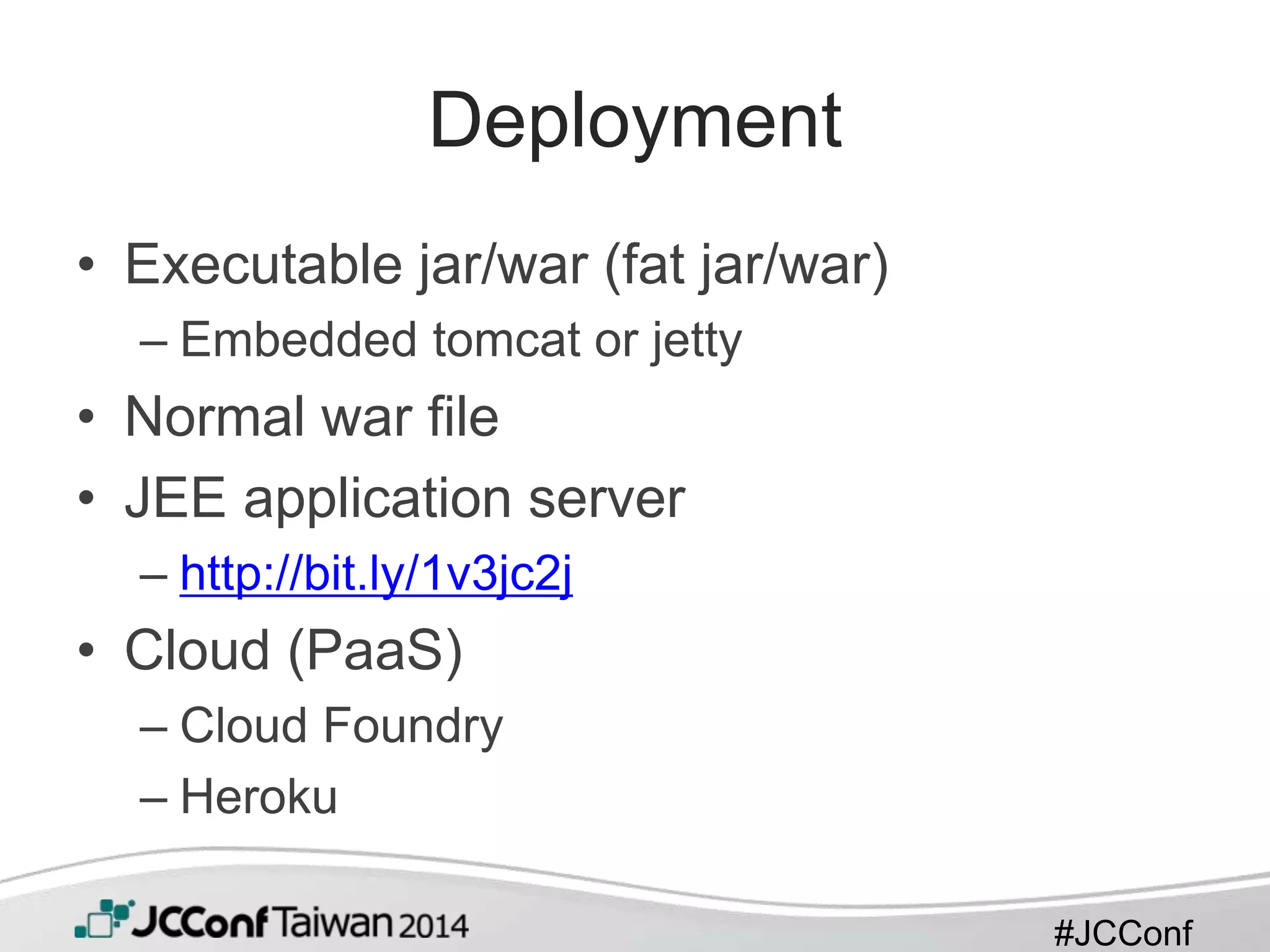
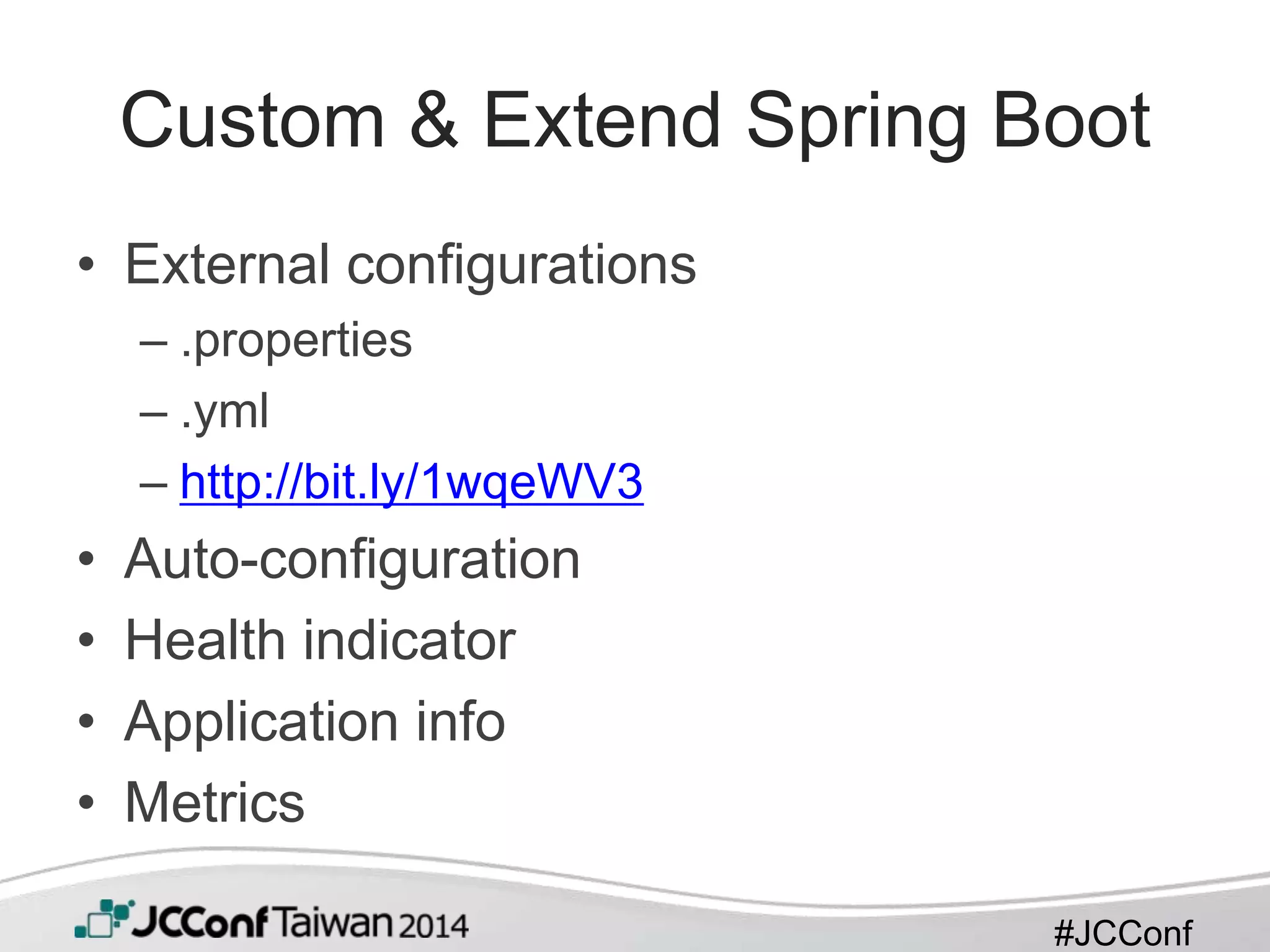
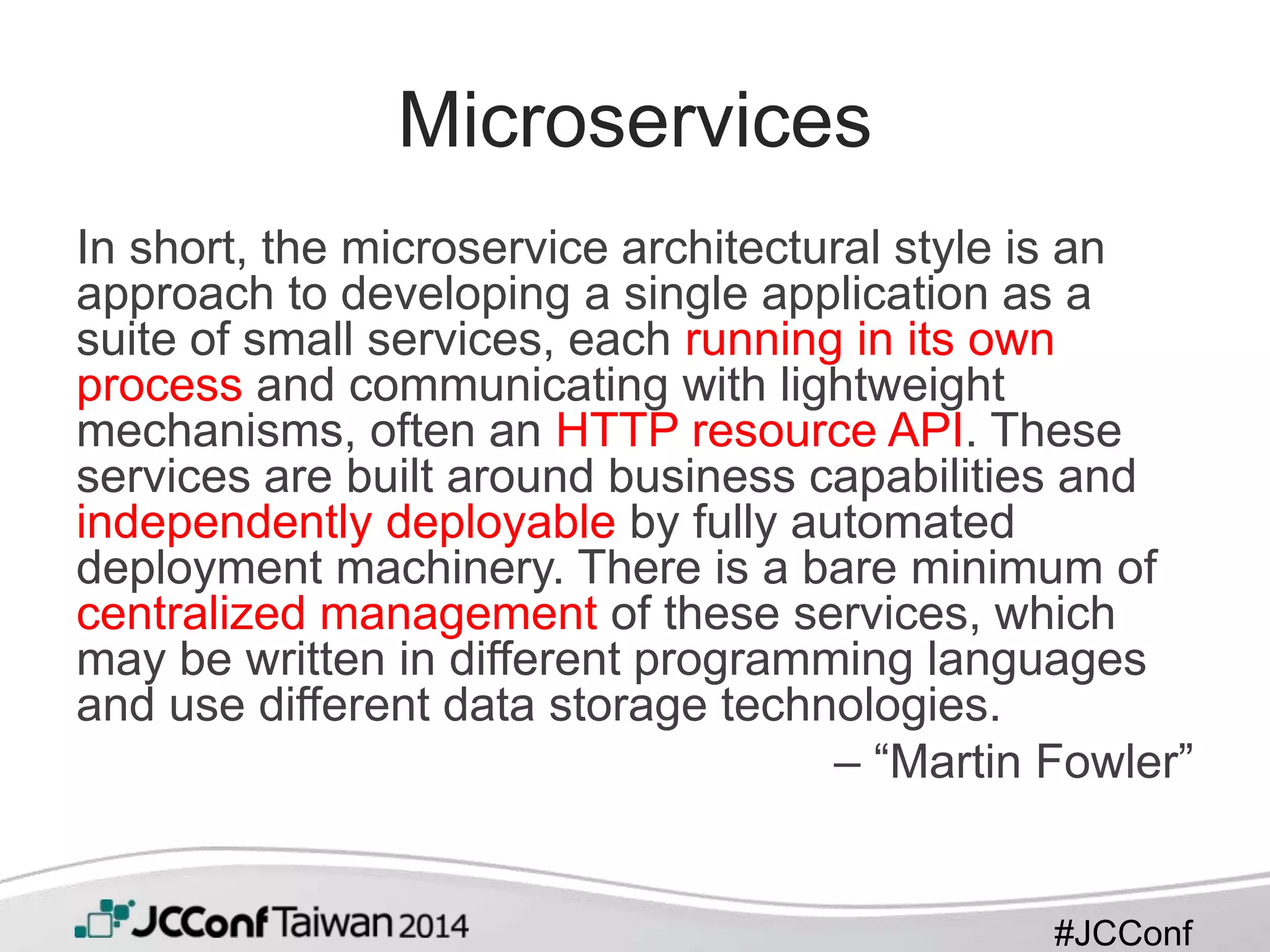
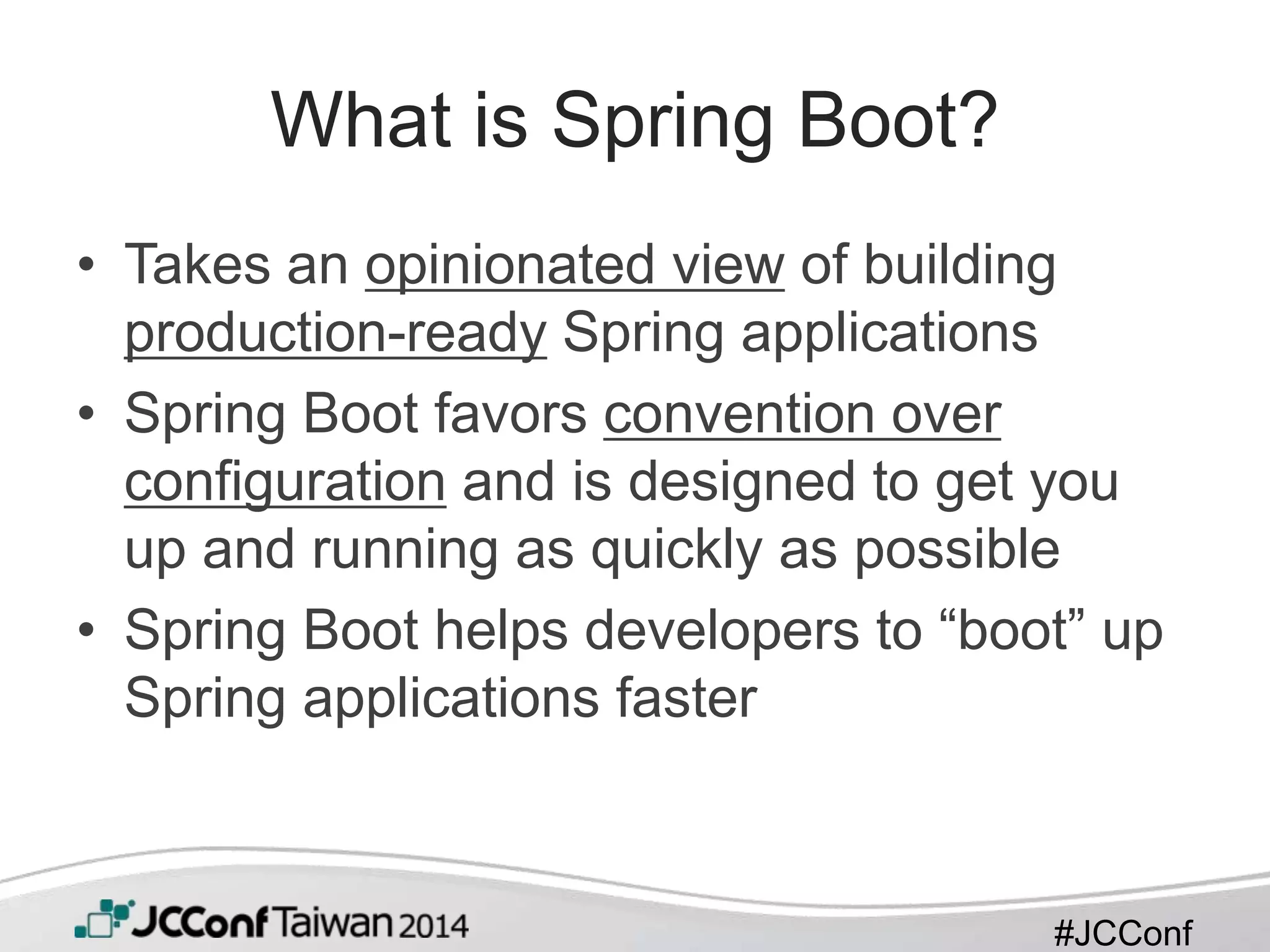
This document provides an overview of Spring Boot. It begins with a brief introduction to Spring Boot, including that it takes an opinionated approach to building production-ready Spring applications quickly. It then discusses features of Spring Boot like providing starter POMs, auto-configuration, and production-ready features out of the box. The document also covers getting started, including a simple example application, and how to customize and extend Spring Boot for microservices development.








![#JCConf
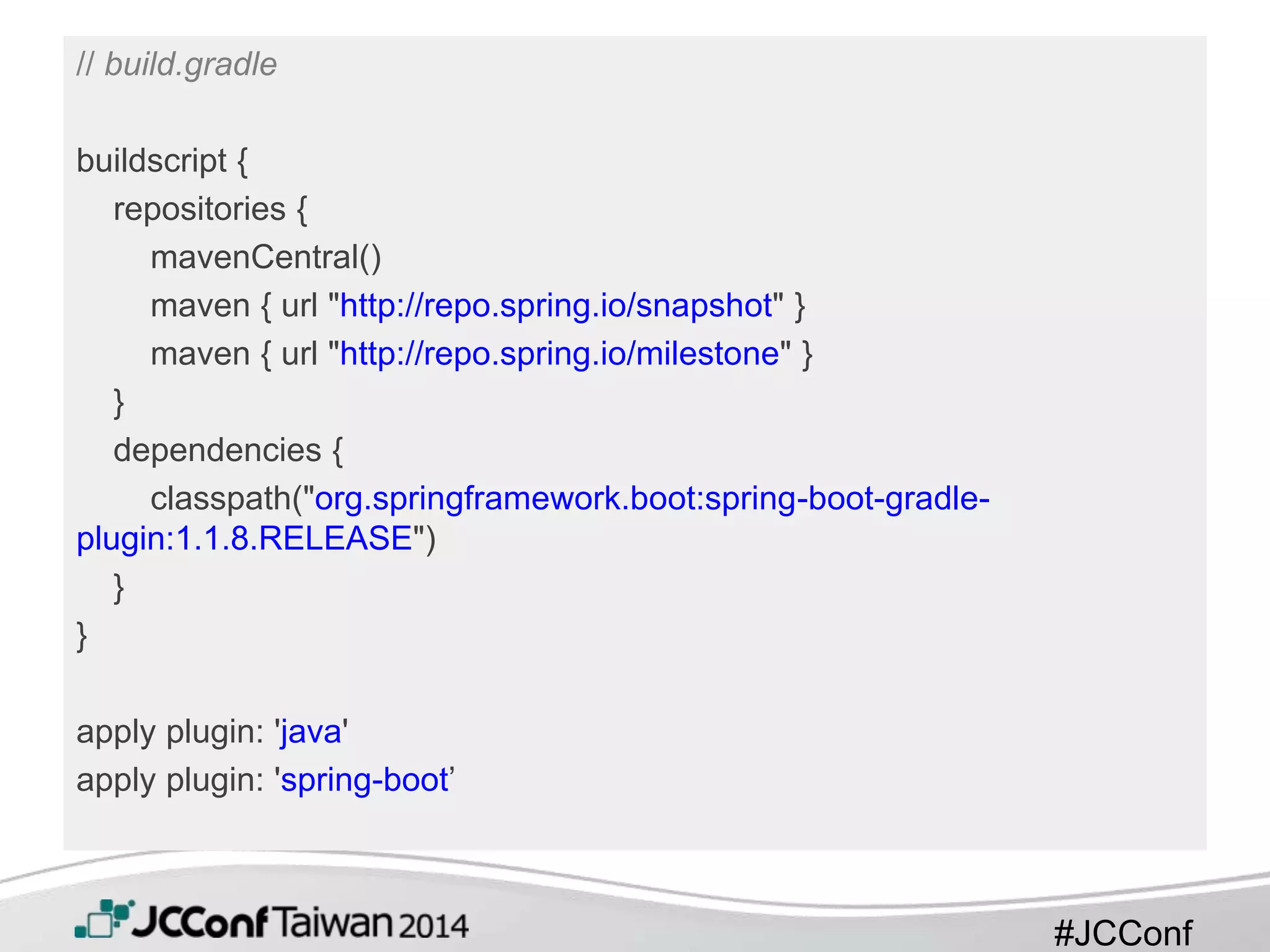
// Appliation.java.
@RestController
@EnableAutoConfiguration
public class Example {
@RequestMapping("/")
String home() {
return "Hello World!";
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
SpringApplication.run(Example.class, args);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bootifyyourspringapplication-141115014258-conversion-gate01/75/Bootify-your-spring-application-11-2048.jpg)