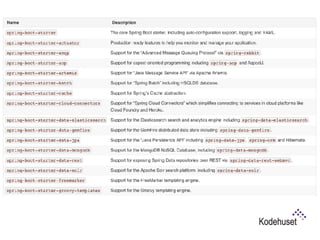
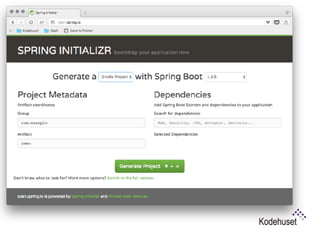
Spring Boot makes it easy to create stand-alone, production-grade Spring applications without needing to deploy files. It provides starter dependencies to simplify configuration, performs automatic configuration, and includes production-ready features like metrics and health checks. This document demonstrates creating a RESTful web service using Spring Boot with Groovy and Gradle by developing an application to manage an RC car registry in 9 steps, covering creating the application, executable JAR, configuration, endpoints, testing, security, and actuators. New features in Spring Boot 1.4 include startup failure analysis, updated dependencies and test annotations, and image banners.