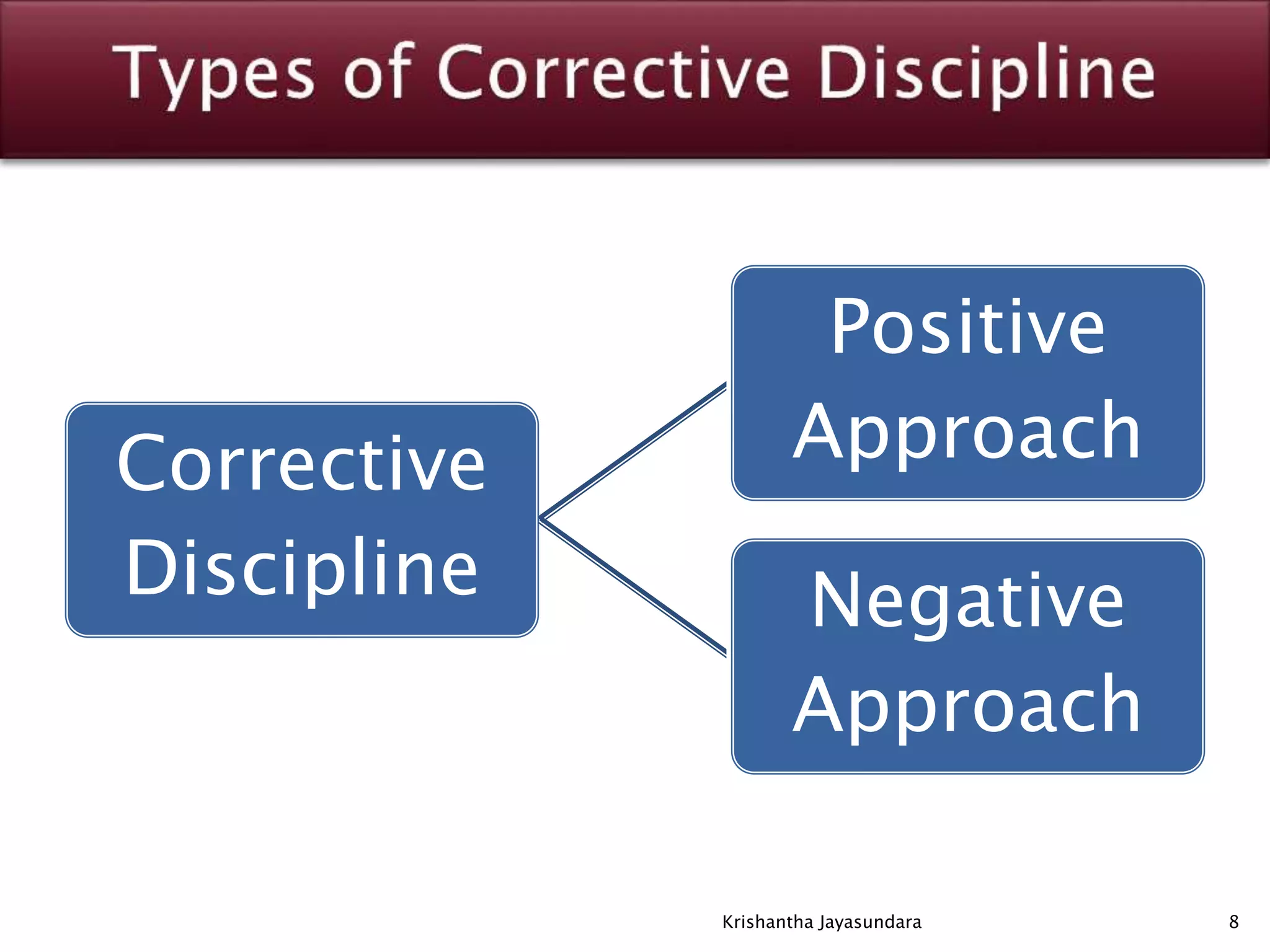
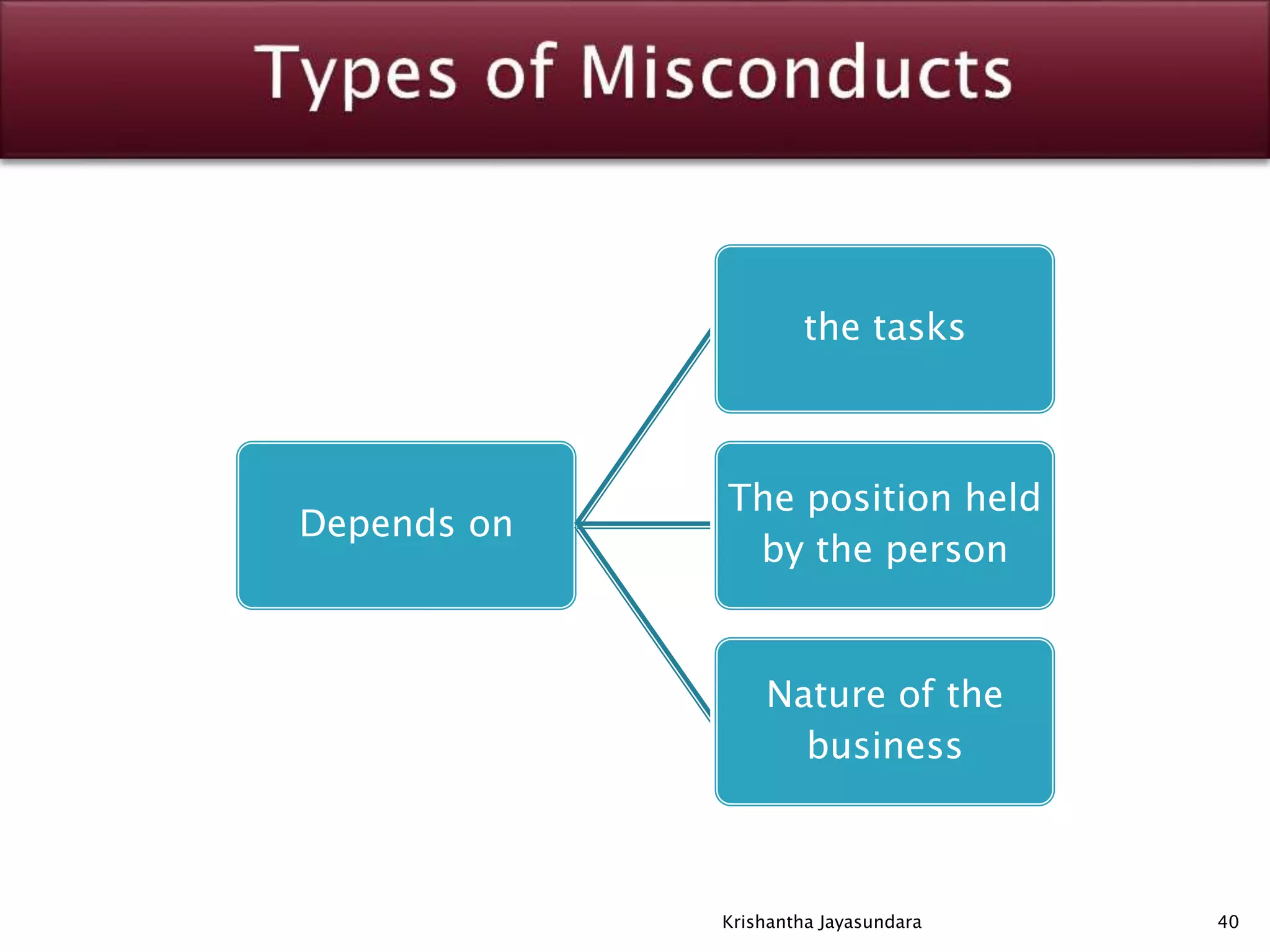
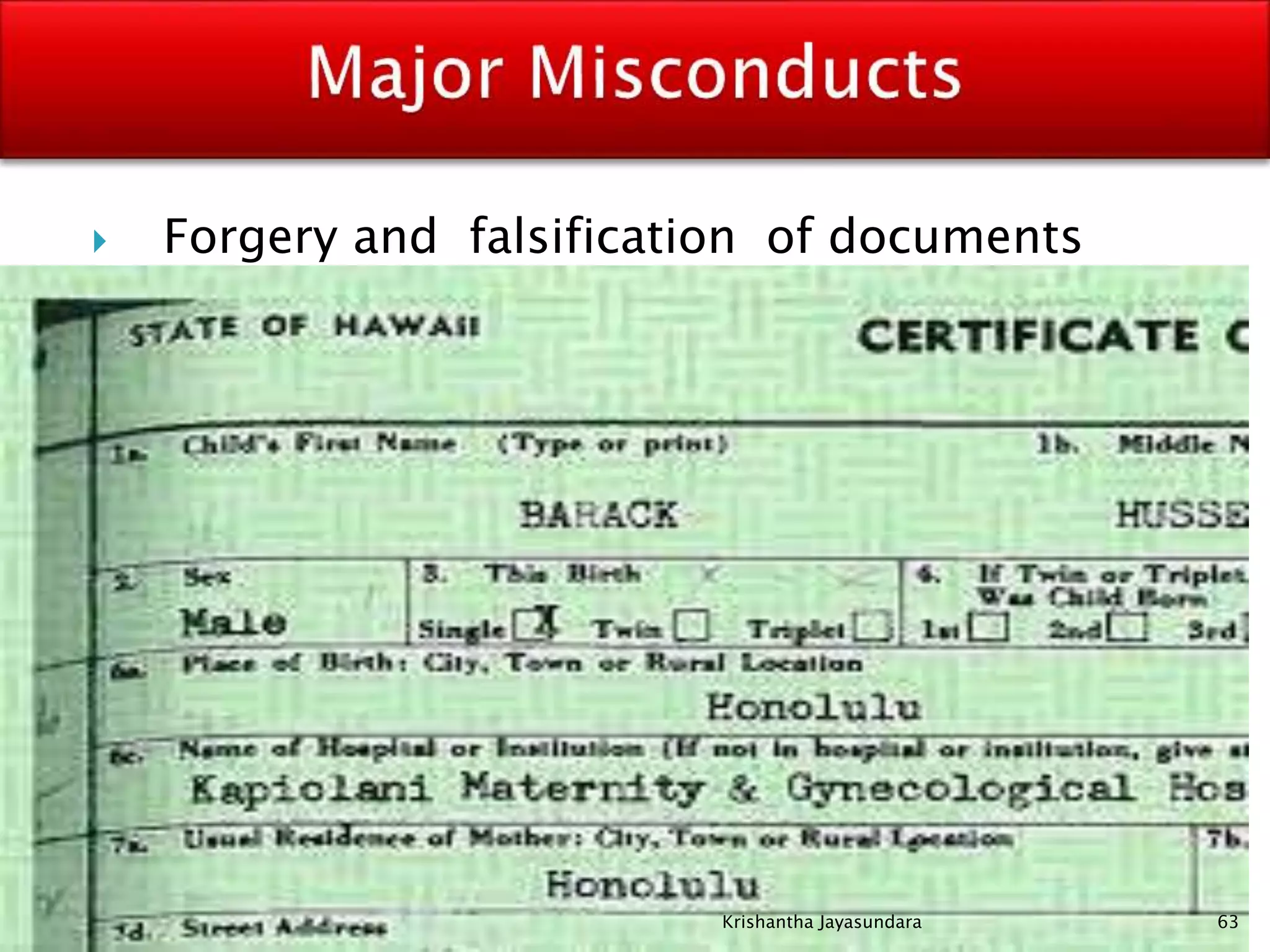
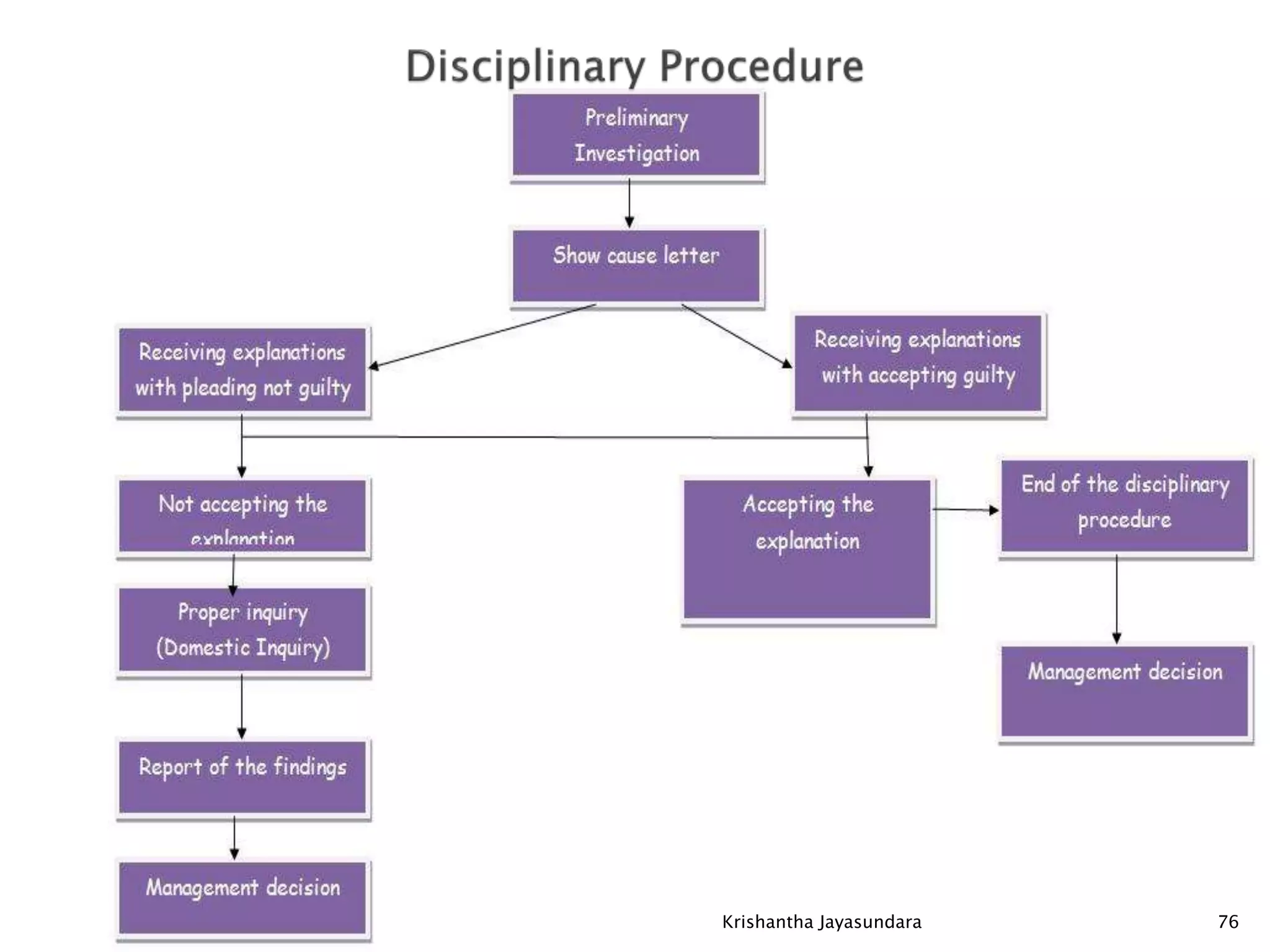
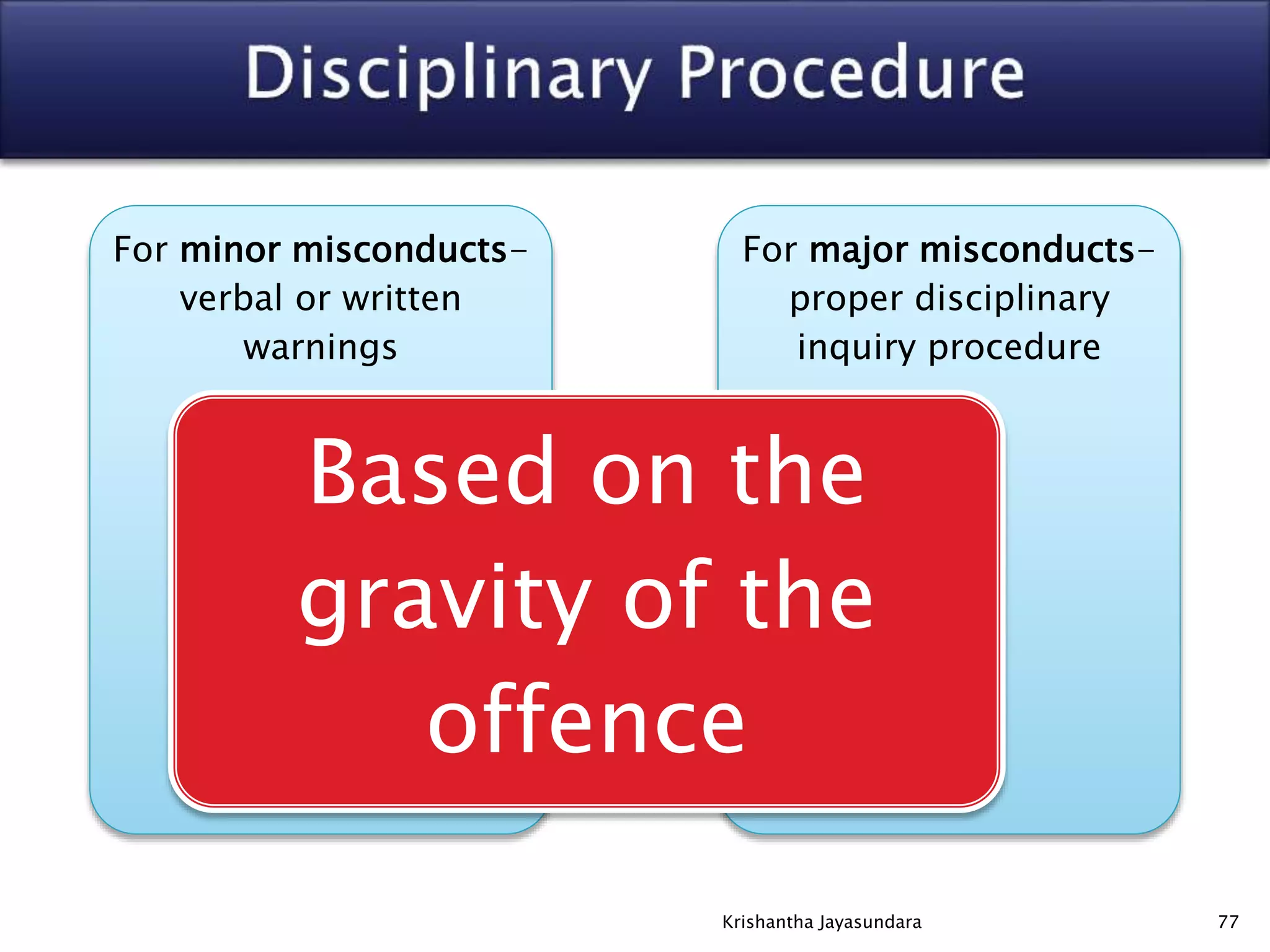
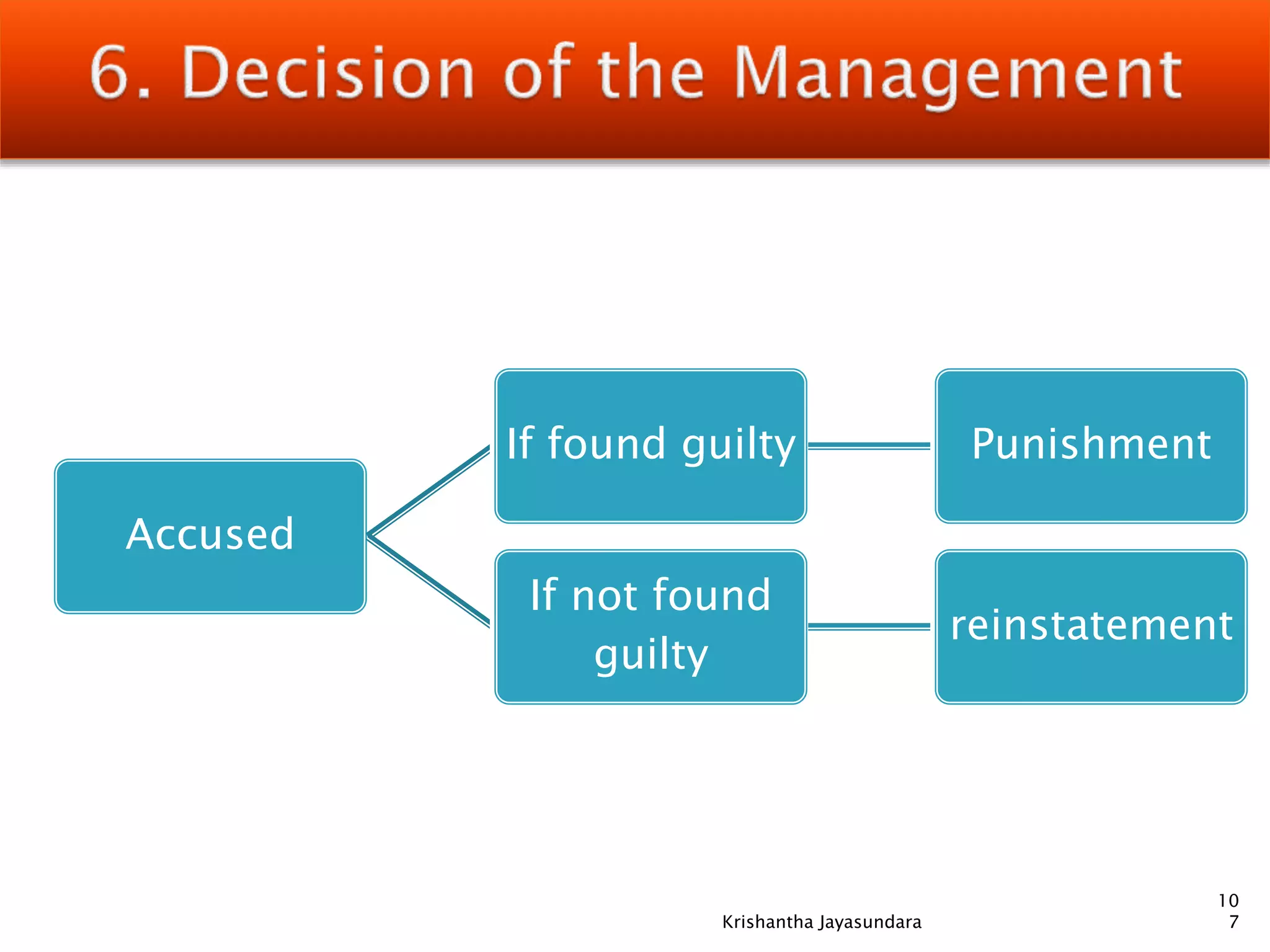
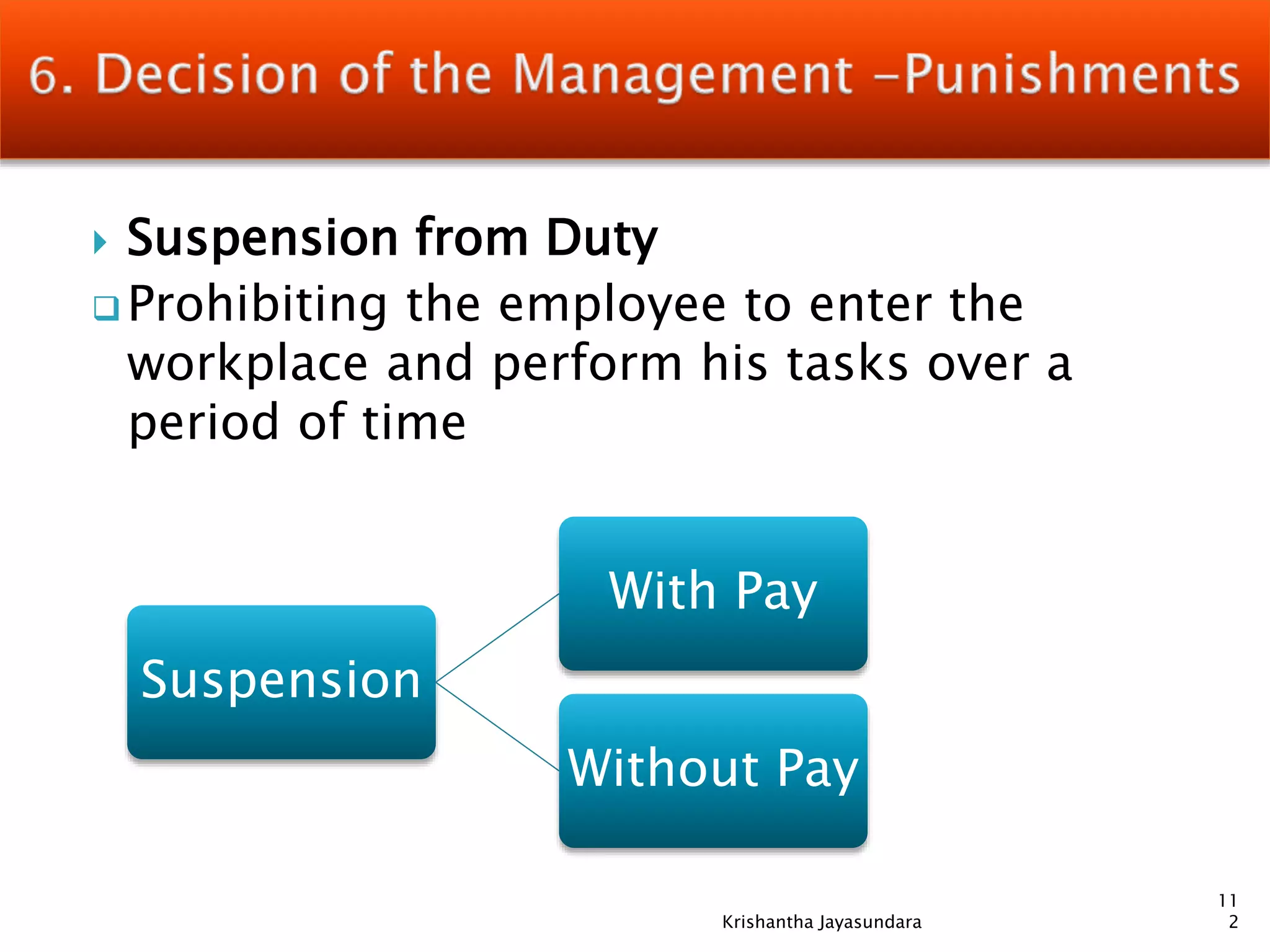
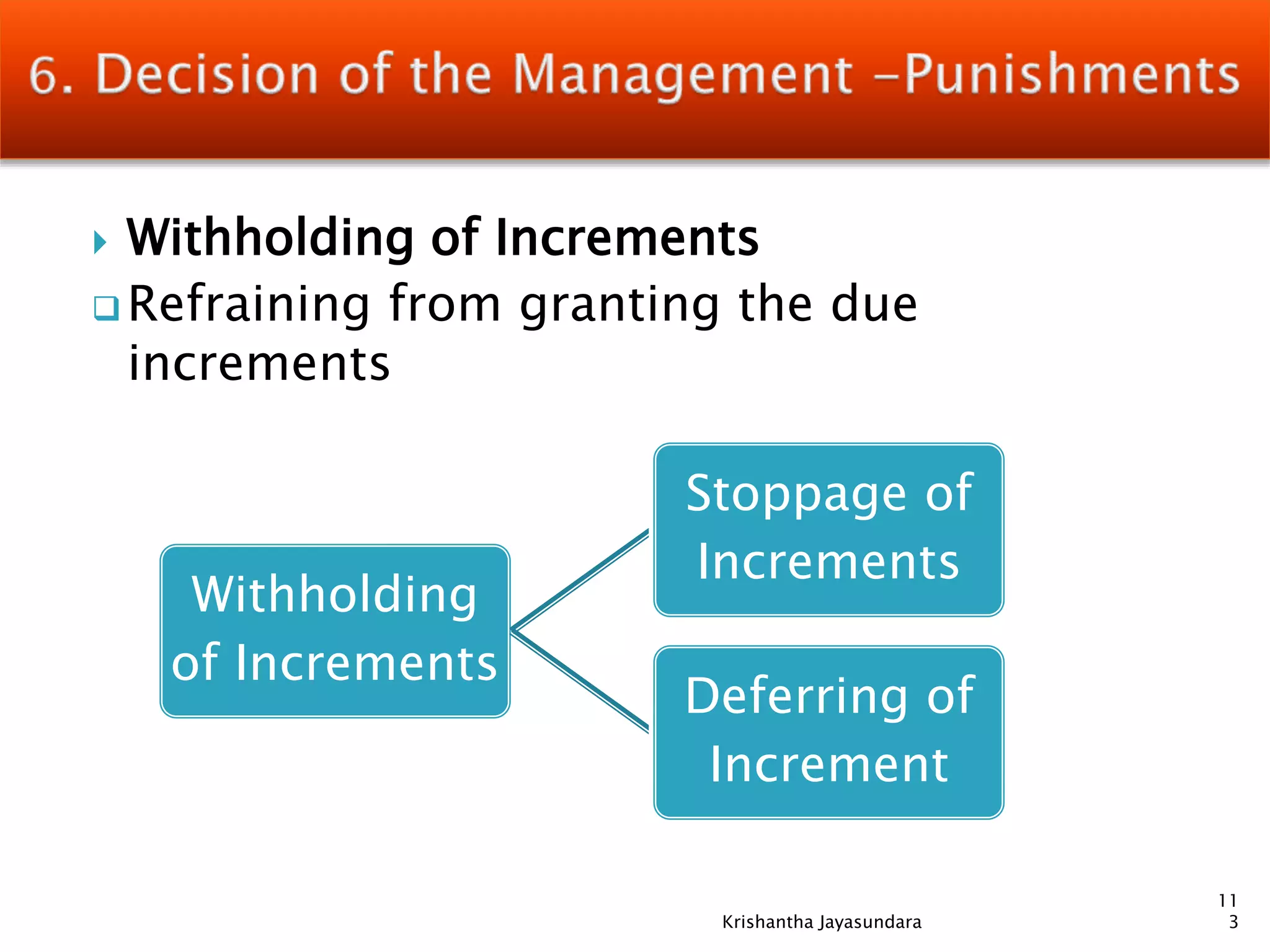
The document discusses discipline in the workplace, focusing on systematic instruction aimed at correcting employee behavior through various methods including preventive and corrective discipline. It outlines principles such as natural justice, fairness, and equity in handling misconduct, as well as distinguishing between minor and major misconducts, and the appropriate disciplinary actions to take. The document further elaborates on the process of investigation, domestic inquiries, and the consequences of various infractions.