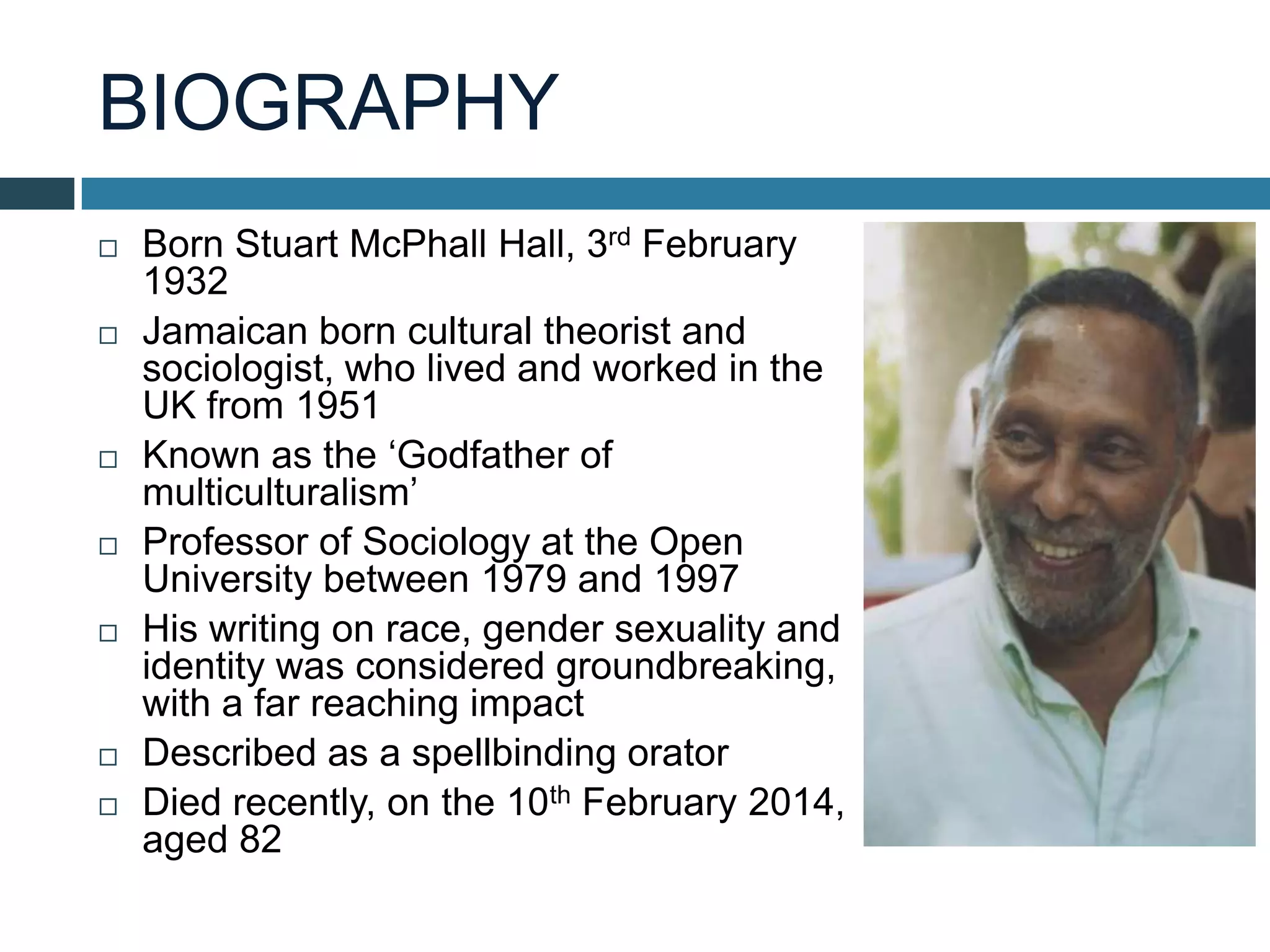
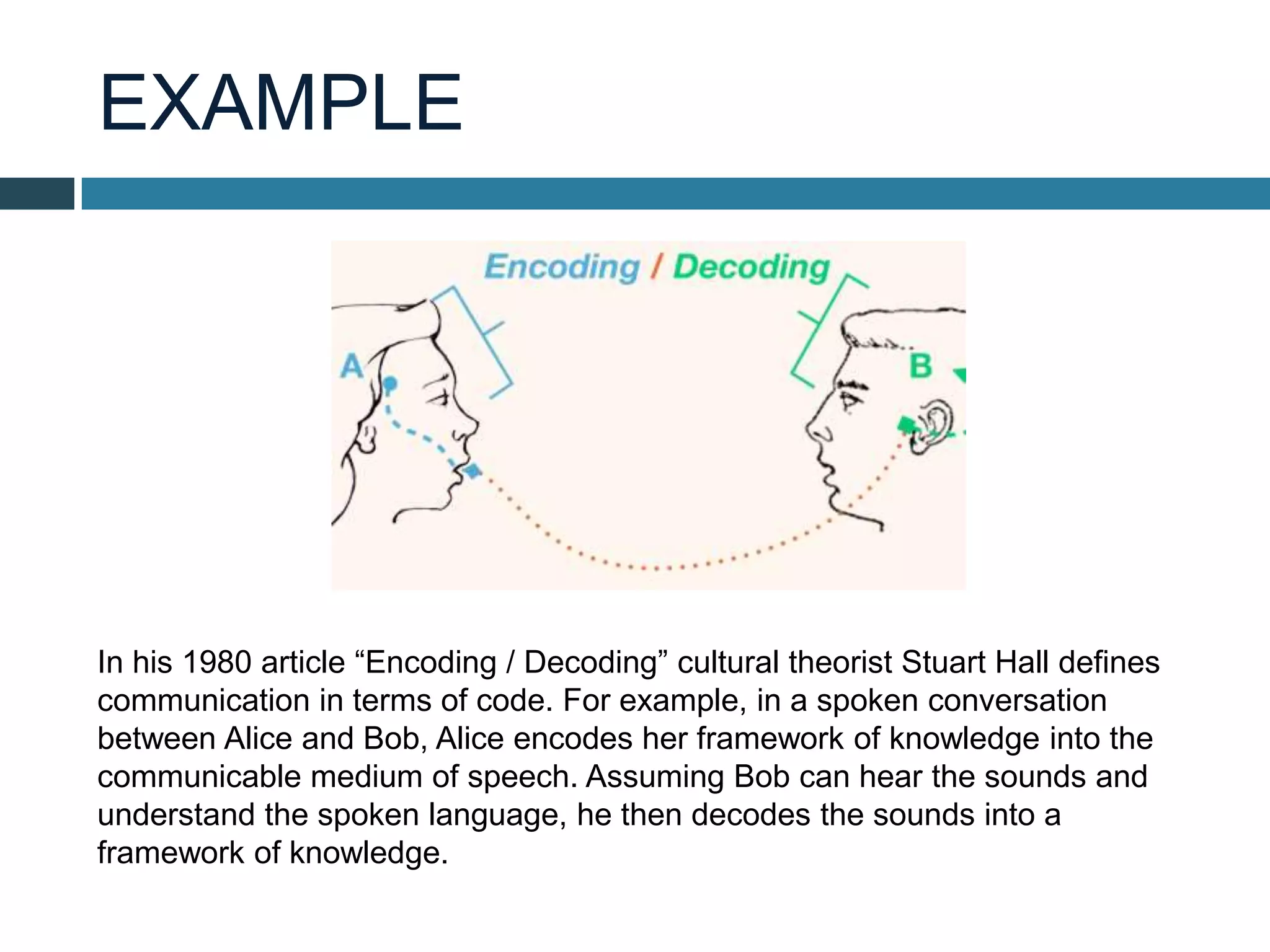
Stuart Hall was a prominent cultural theorist and sociologist from Jamaica who worked in the UK. He developed theories of encoding and decoding in media where the producer encodes a message and the audience can interpret it in dominant, negotiated, or oppositional ways depending on their background and experiences. Hall argued that audiences are not passive and can change the intended meaning. He provided the example of a conversation where one person encodes knowledge into speech and the other decodes it based on their understanding of language.