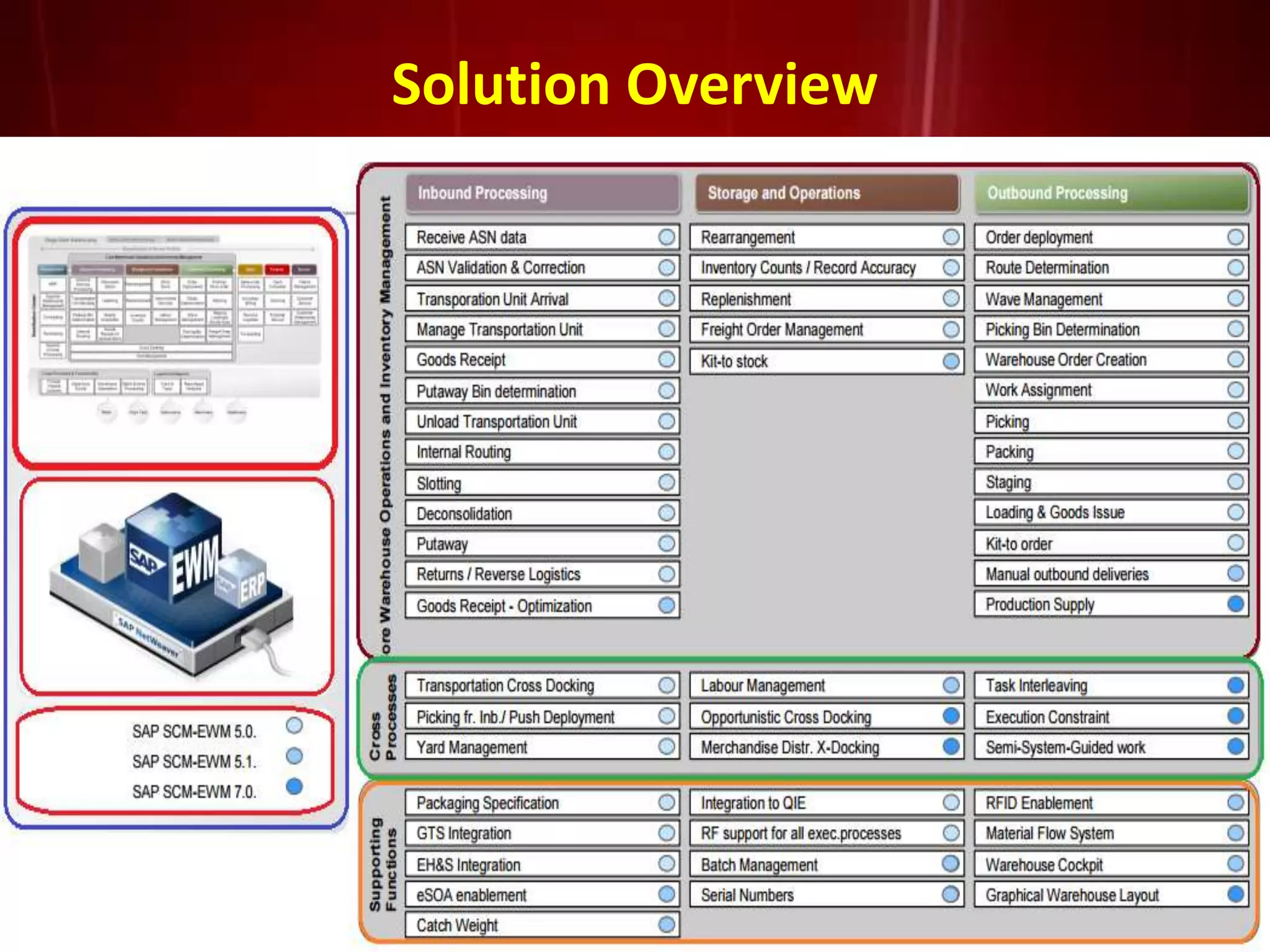
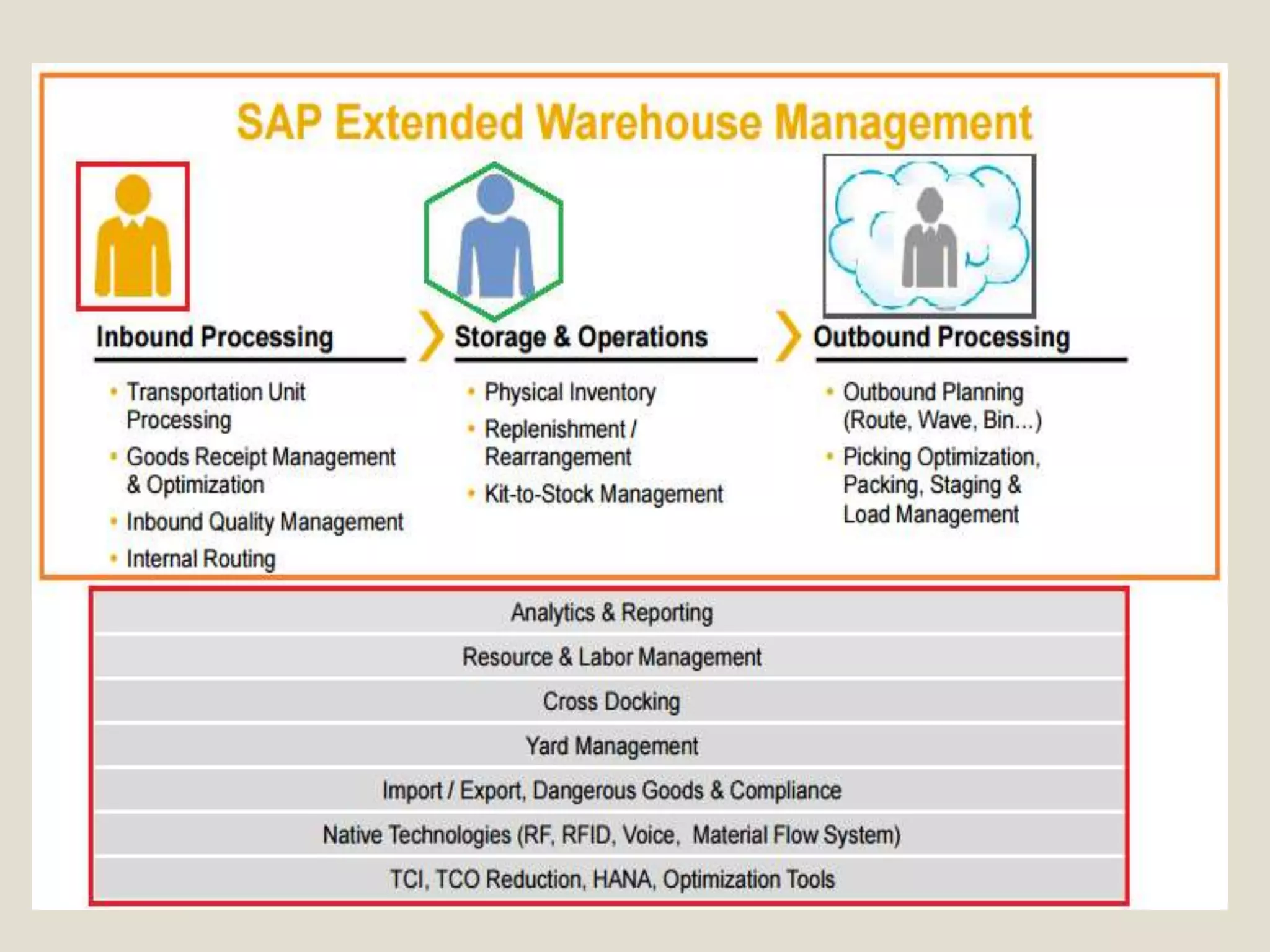
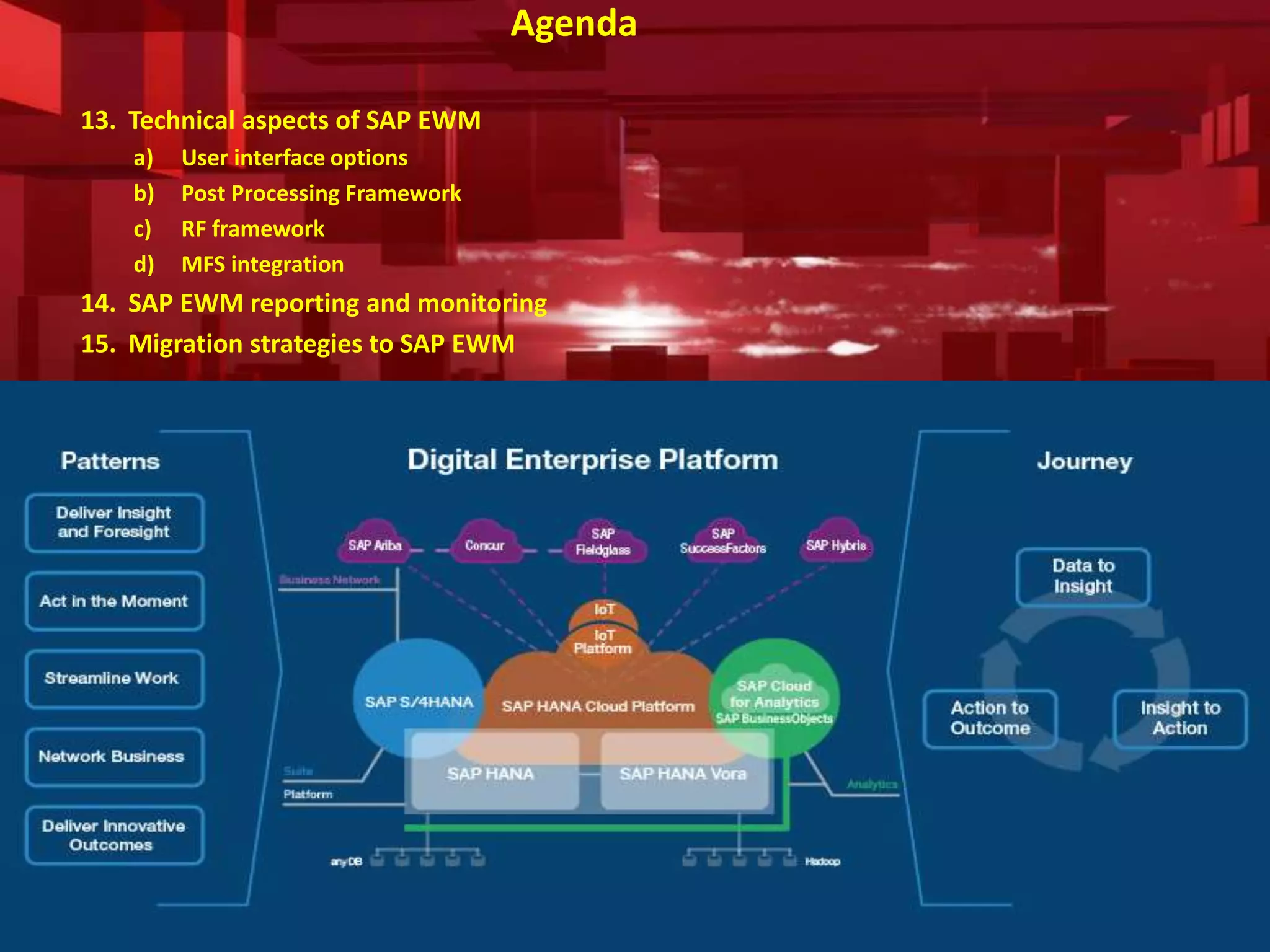
The document introduces SAP EWM, a comprehensive warehouse management solution within supply chain management that optimizes logistics execution processes. It highlights the critical role of warehousing in the supply chain, detailing its types, functions, and benefits, such as improved productivity and customer service. The document also outlines key capabilities of EWM, including stock transparency and seamless automation integration, as well as various processes and technical aspects related to EWM implementation.