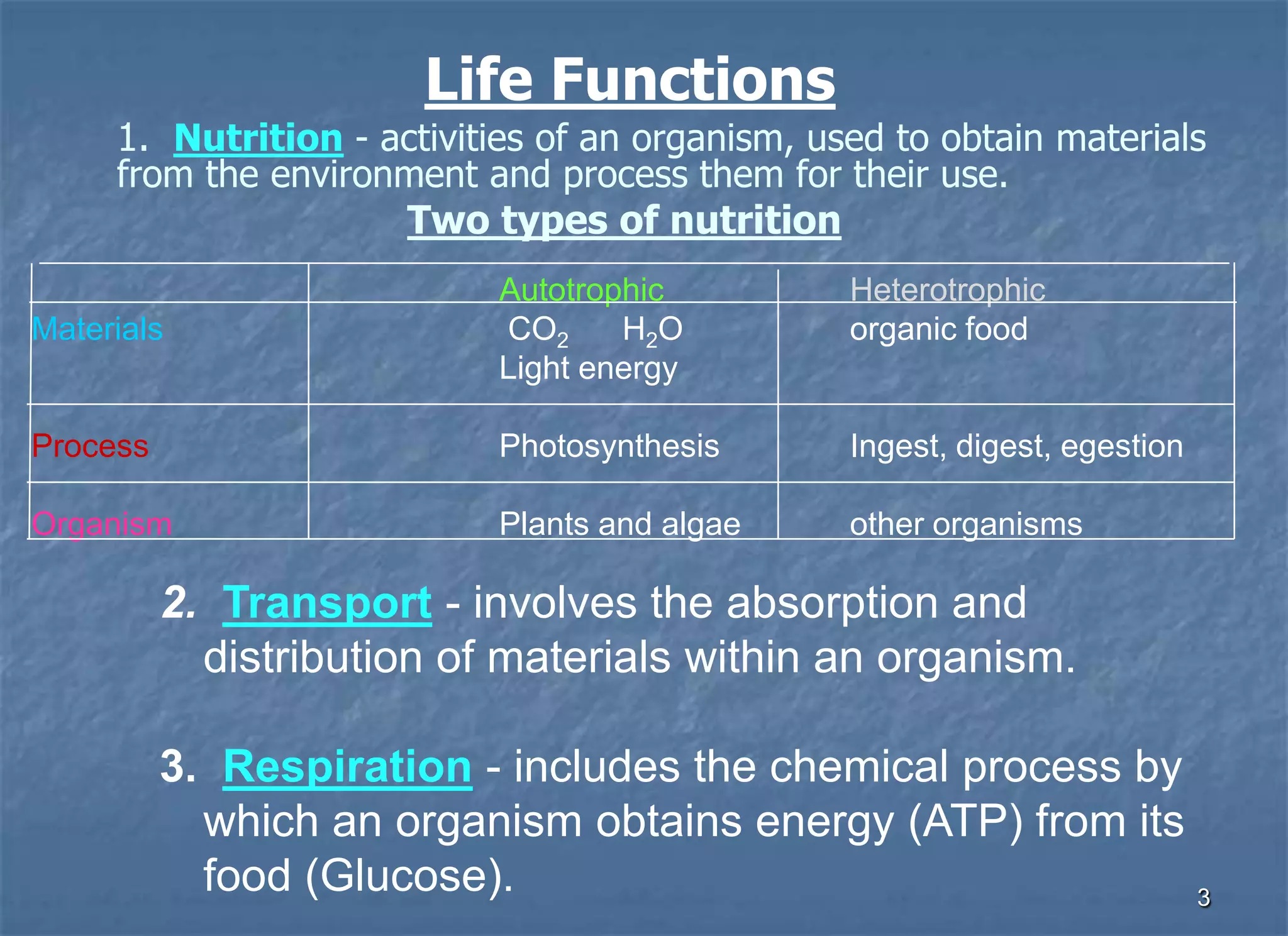
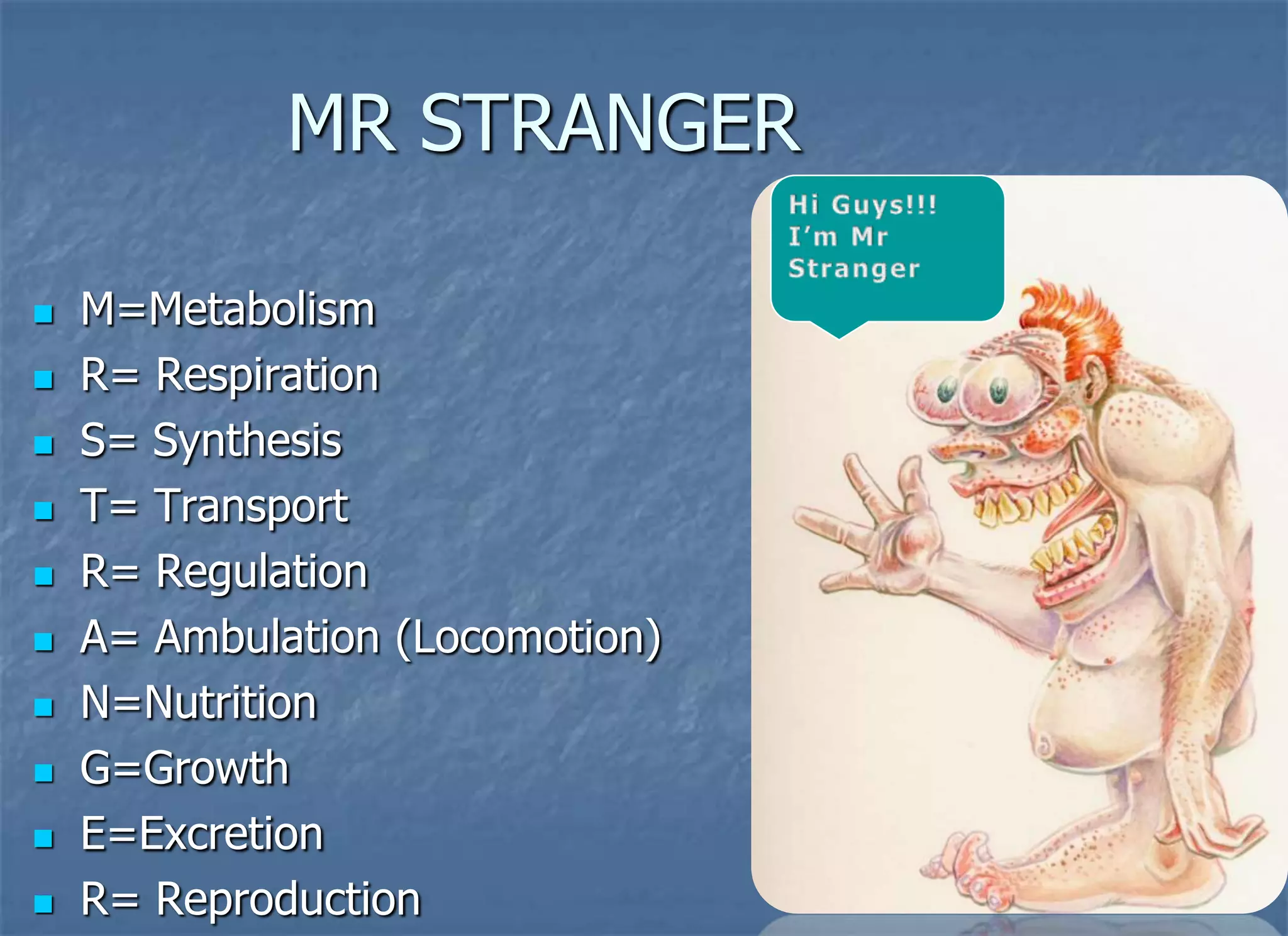
Biology is the study of life. All living organisms share certain characteristics and life functions including nutrition, transport, respiration, excretion, synthesis, regulation, growth, and reproduction. These life functions allow organisms to sustain life through metabolic activities and maintain homeostasis.