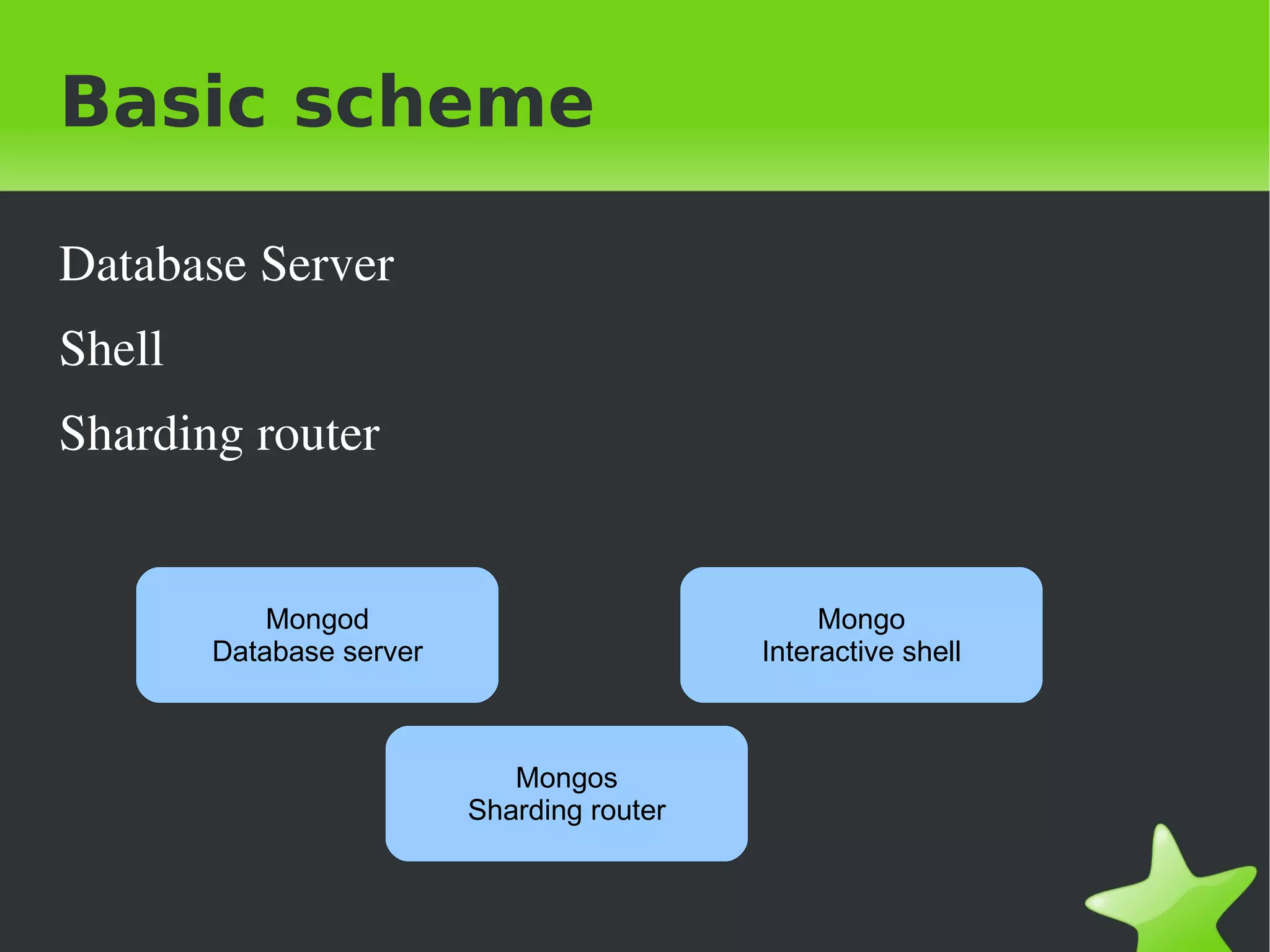
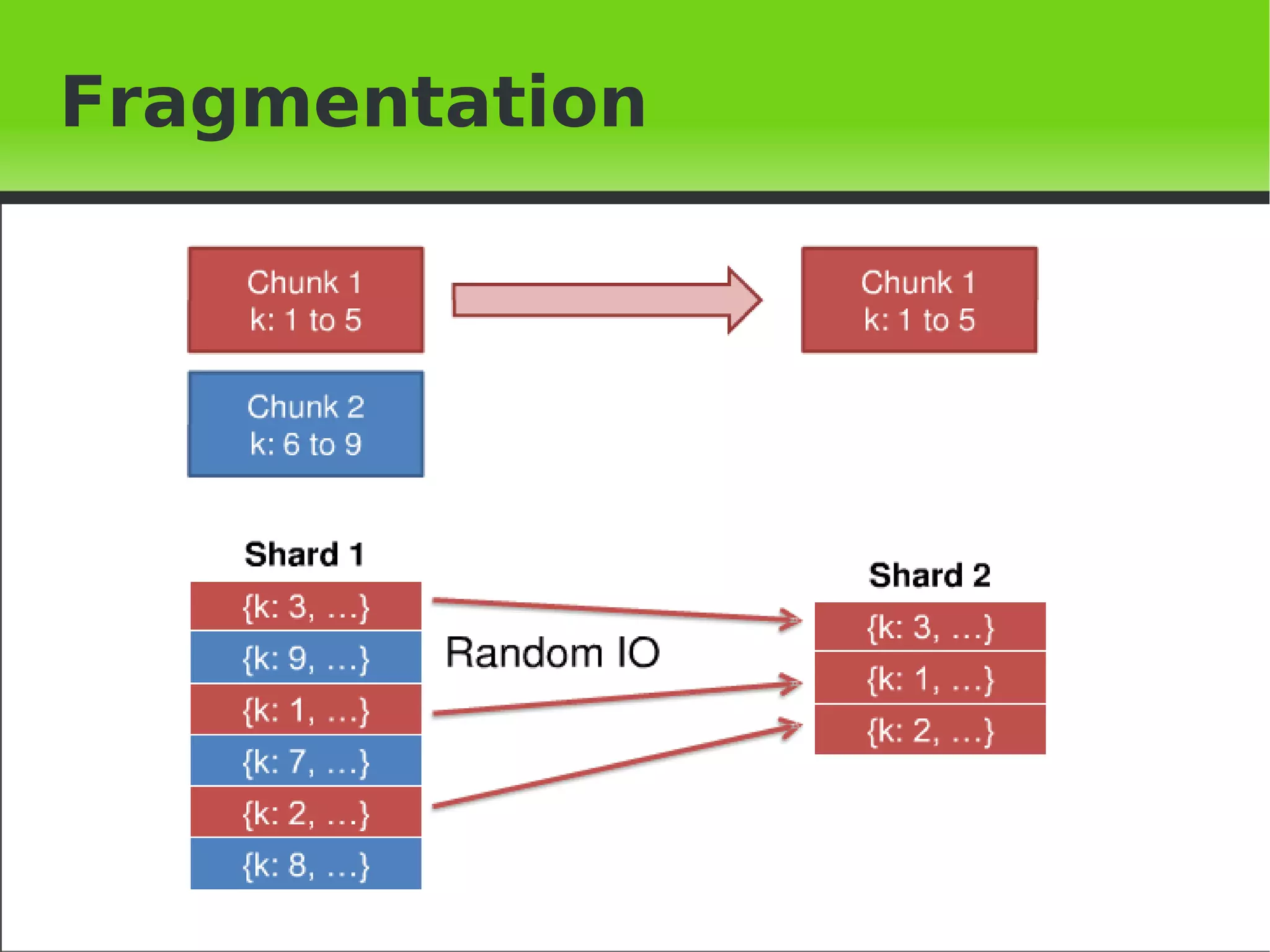
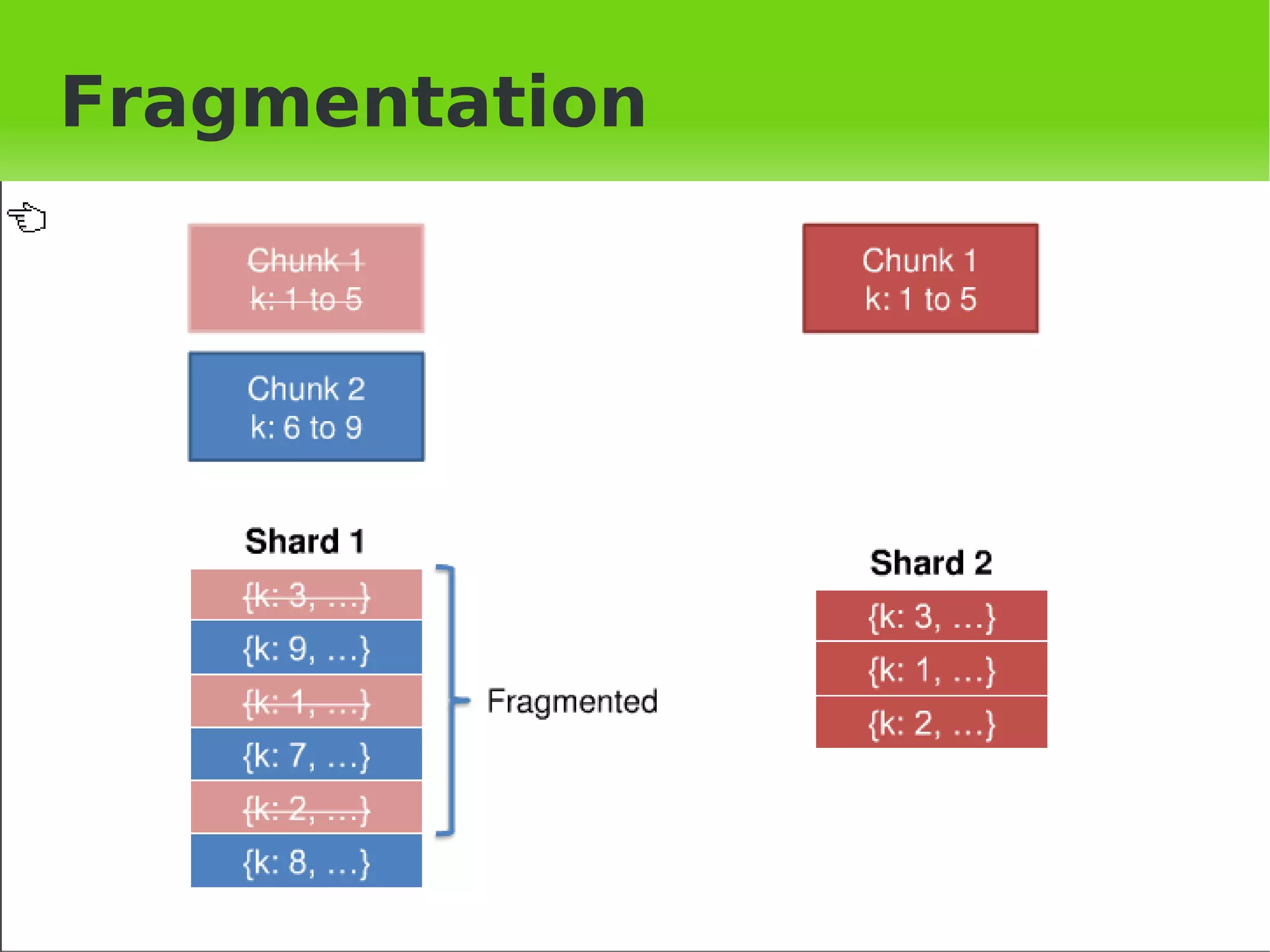
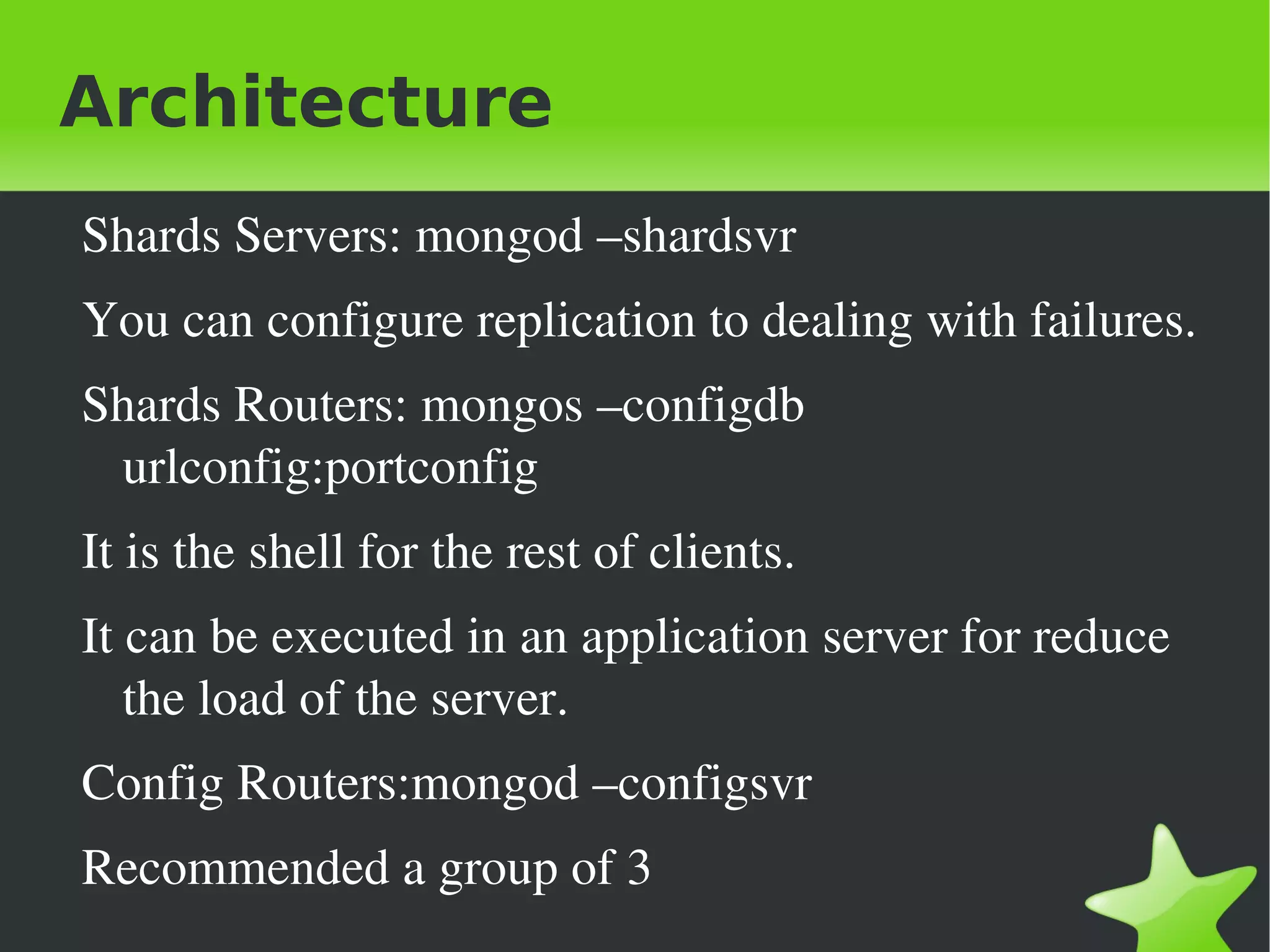
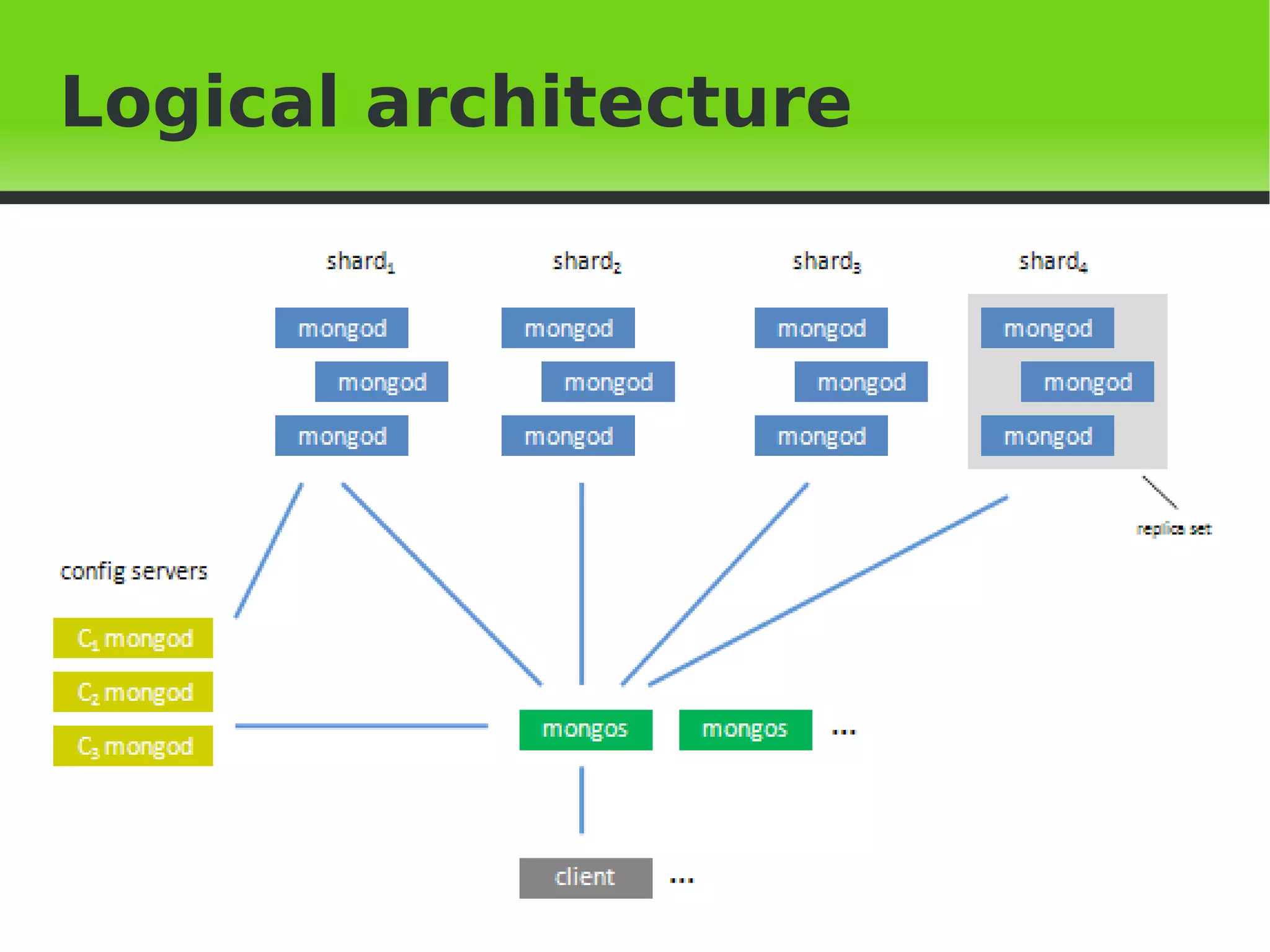
This document provides an introduction to MongoDB, including when to use and not use MongoDB, features of MongoDB like document structure, indexing, replication, sharding, and architecture. It outlines the basic MongoDB scheme including databases, collections, and documents. It describes concepts like replication, auto-sharding, and the logical and physical architecture of MongoDB. Finally, it provides steps for initial sharding configuration and backup recommendations.