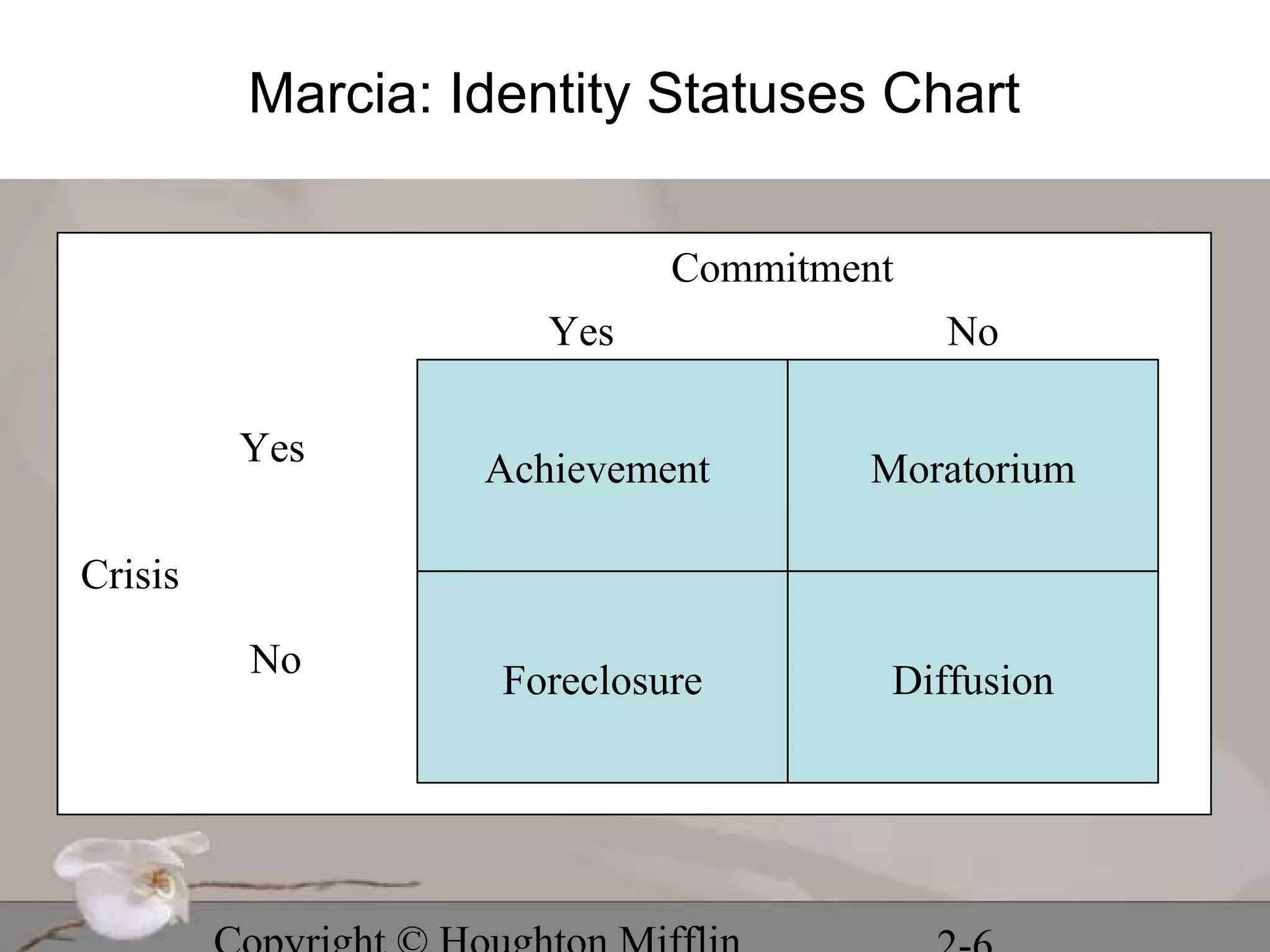
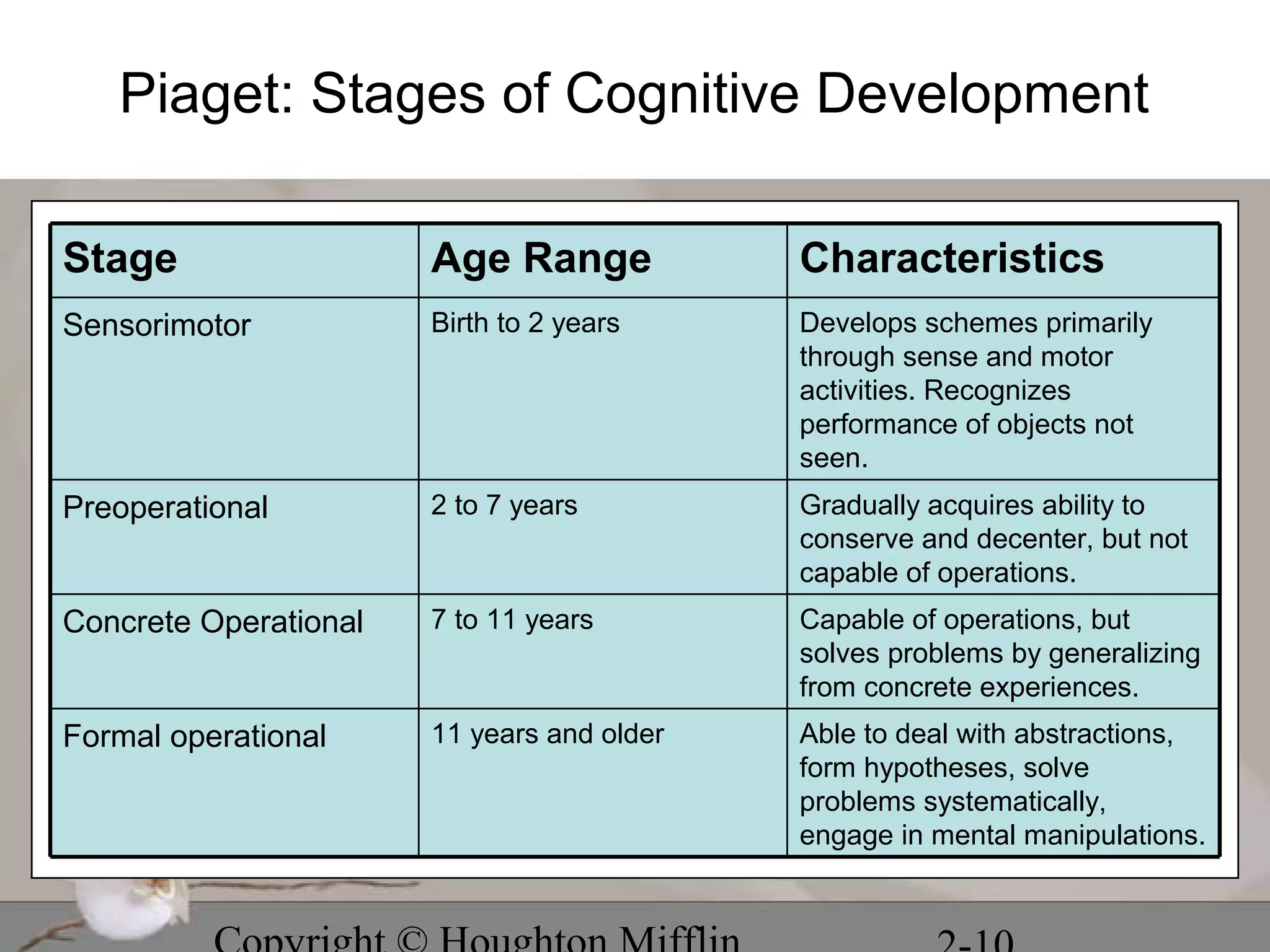
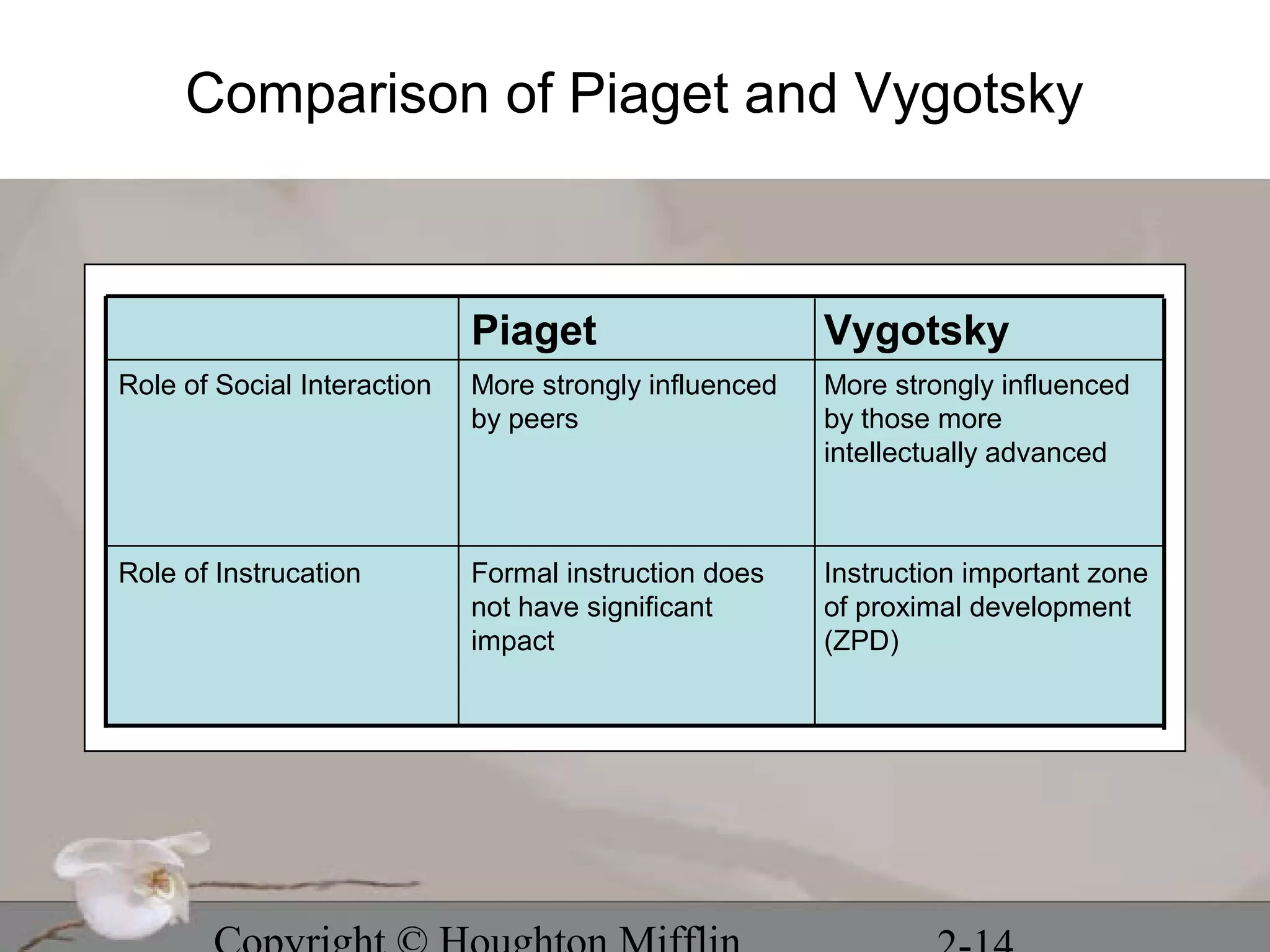
This chapter discusses several stage theories of development:
1. Erikson's psychosocial development theory outlines 8 stages from infancy to old age centered around resolving psychosocial crises.
2. Piaget's cognitive development theory describes 4 stages from birth to adulthood where children construct understanding through schemes and adaptation.
3. Vygotsky emphasized social interaction and culture in cognitive development and the zone of proximal development.
4. Theories on moral development include Piaget, Kohlberg focusing on reasoning, and Gilligan noting females prioritize caring relationships over independence.