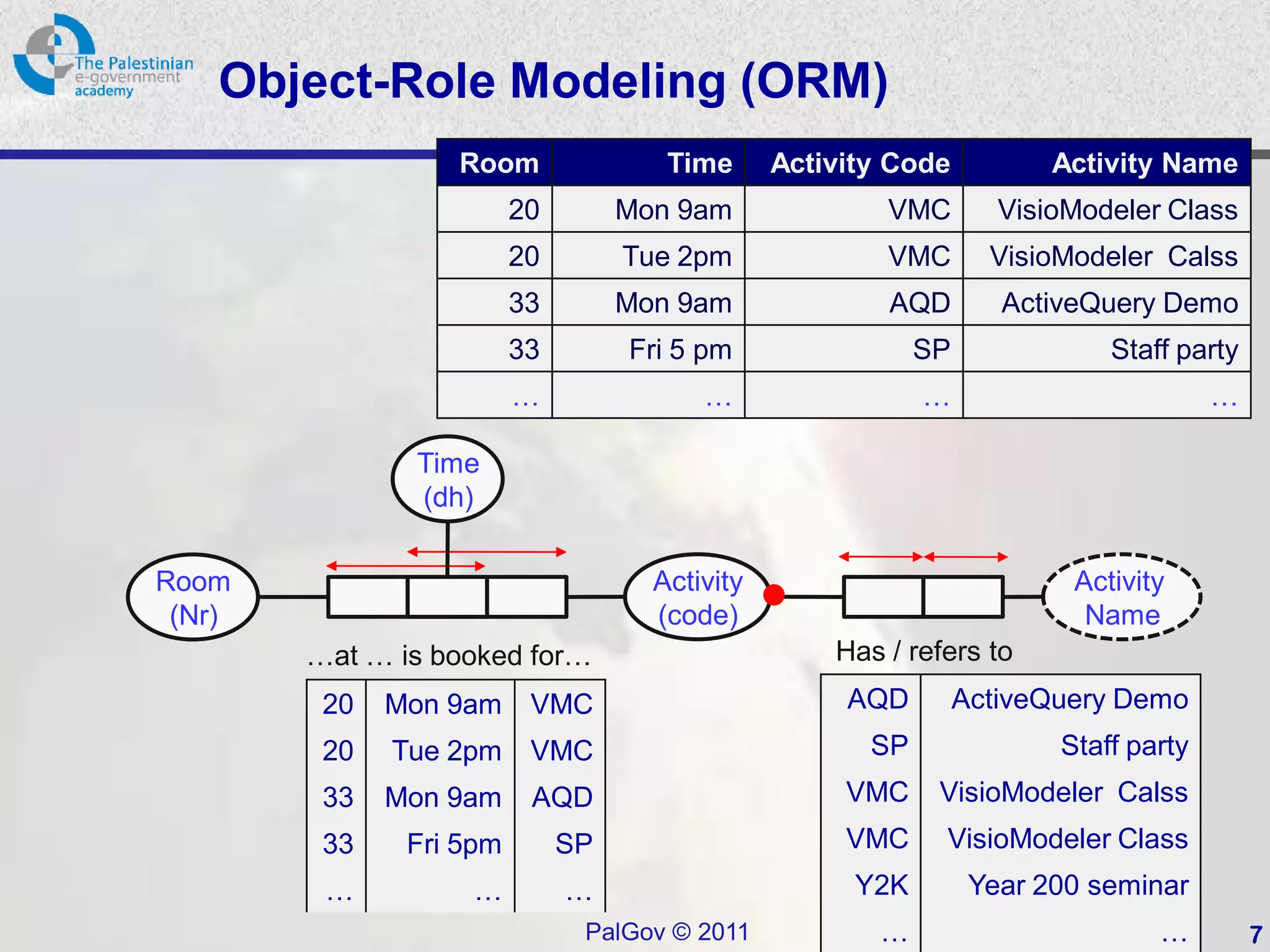
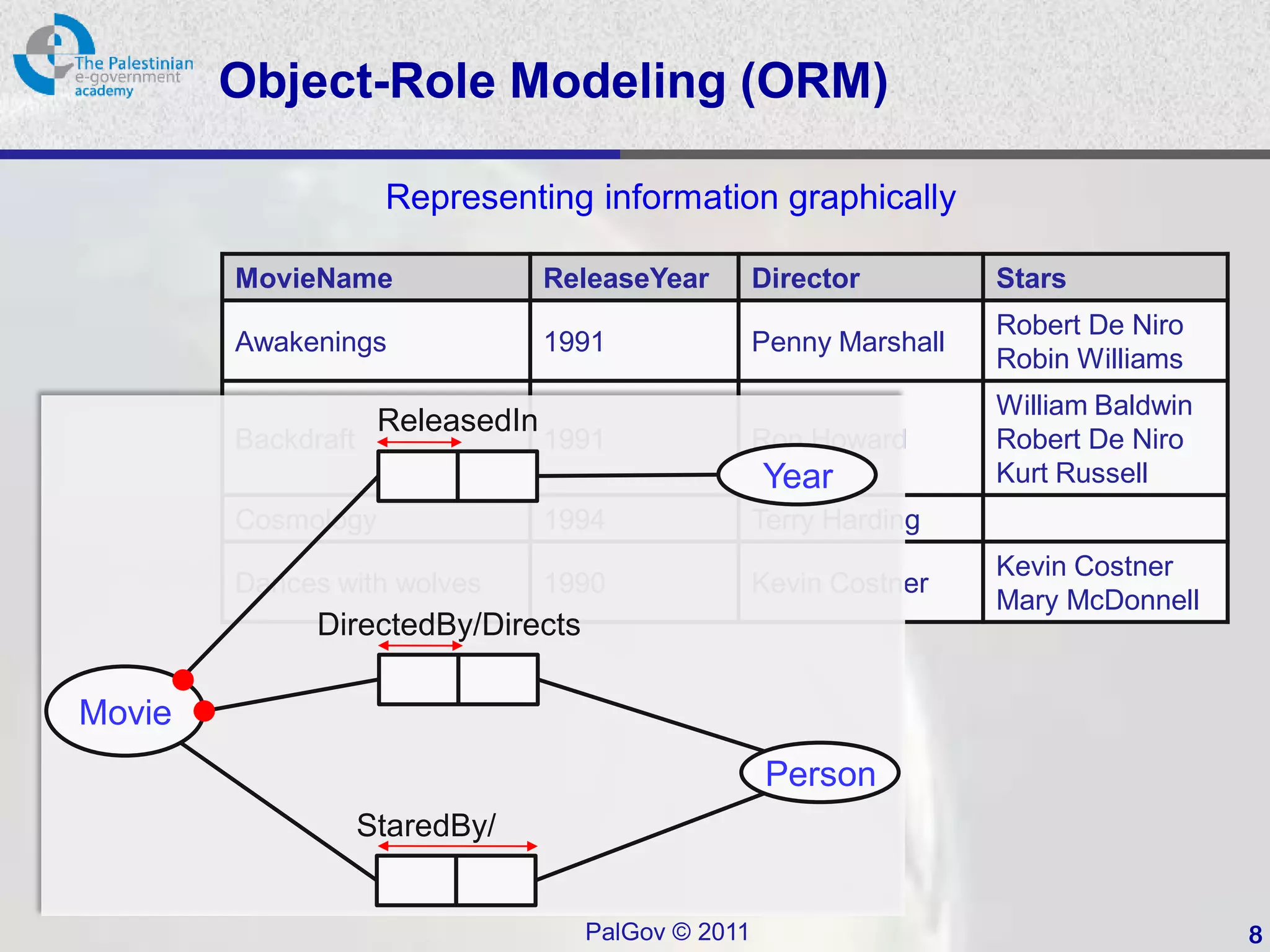
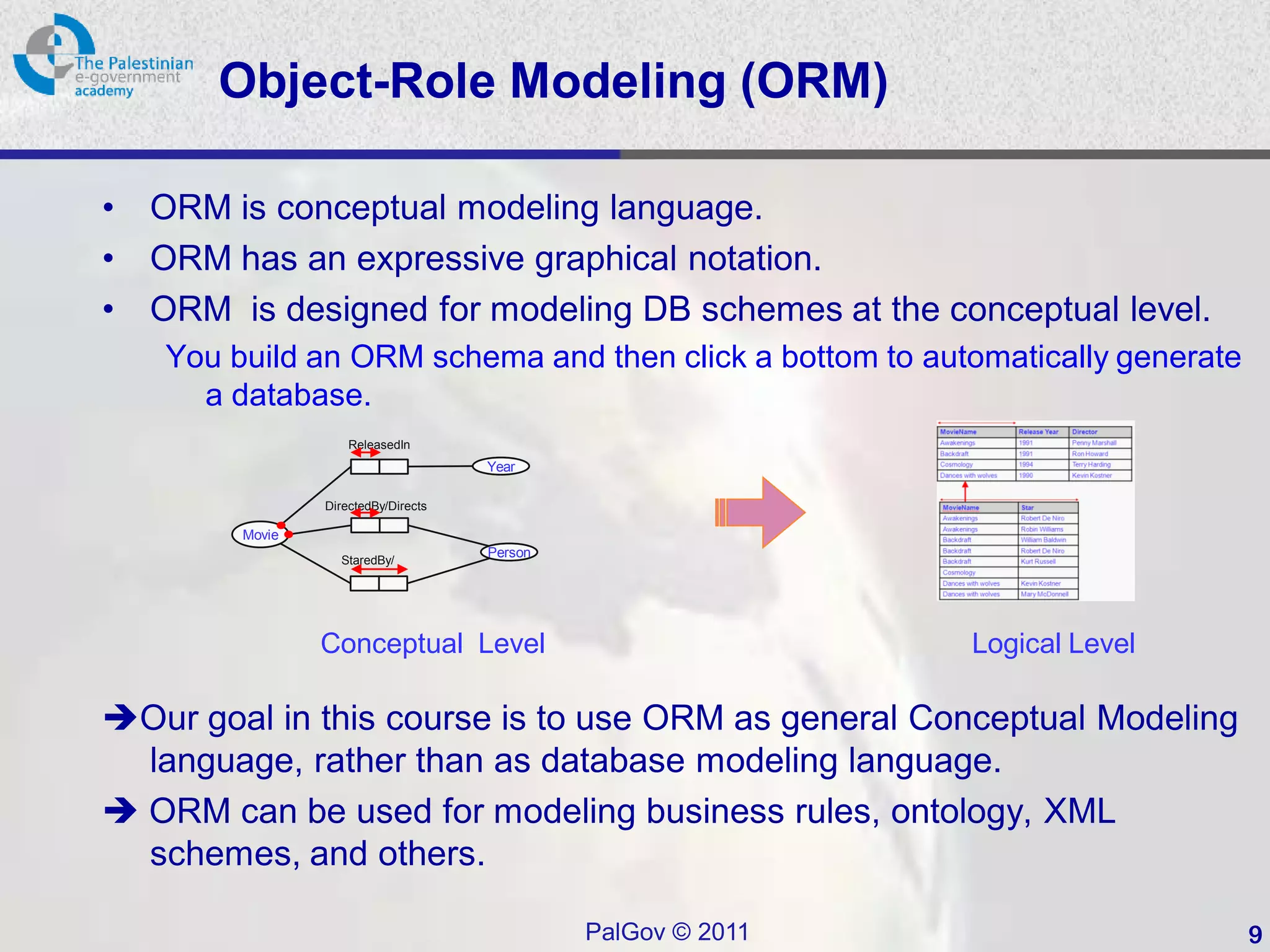
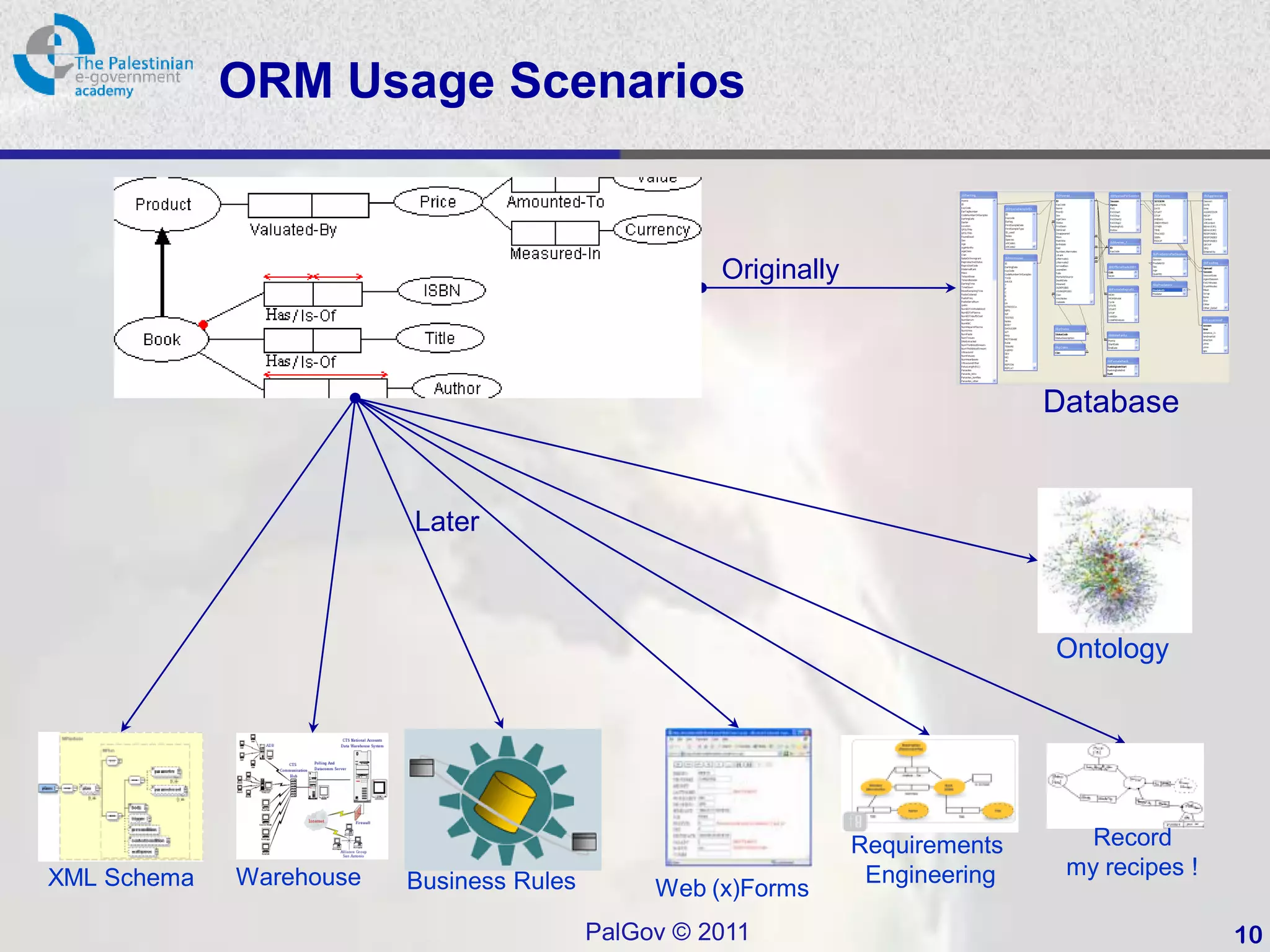
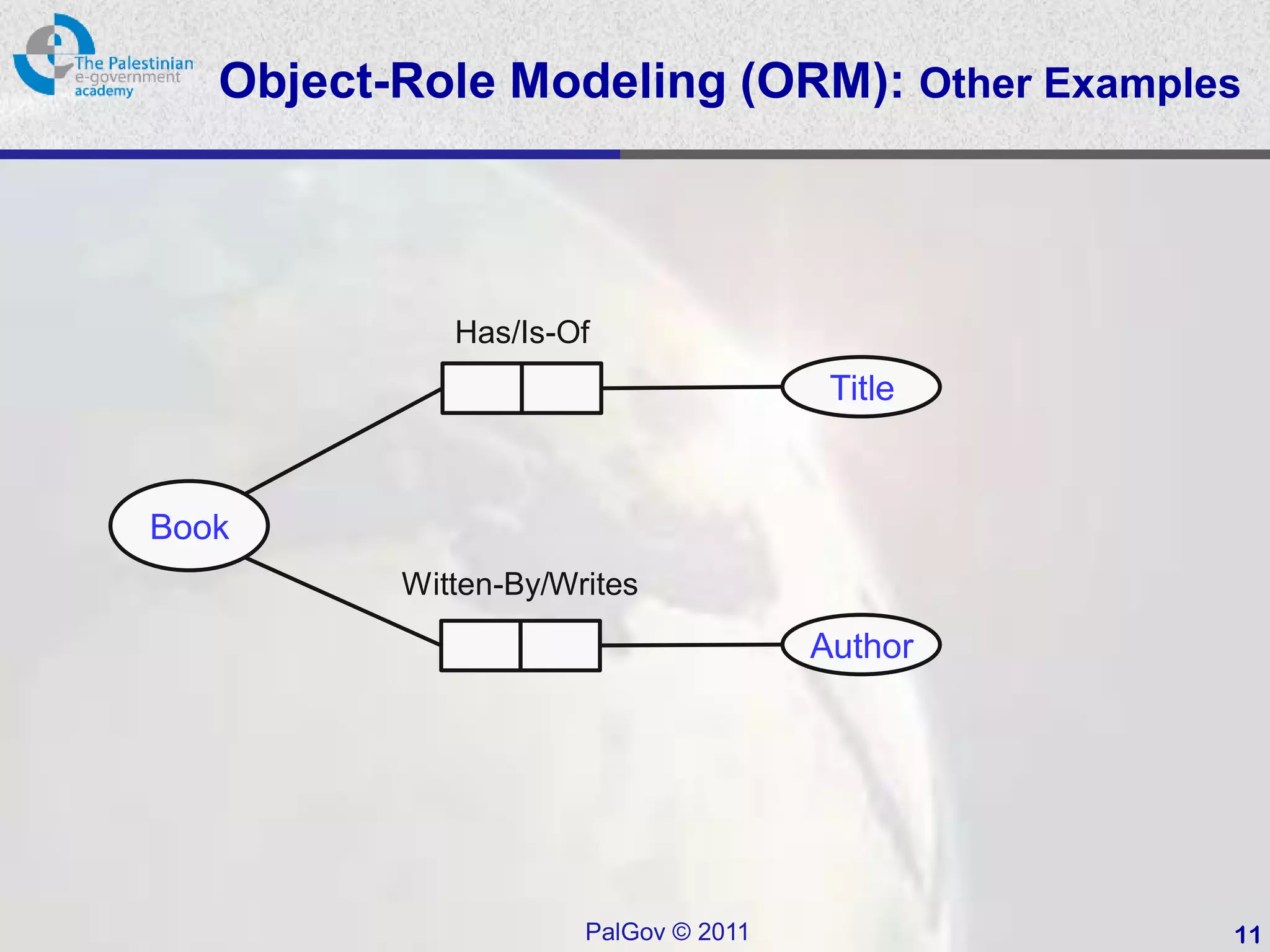
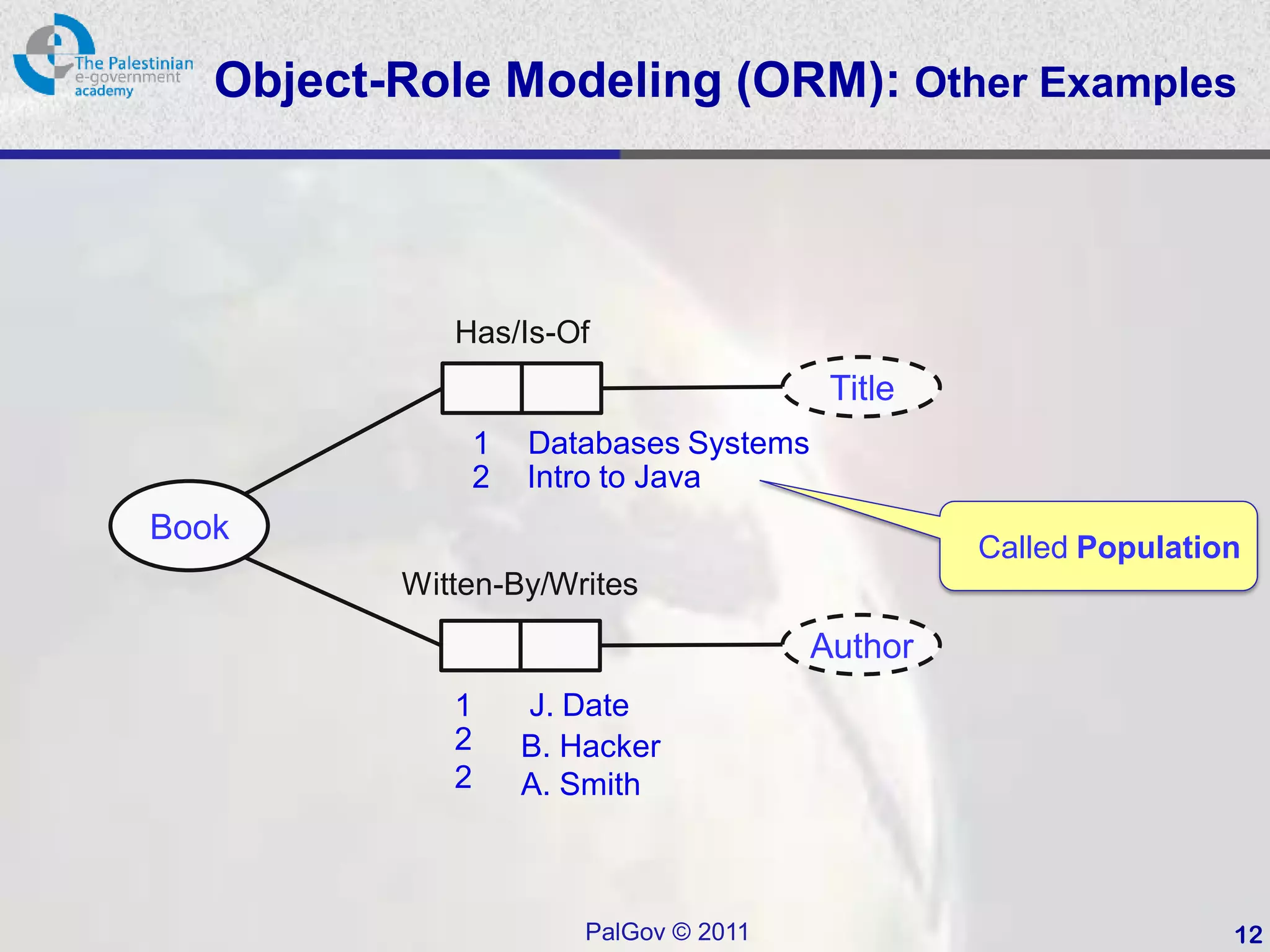
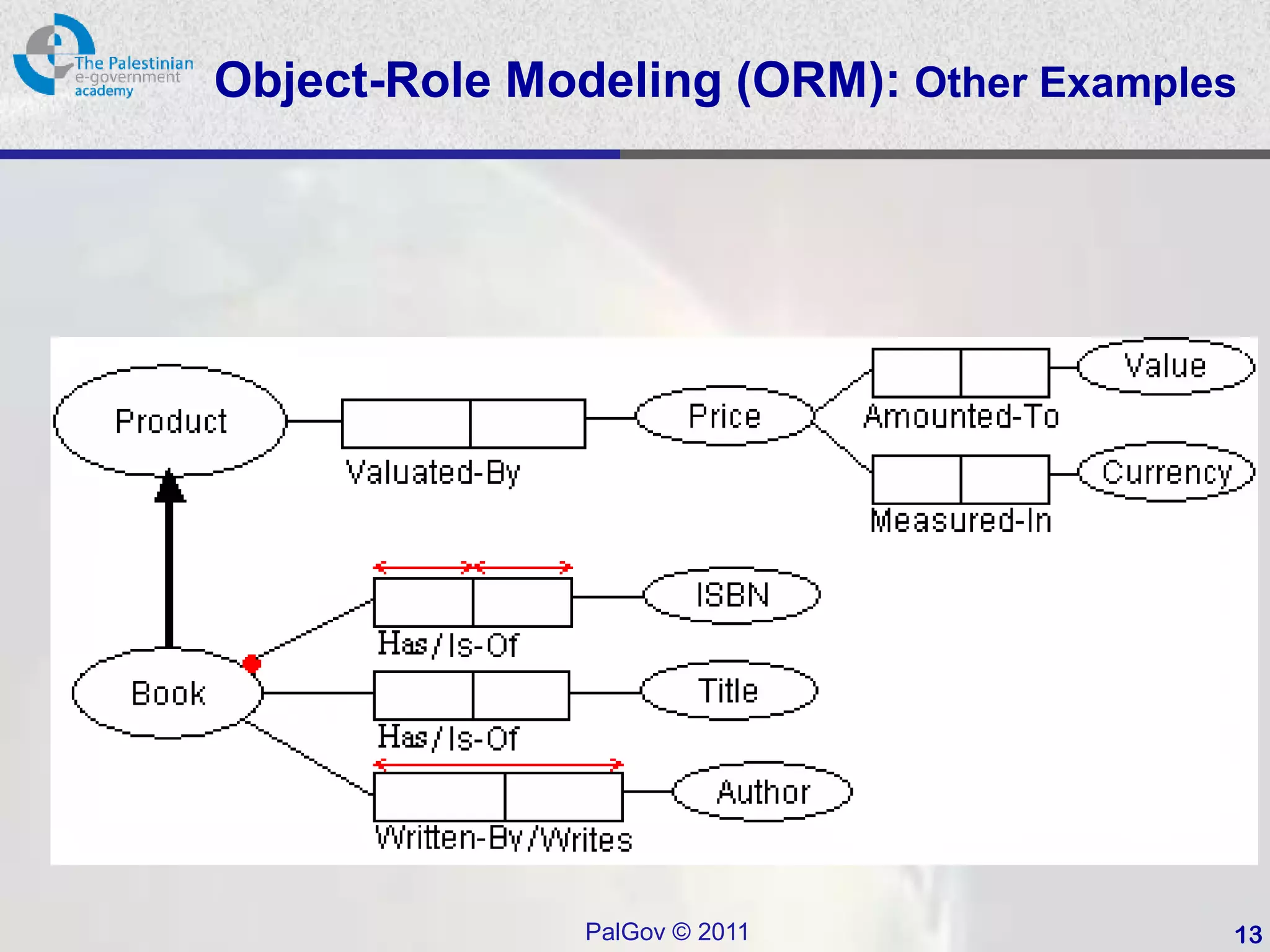
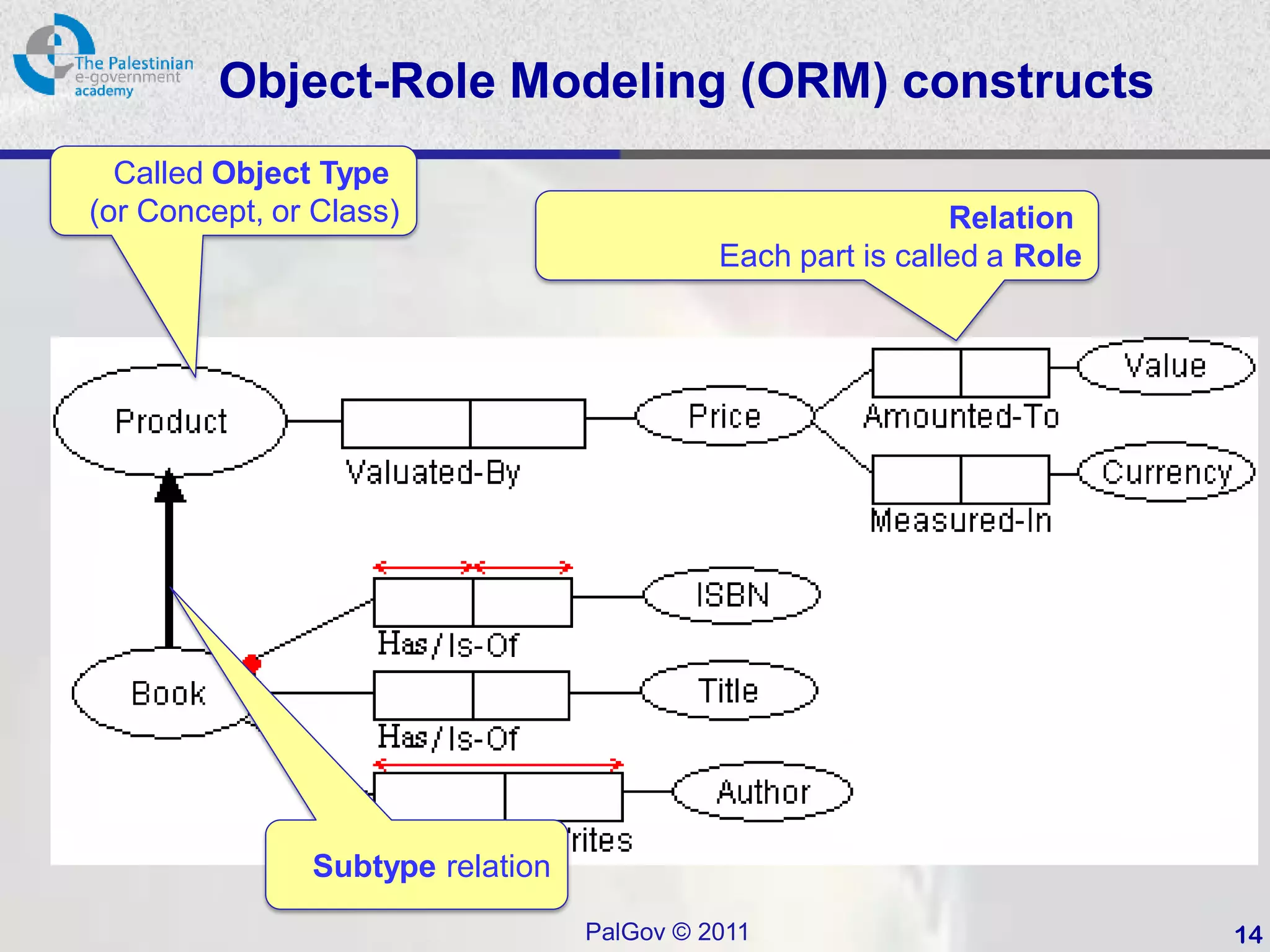
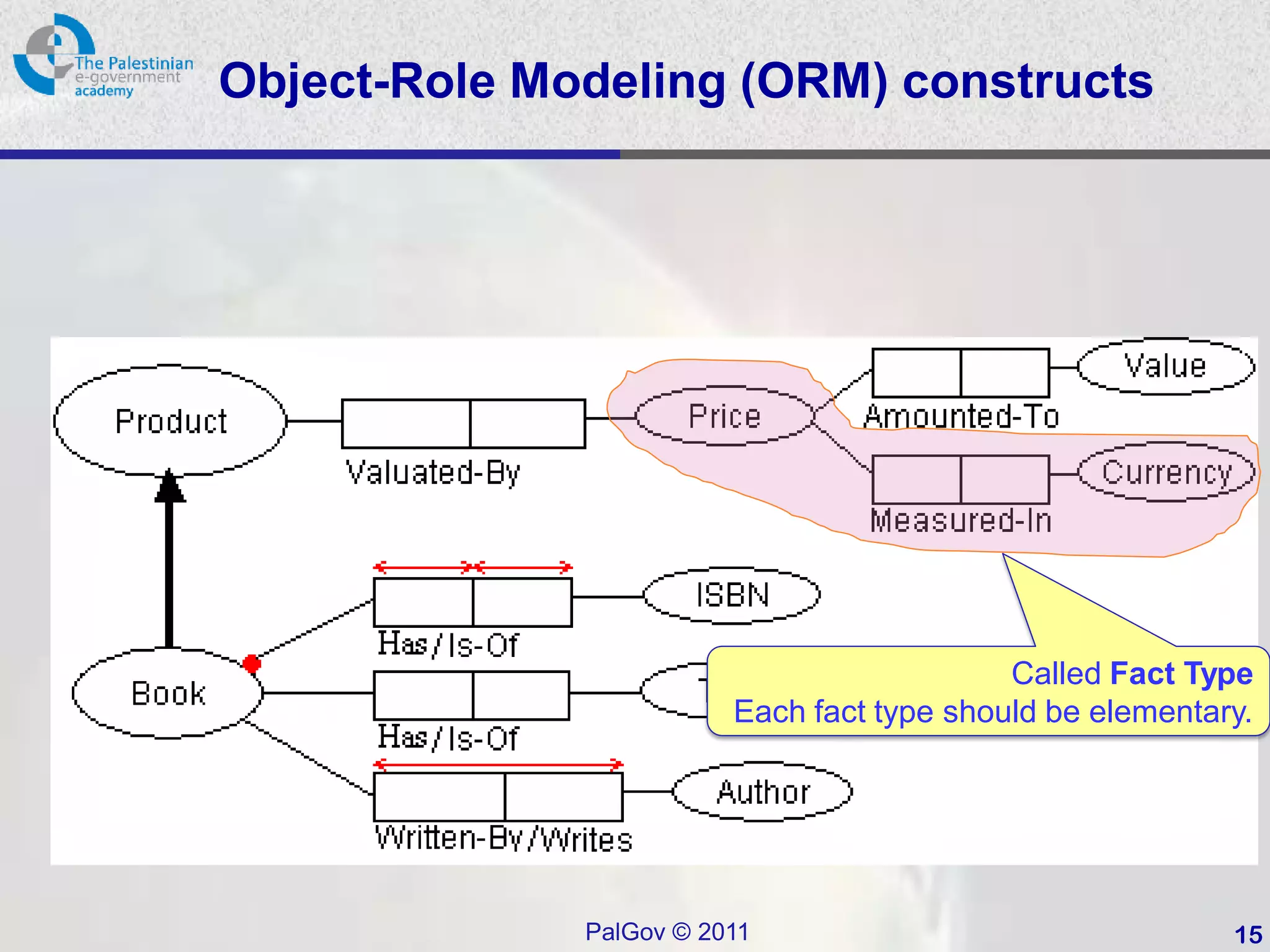
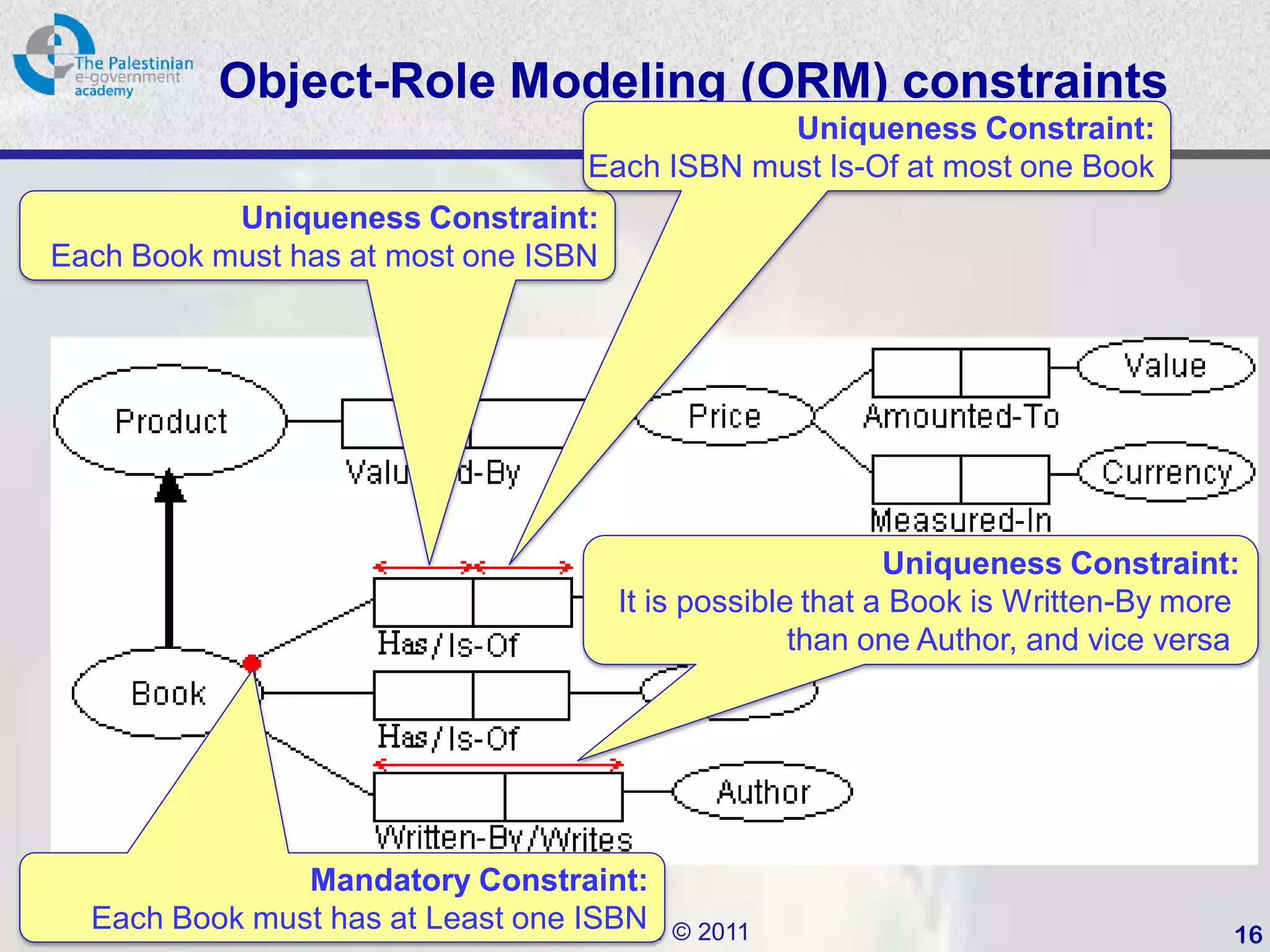
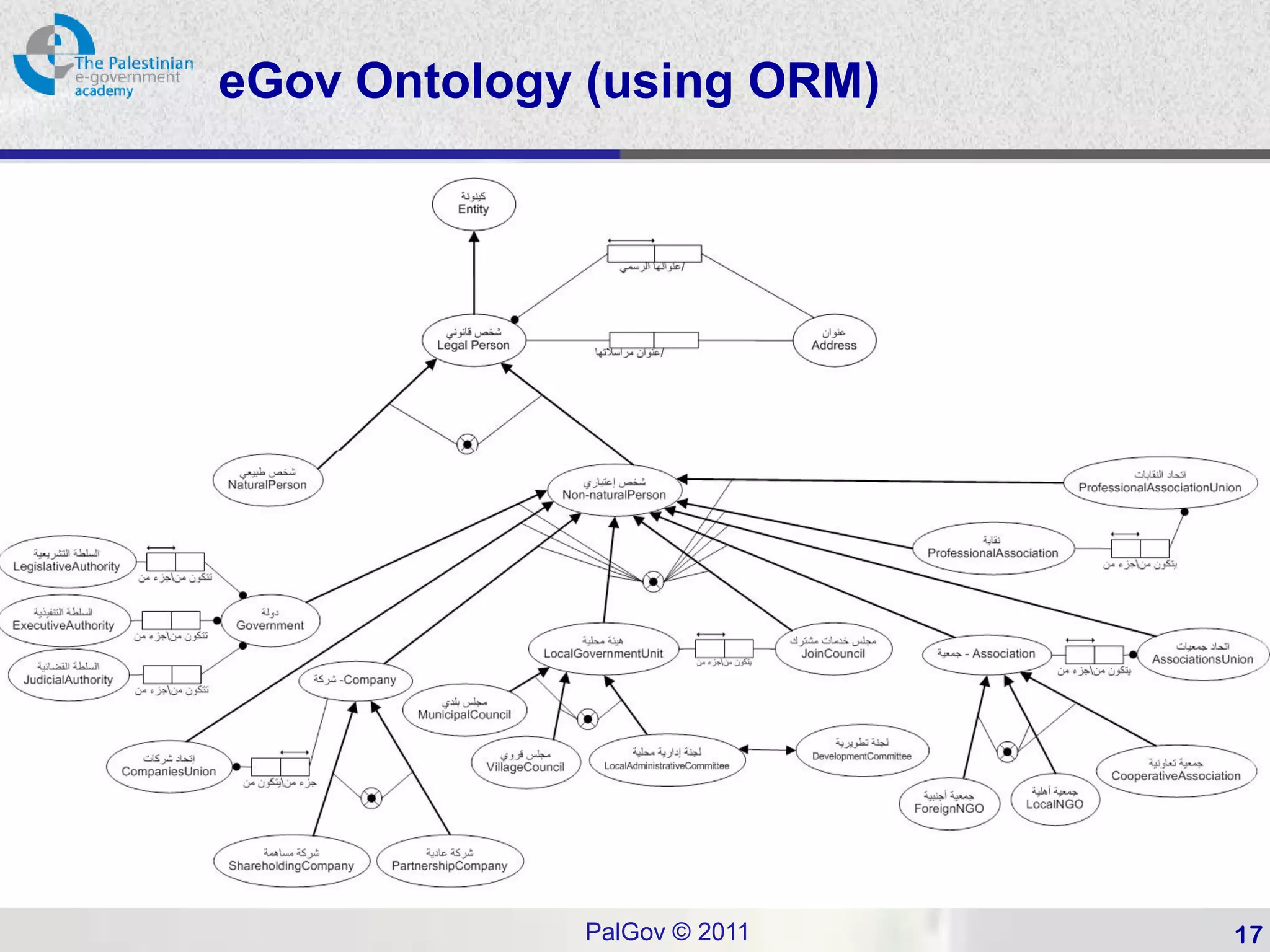
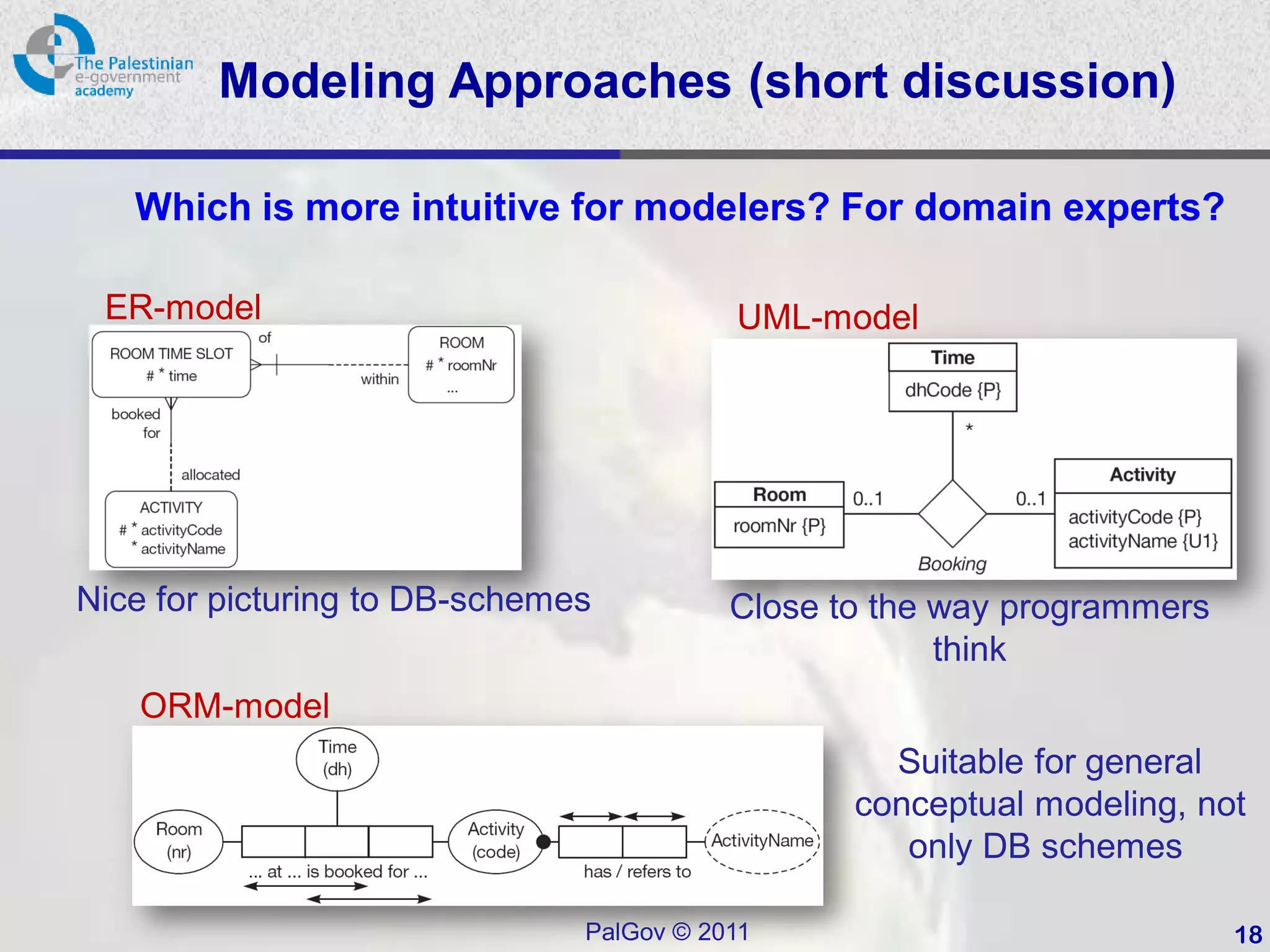
This document provides an introduction to Object-Role Modeling (ORM), which is a conceptual modeling language. ORM uses a graphical notation to represent information and can be used for database modeling, business rules, ontologies, and other scenarios. The key constructs in ORM include object types, relations between objects, and constraints. Several examples are provided to illustrate how ORM can be used to model concepts such as books, authors, and an eGovernment ontology. Other modeling approaches like ER and UML are briefly discussed in comparison to the benefits of ORM for conceptual modeling.