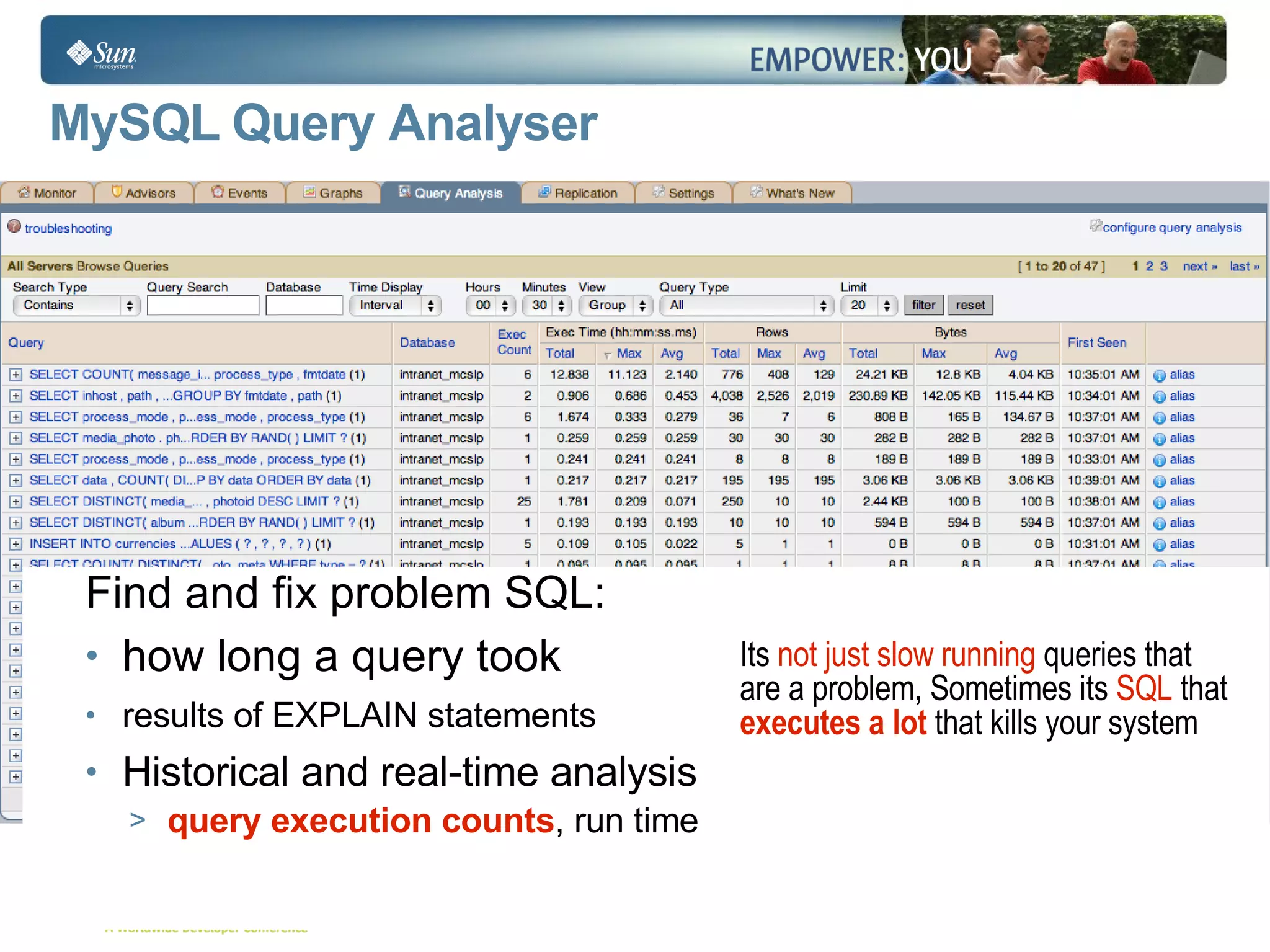
The document discusses best practices for using the Java Persistence API (JPA). It covers:
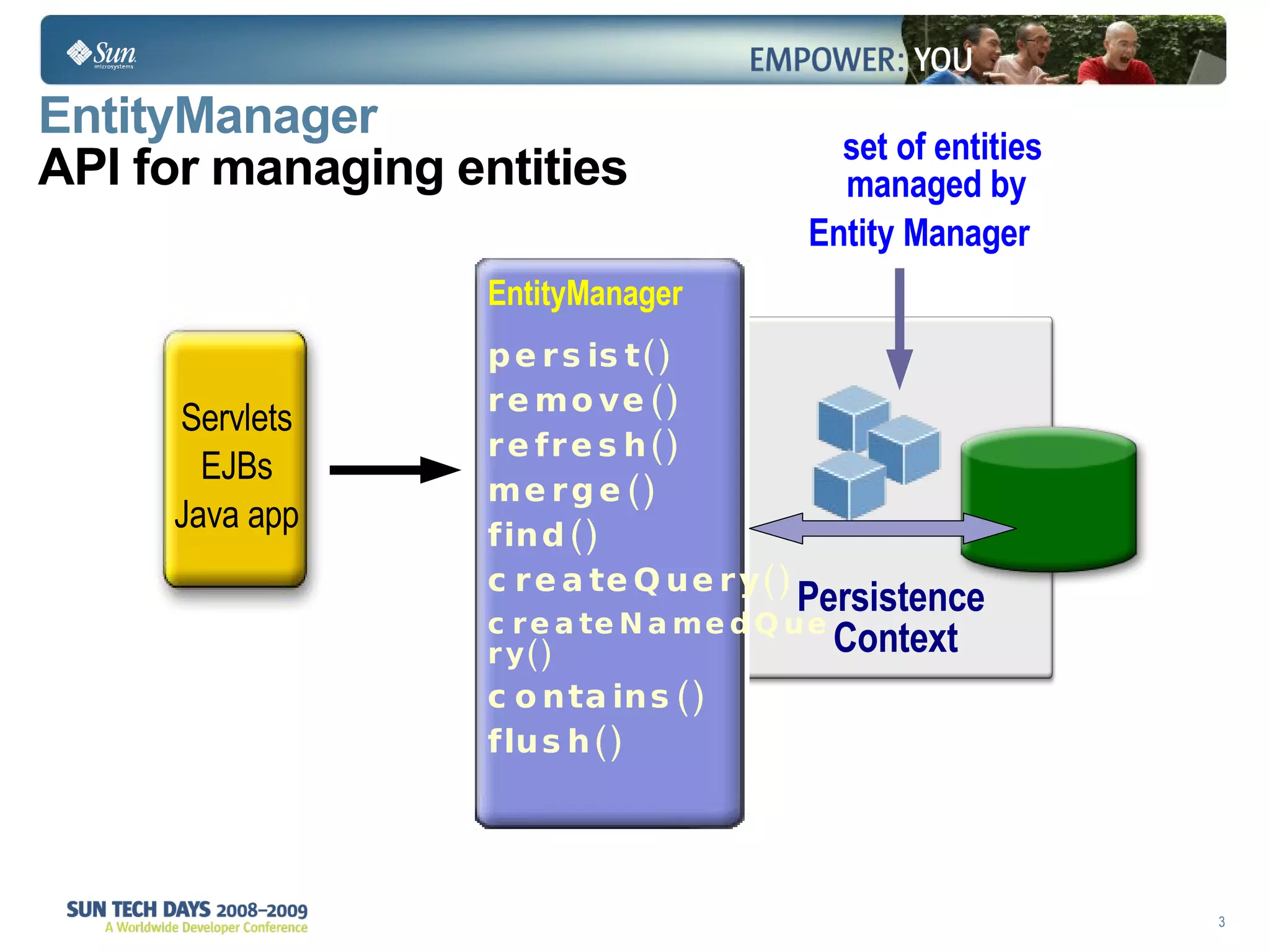
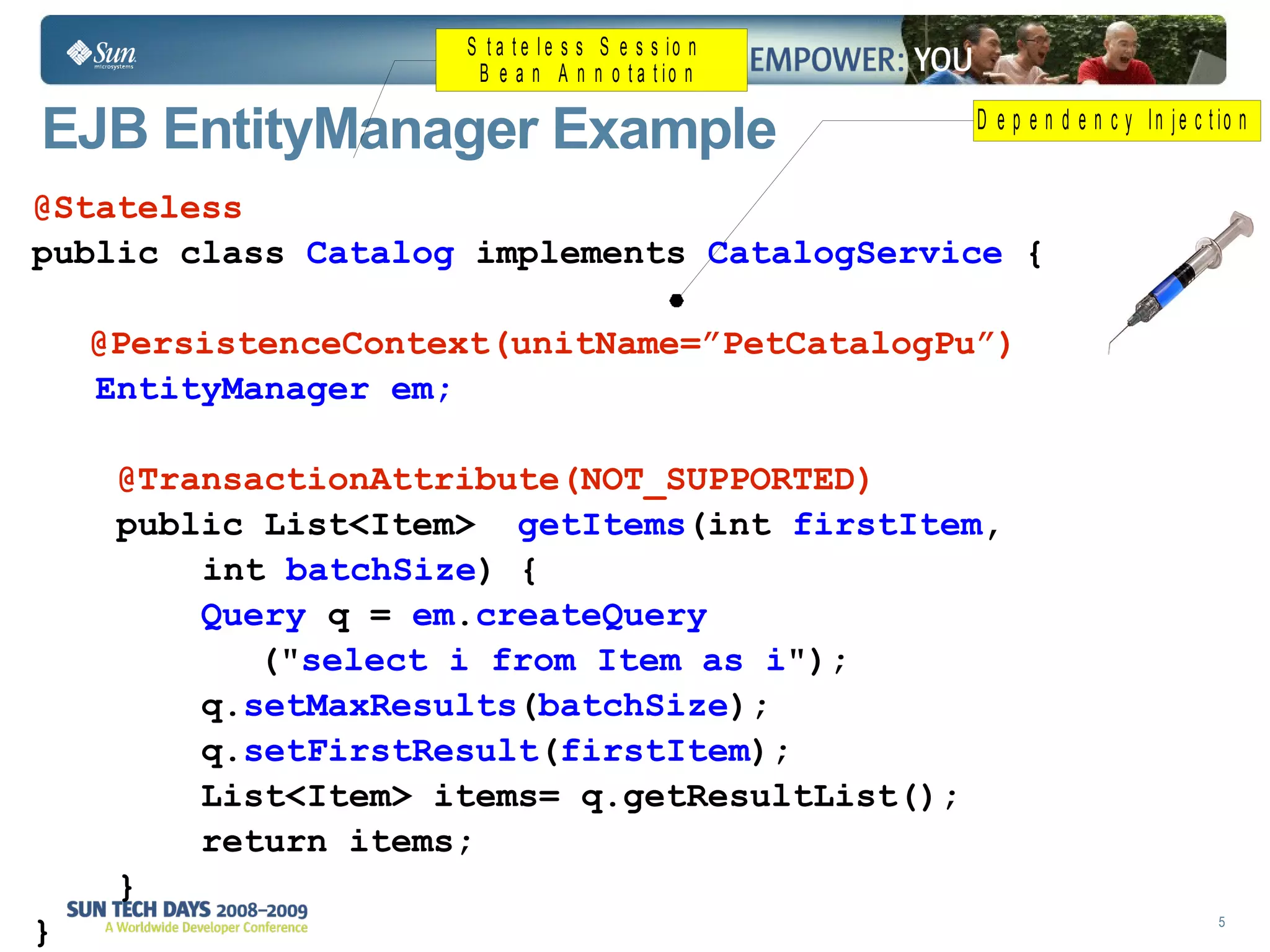
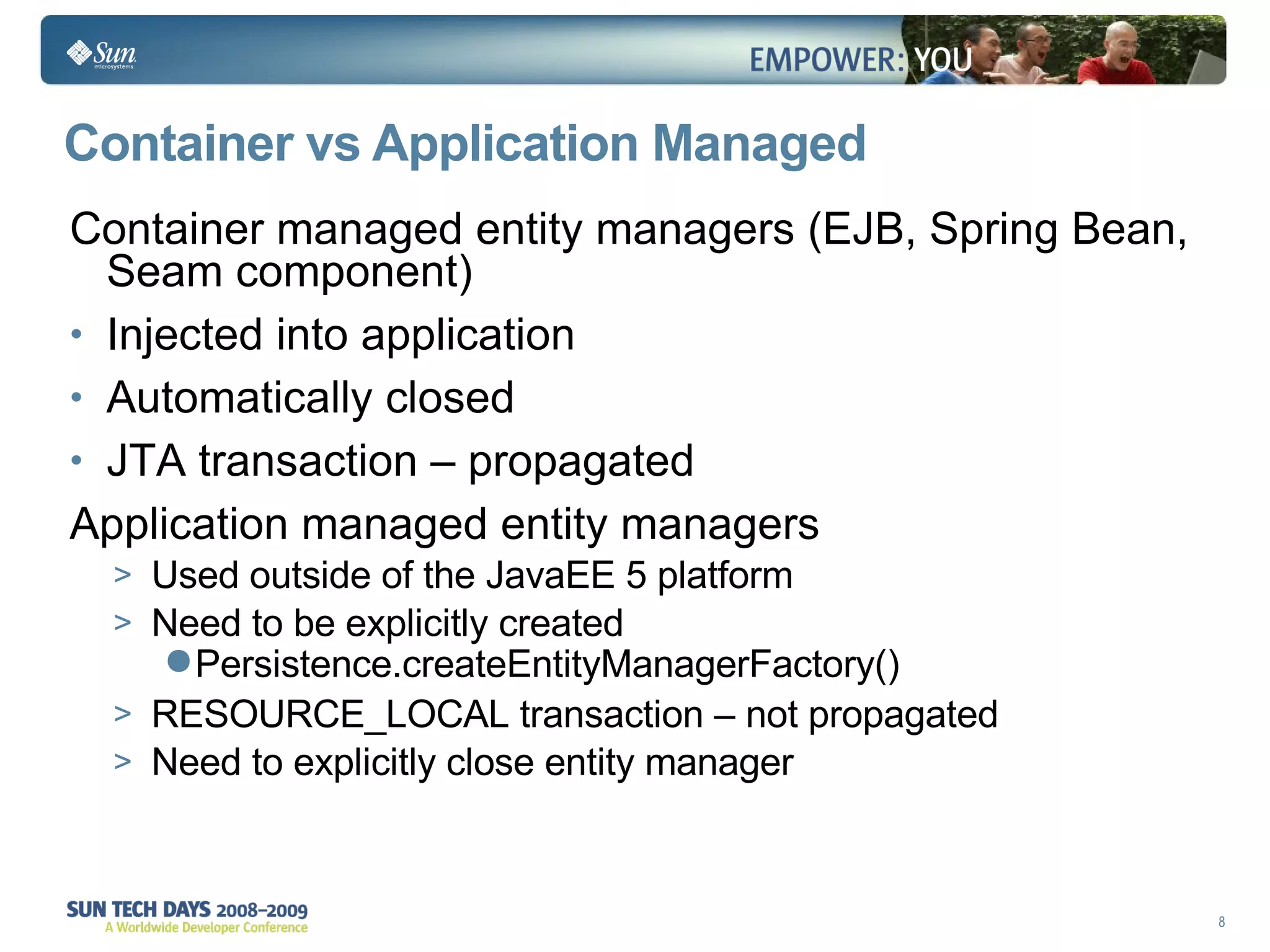
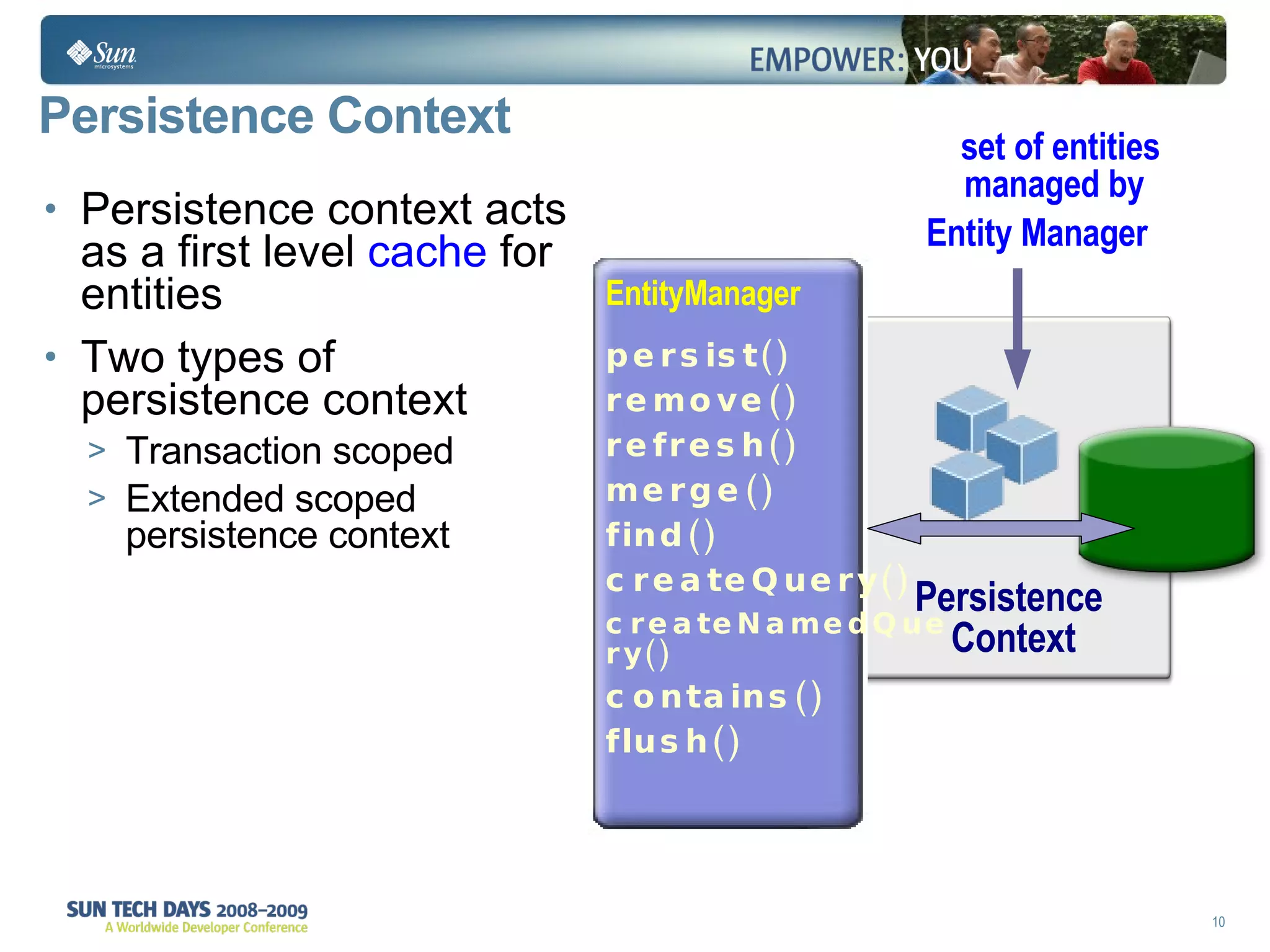
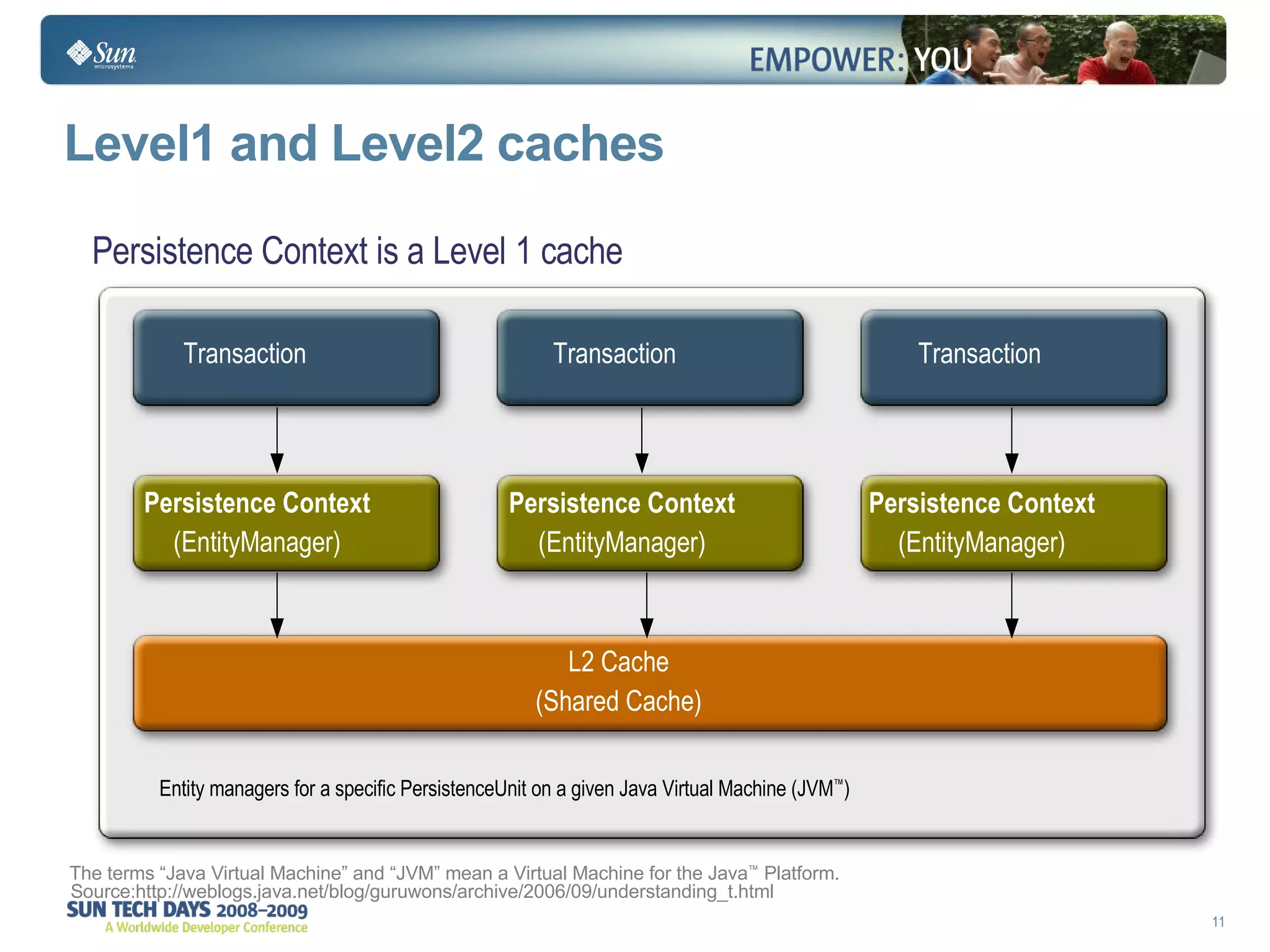
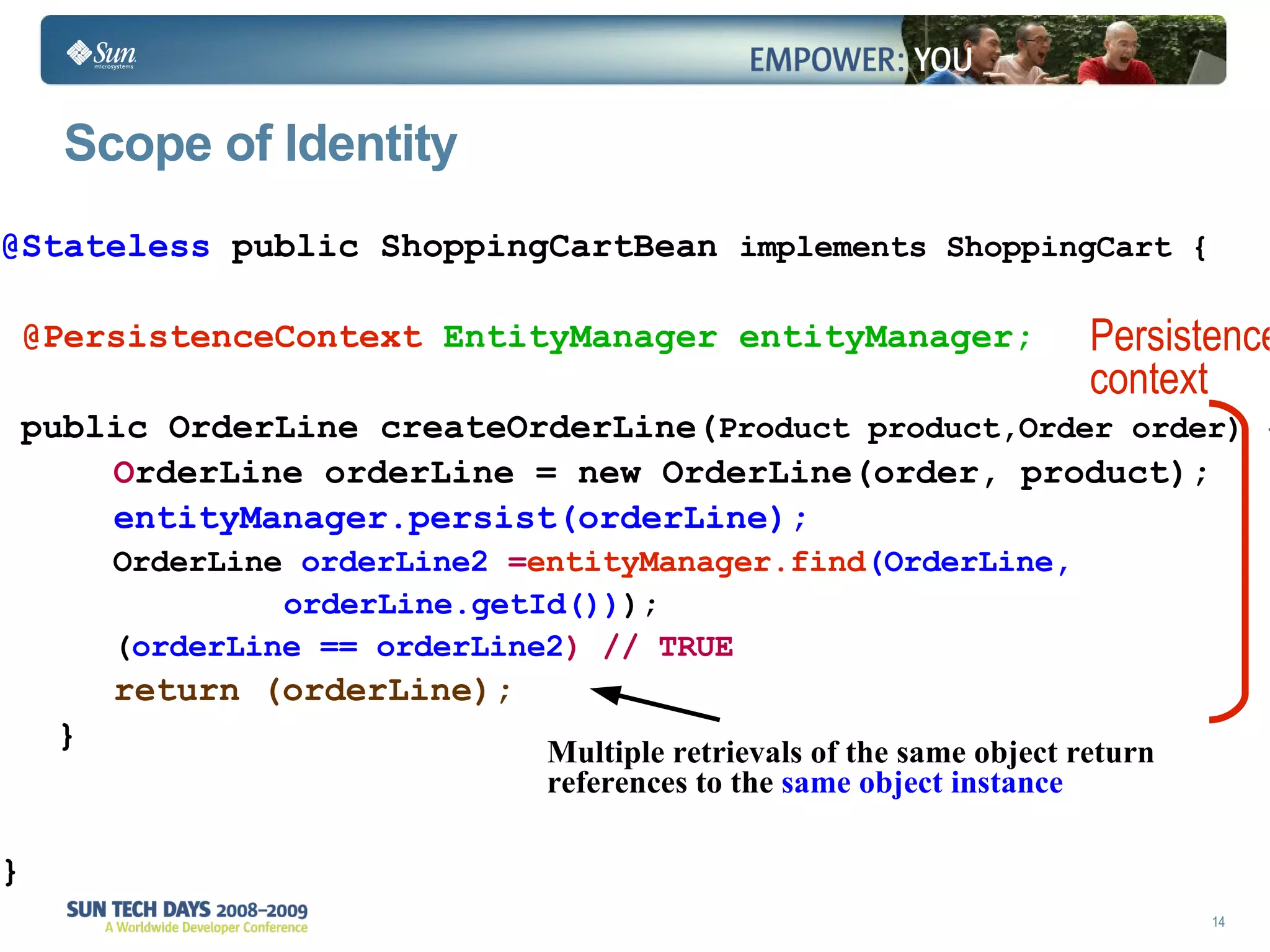
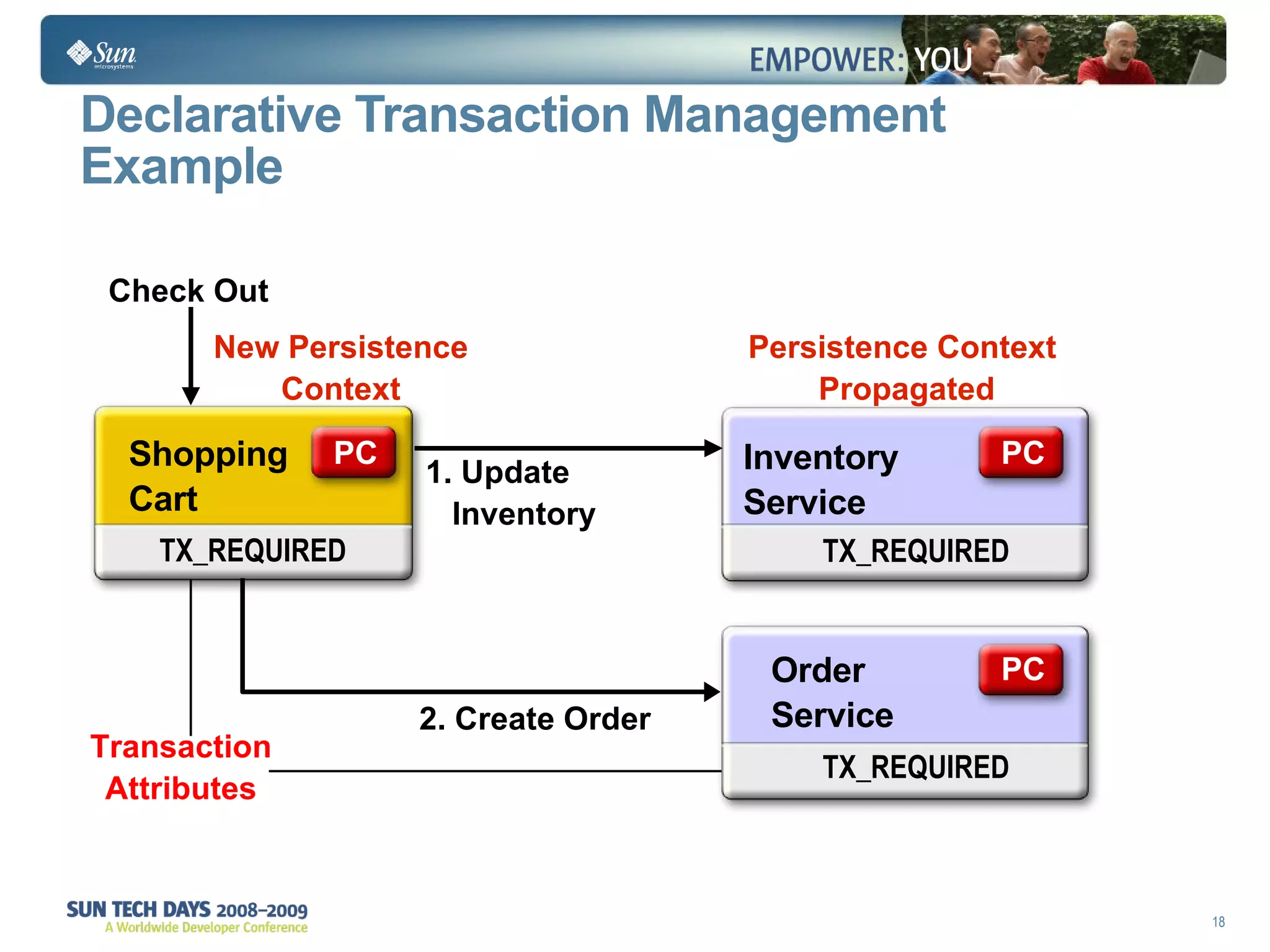
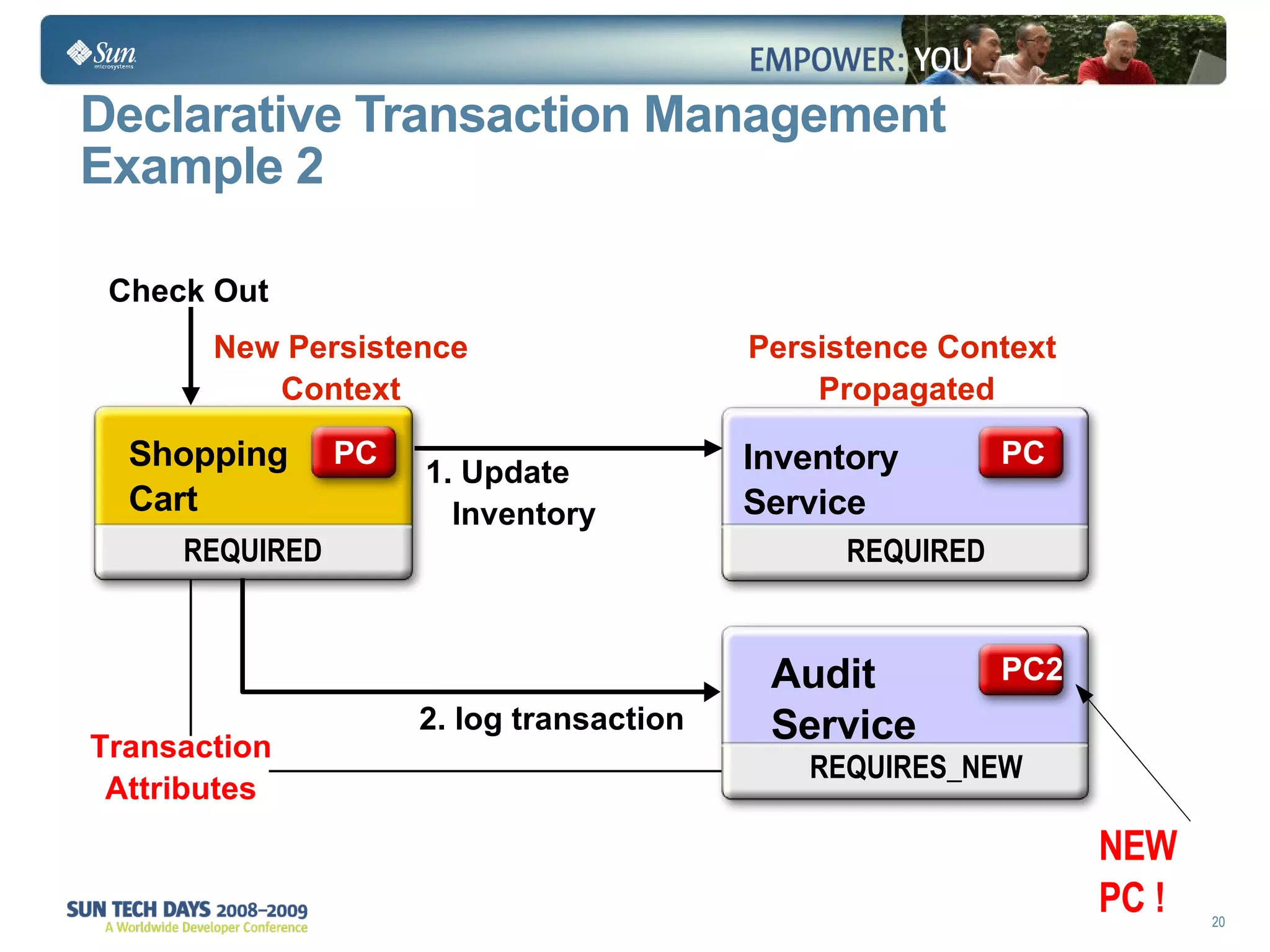
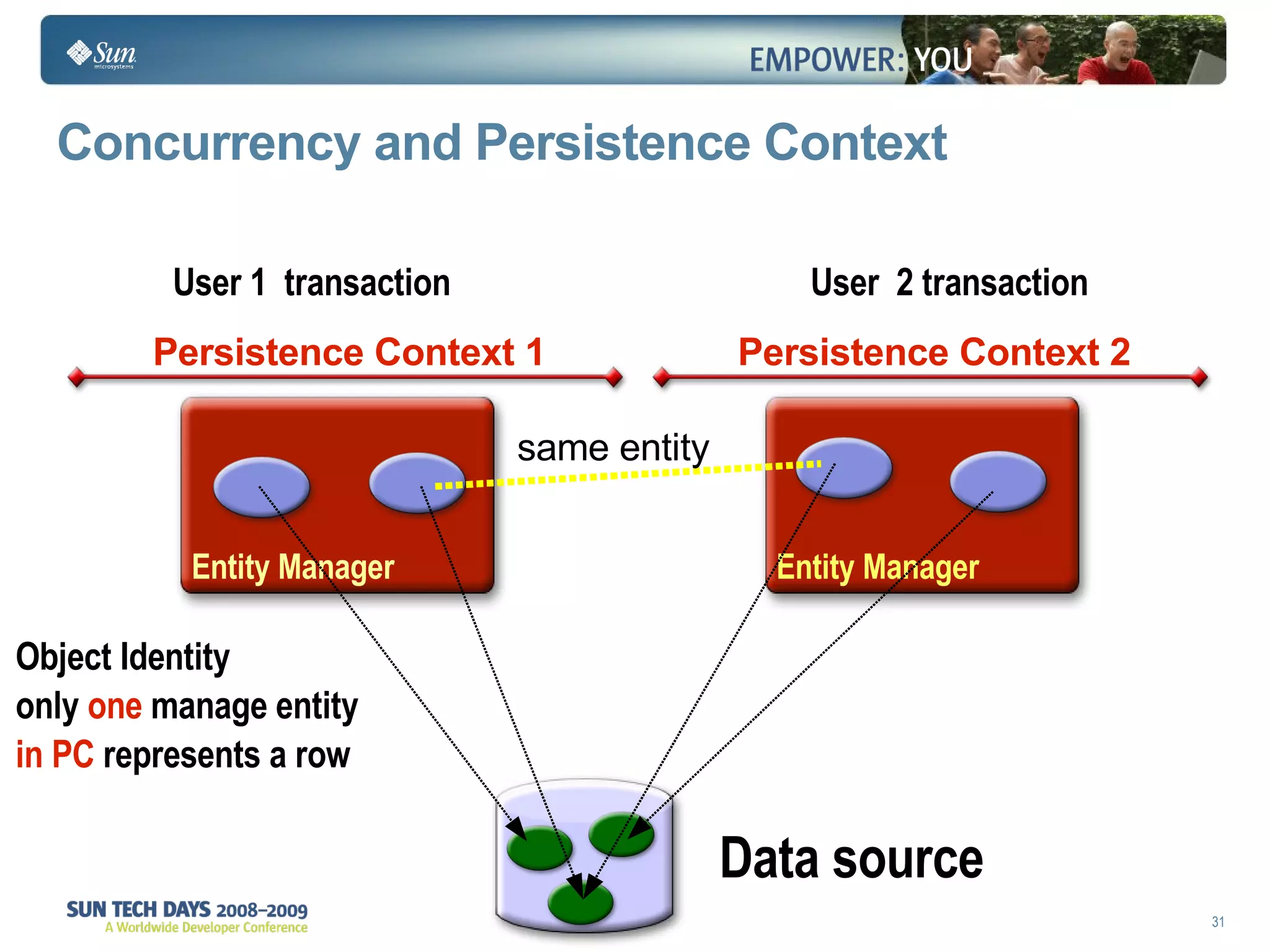
- The entity manager and persistence context manage entities within a scope like a transaction.
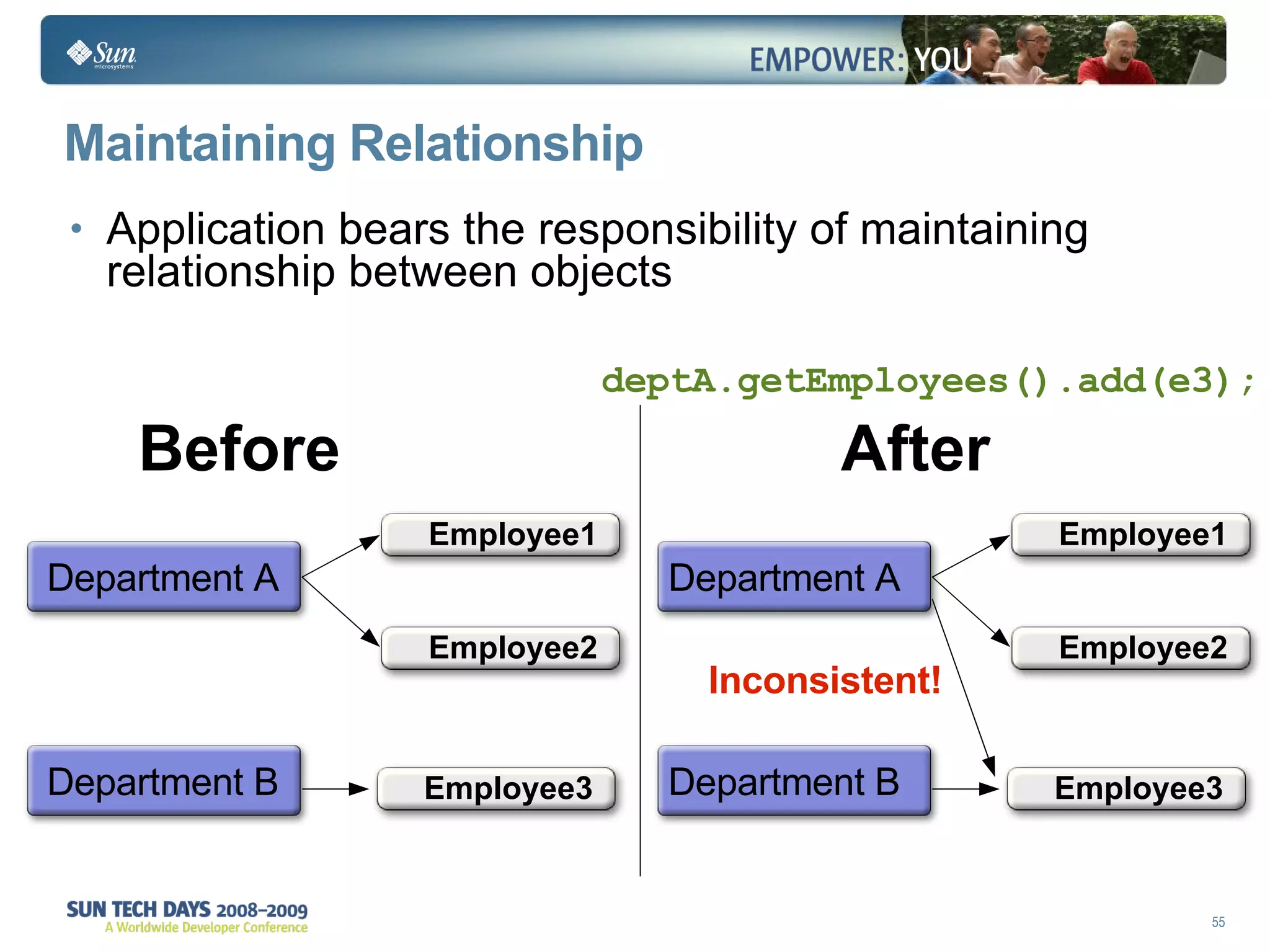
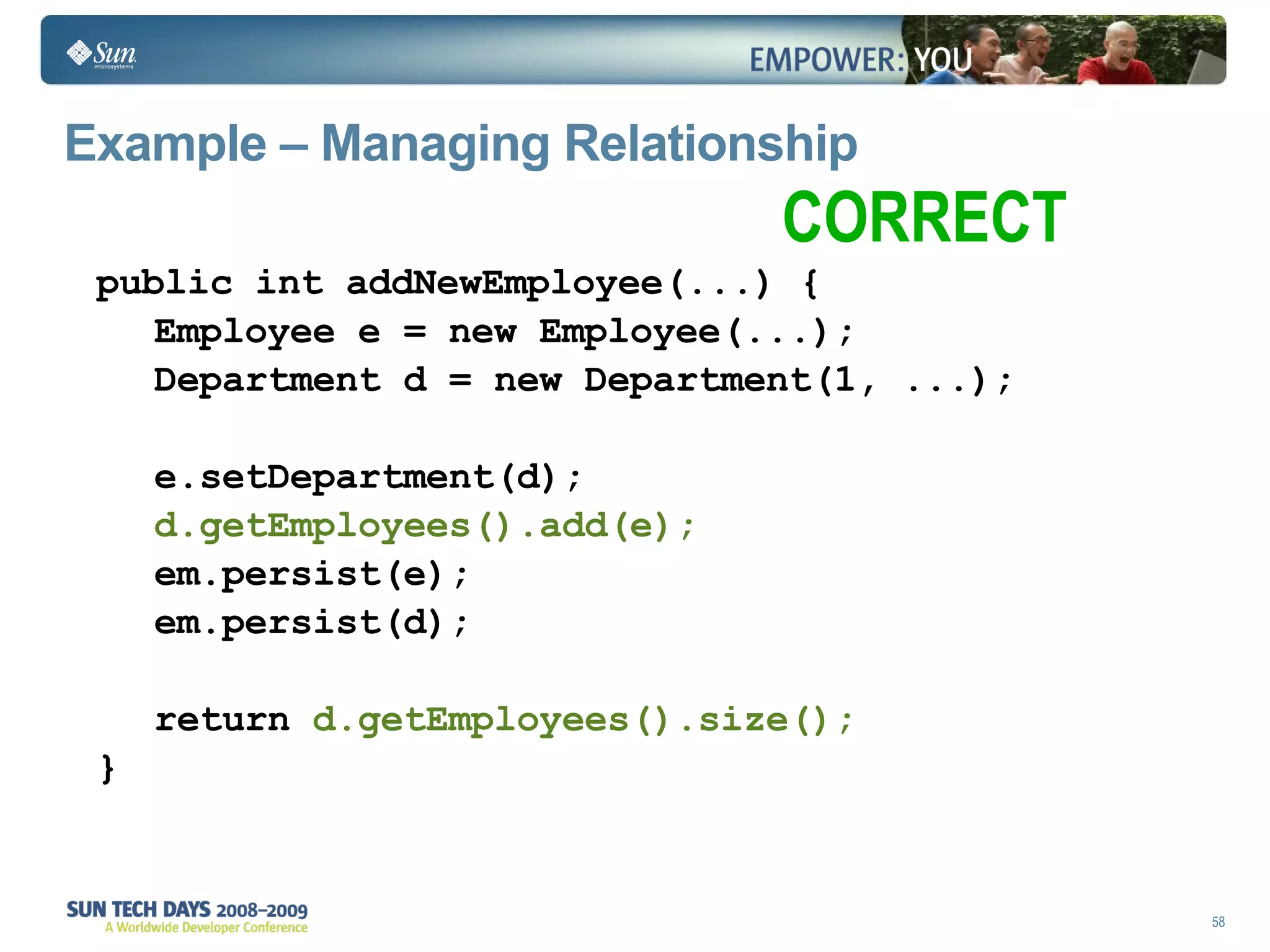
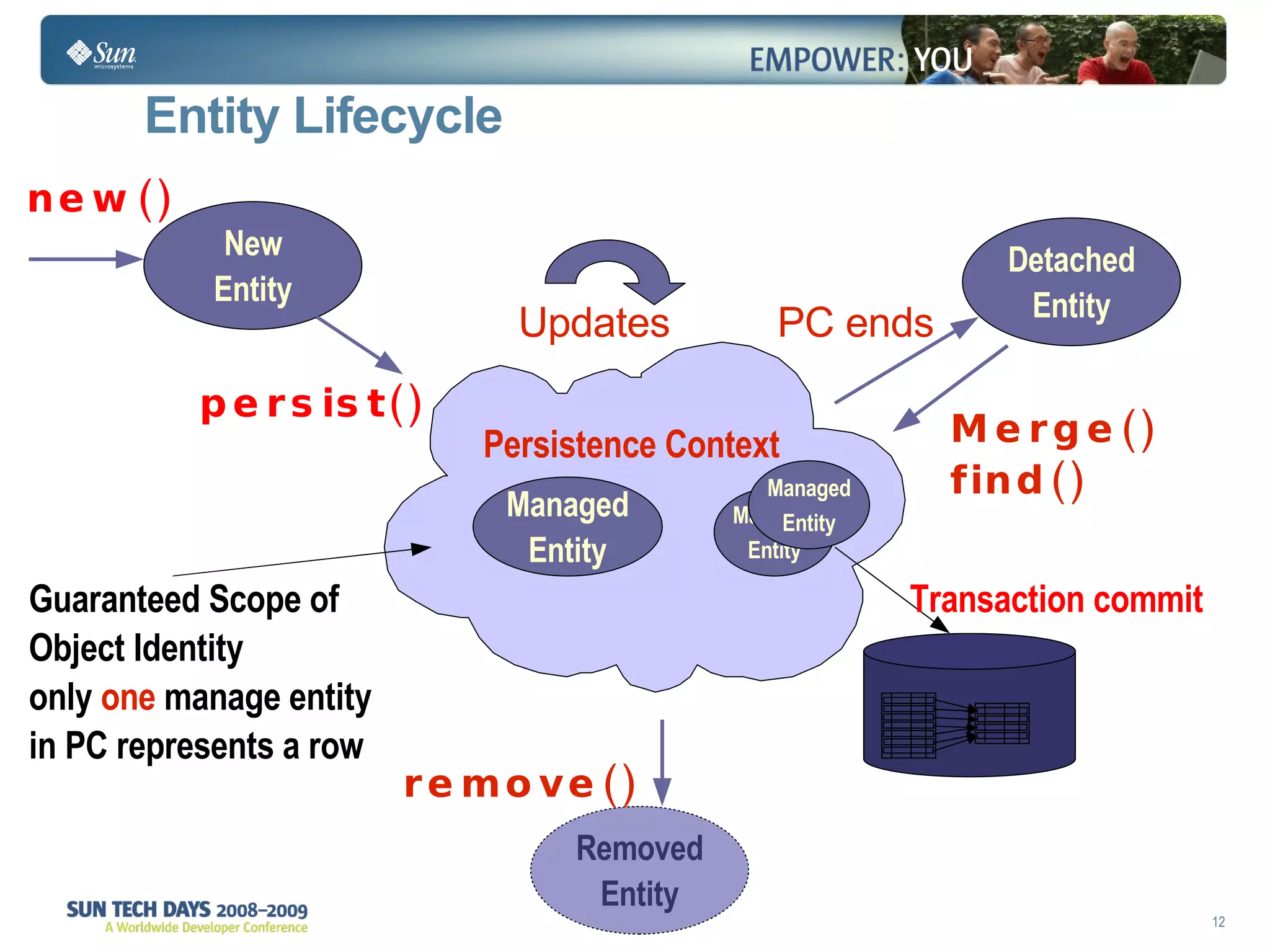
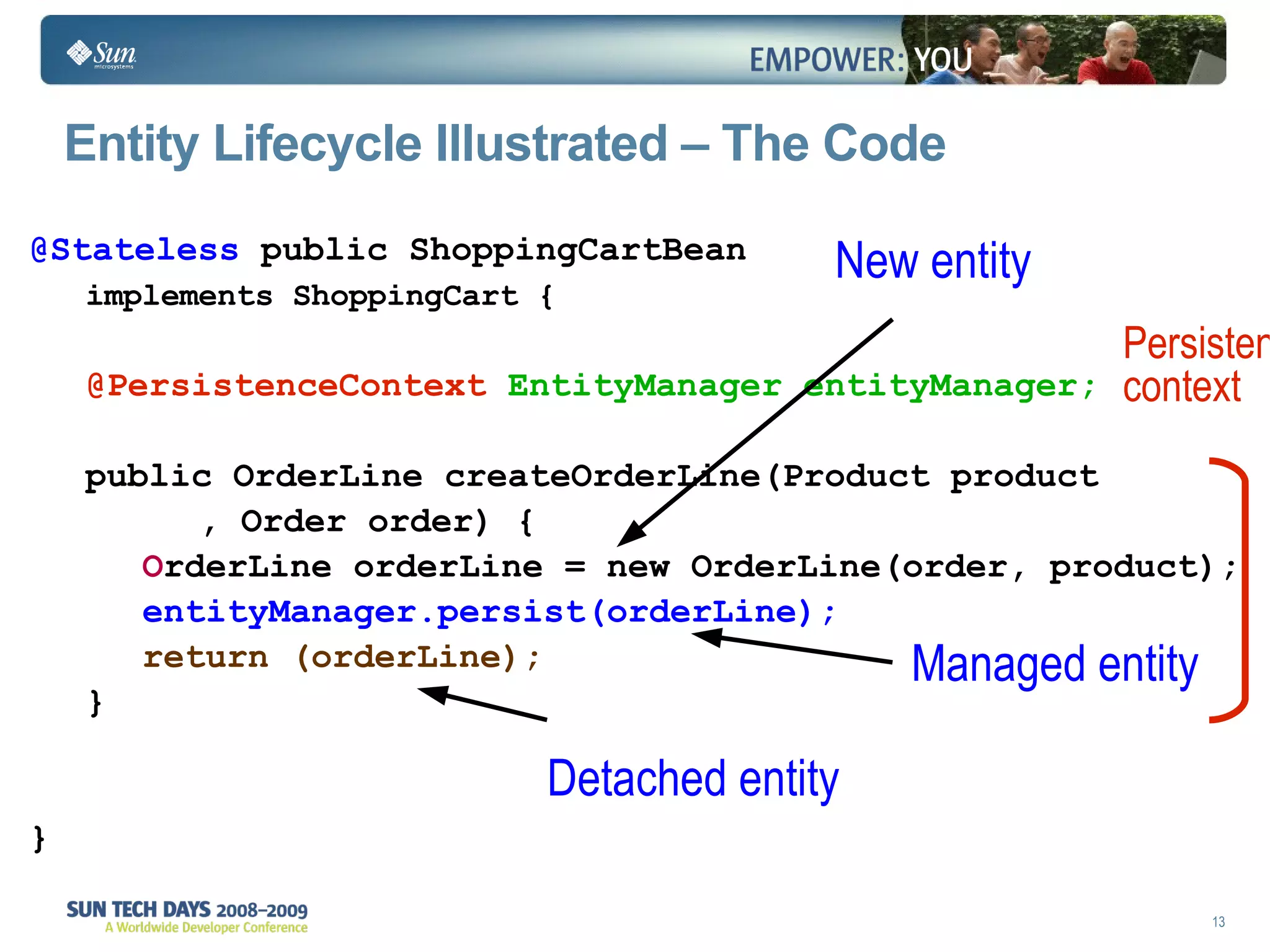
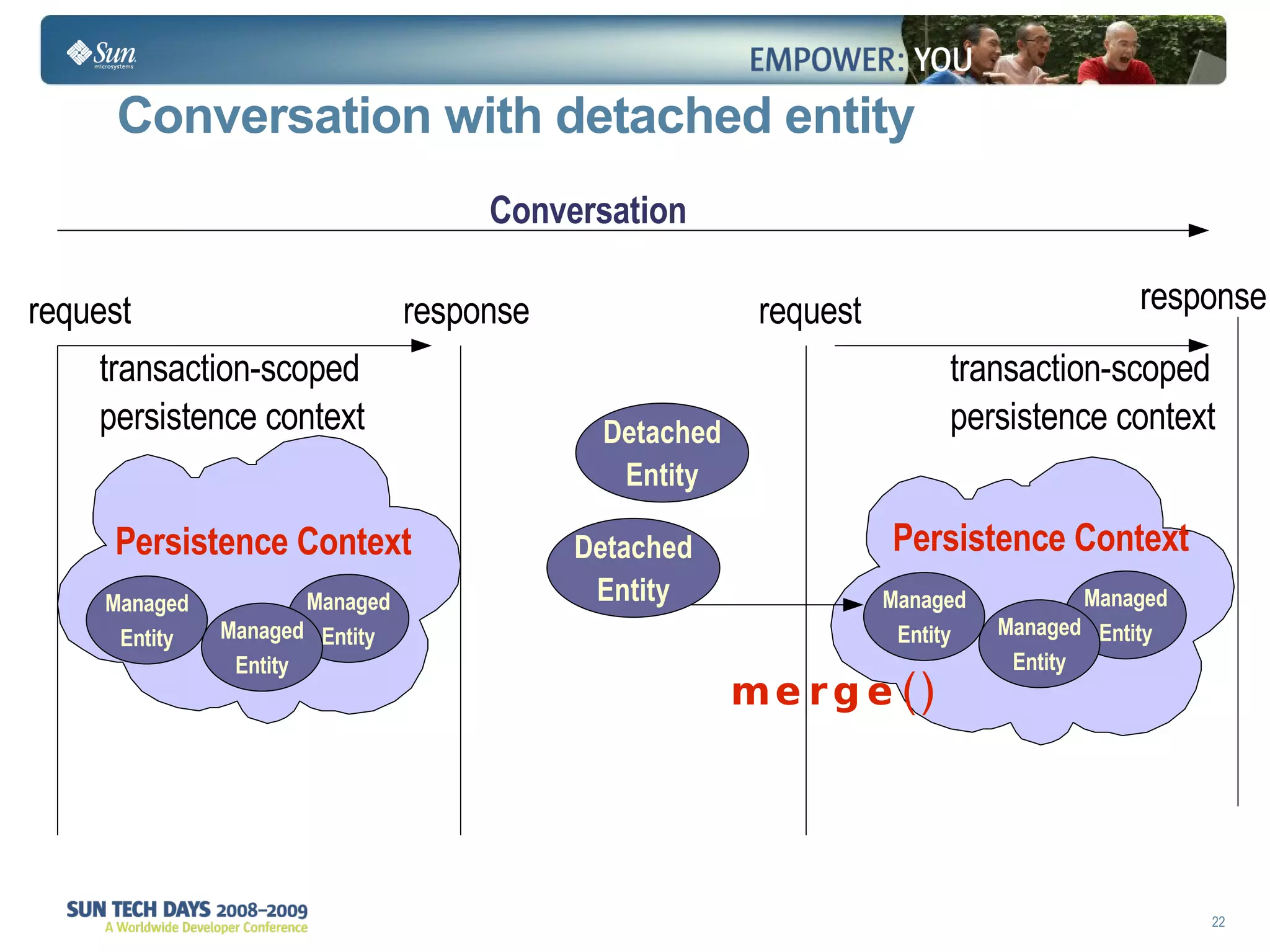
- Entities transition between managed, detached, and removed states that impact database synchronization.
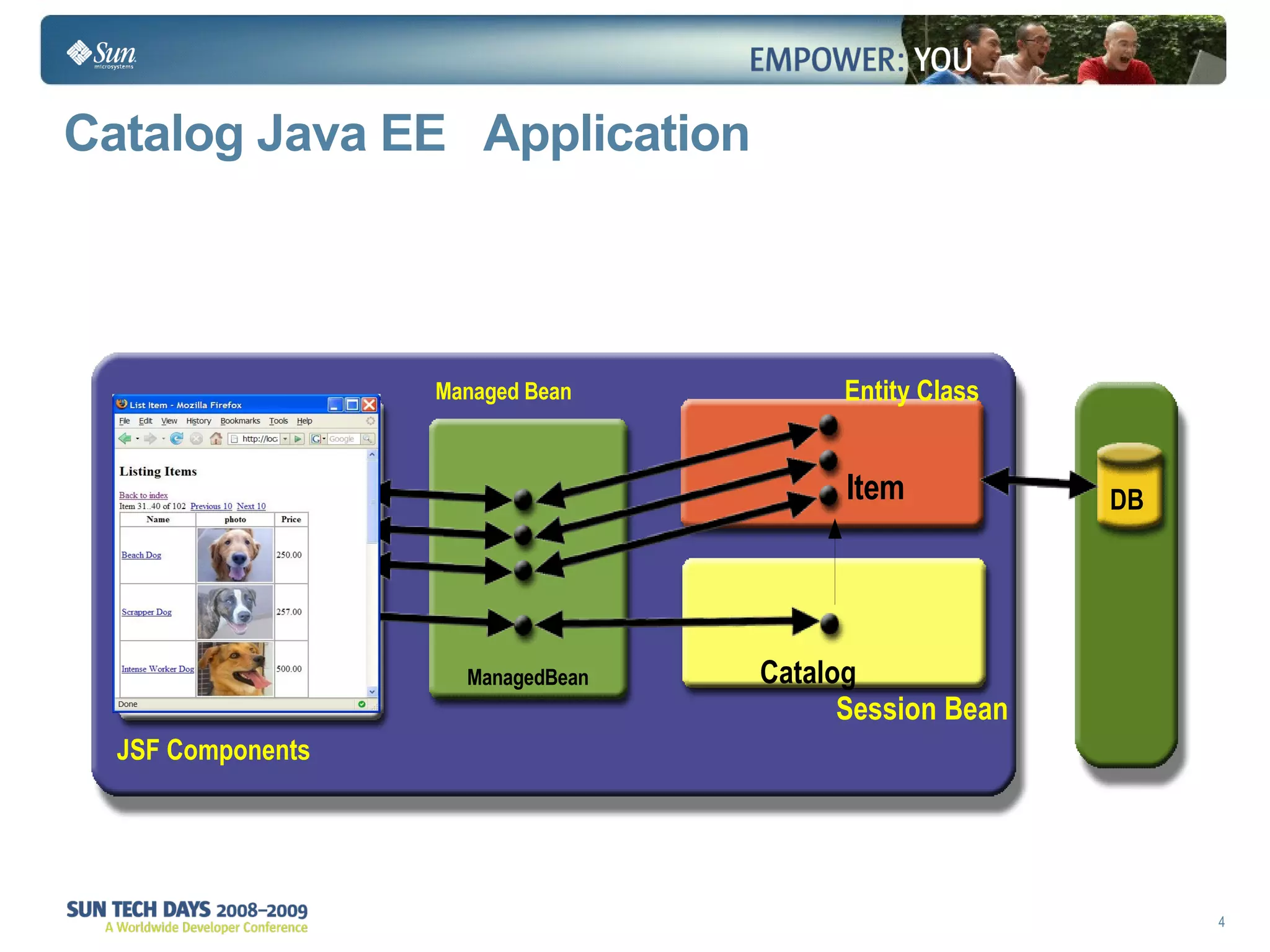
- Queries retrieve and manage entities from the persistence context and database.
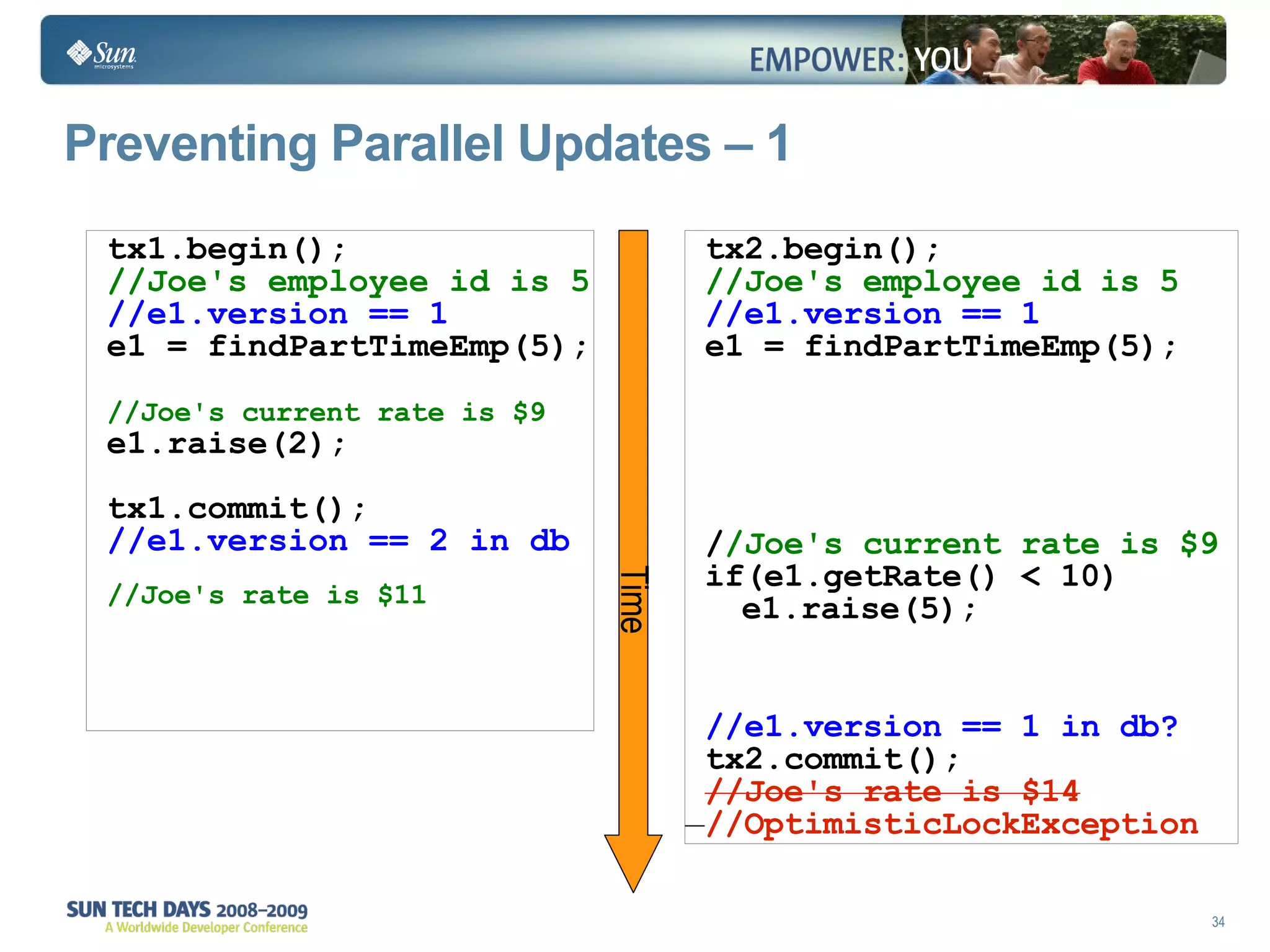
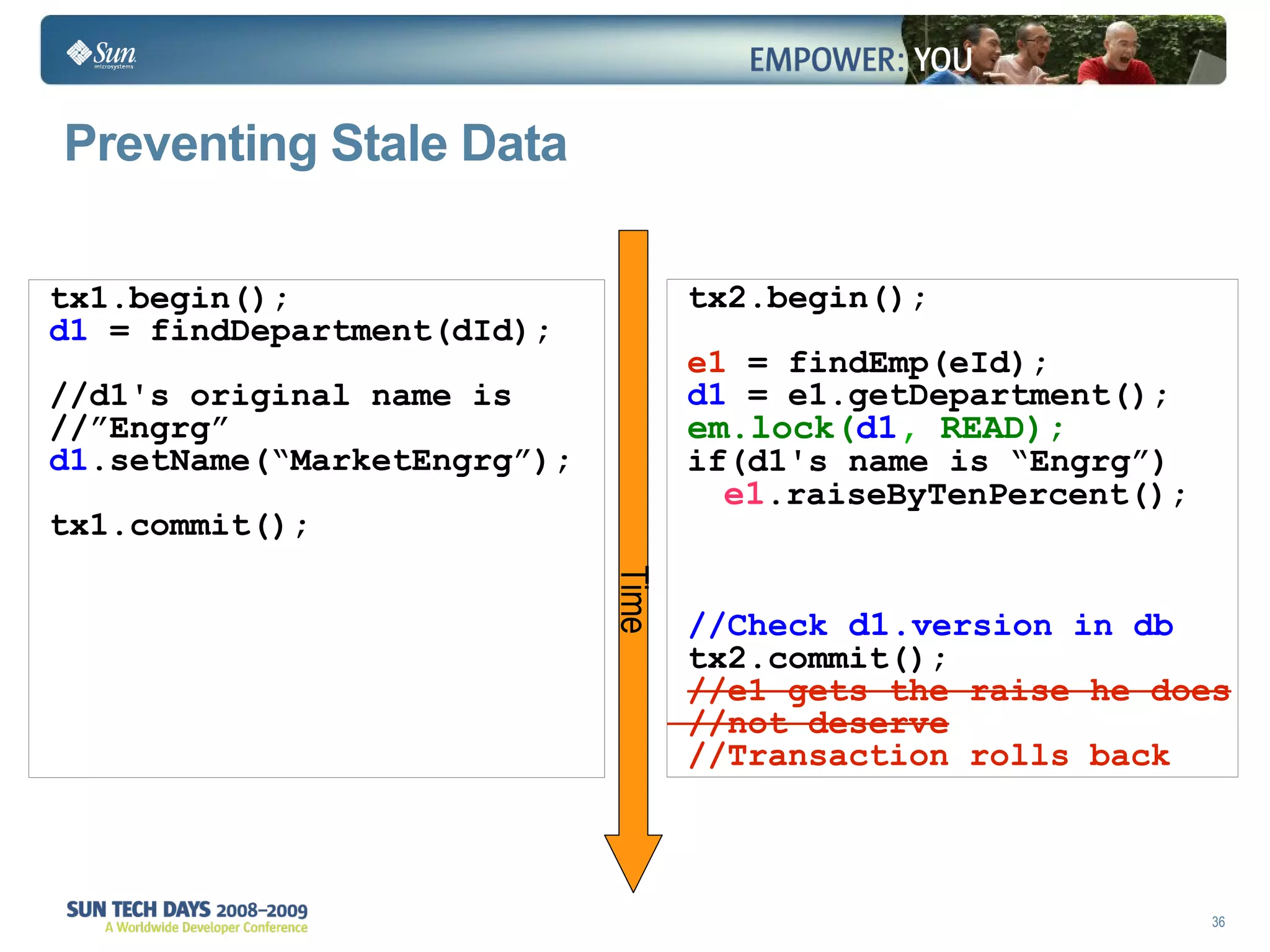
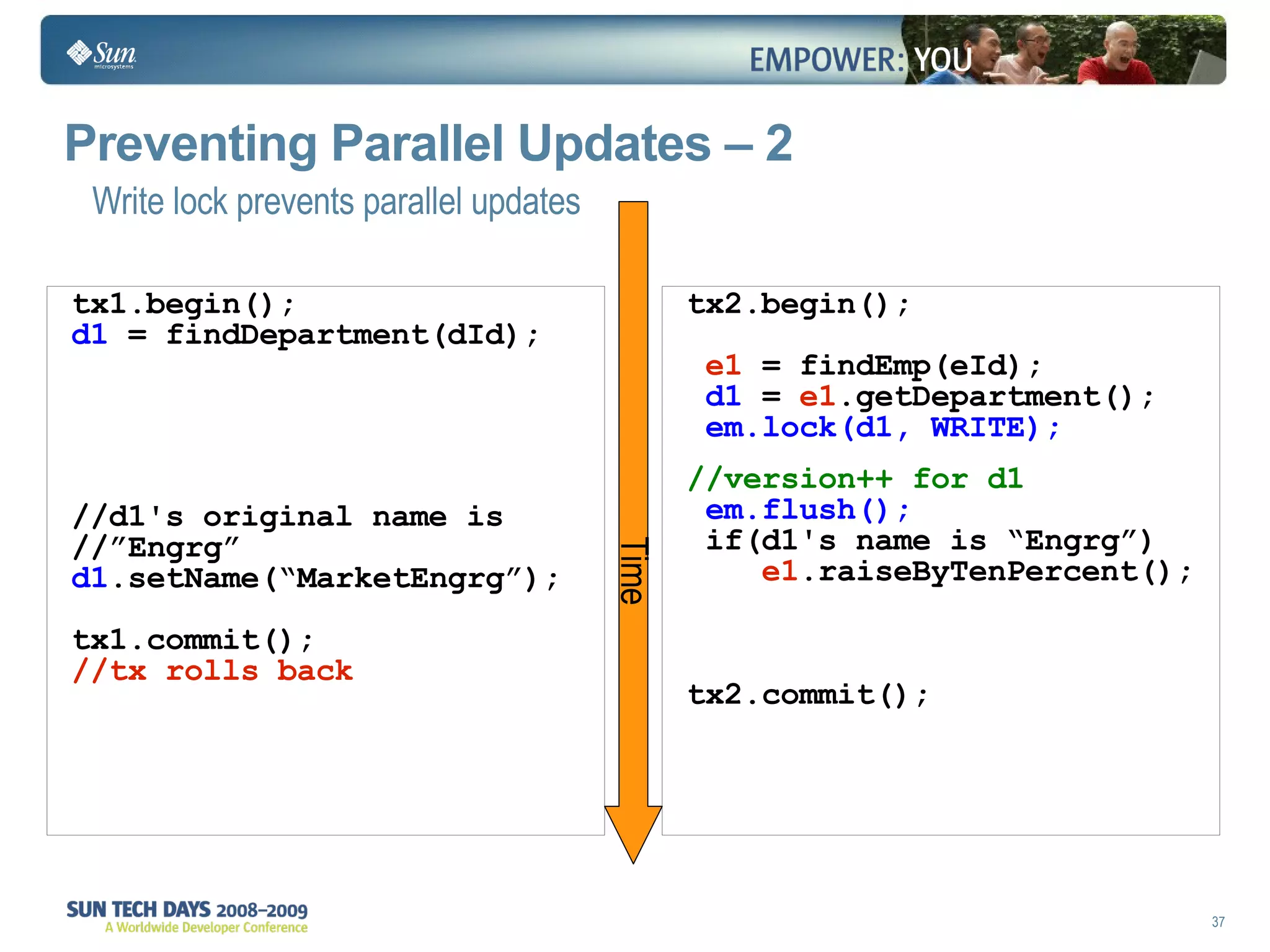
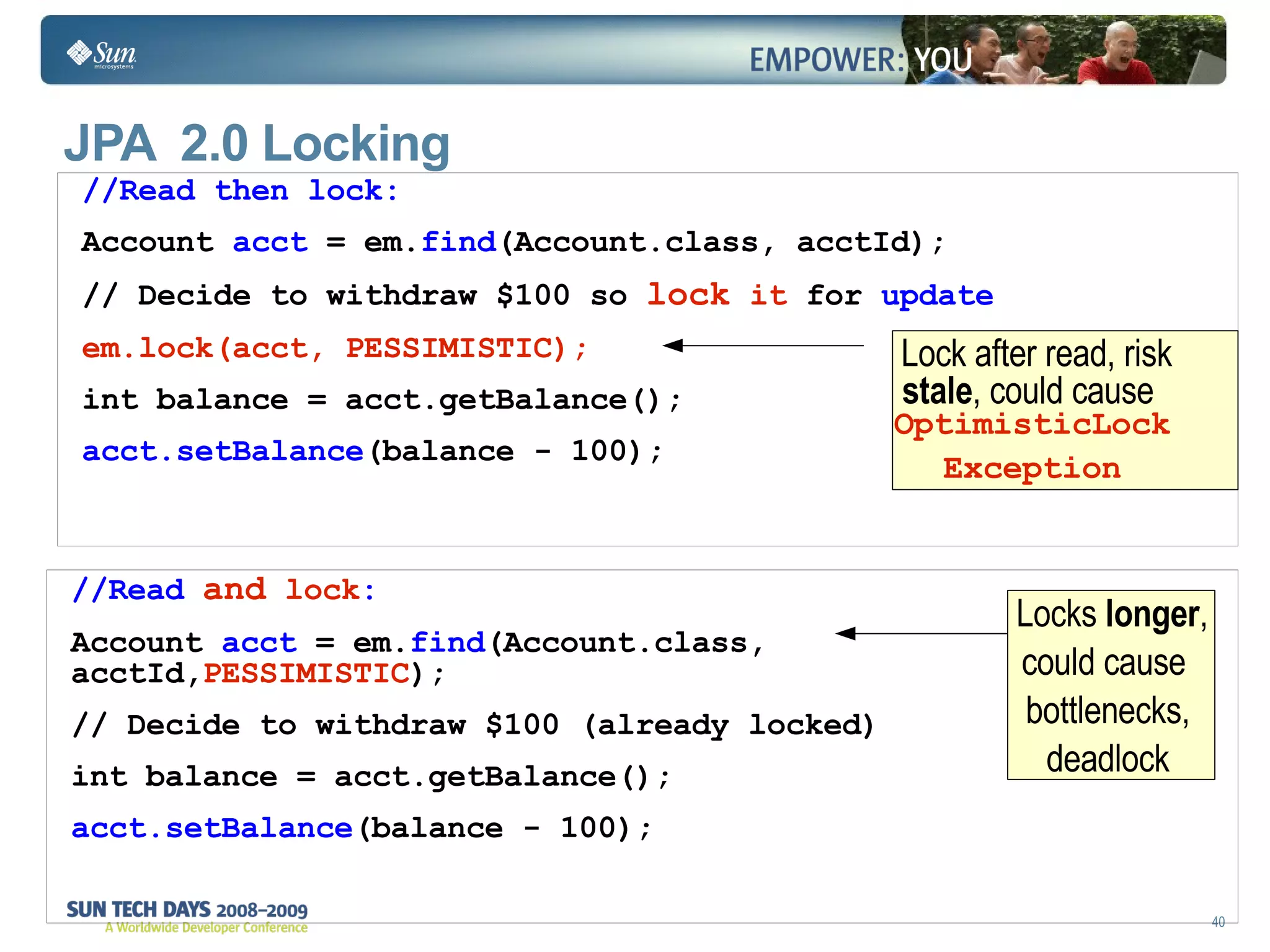
- Transactions and locking strategies like optimistic and pessimistic concurrency control how changes are made.
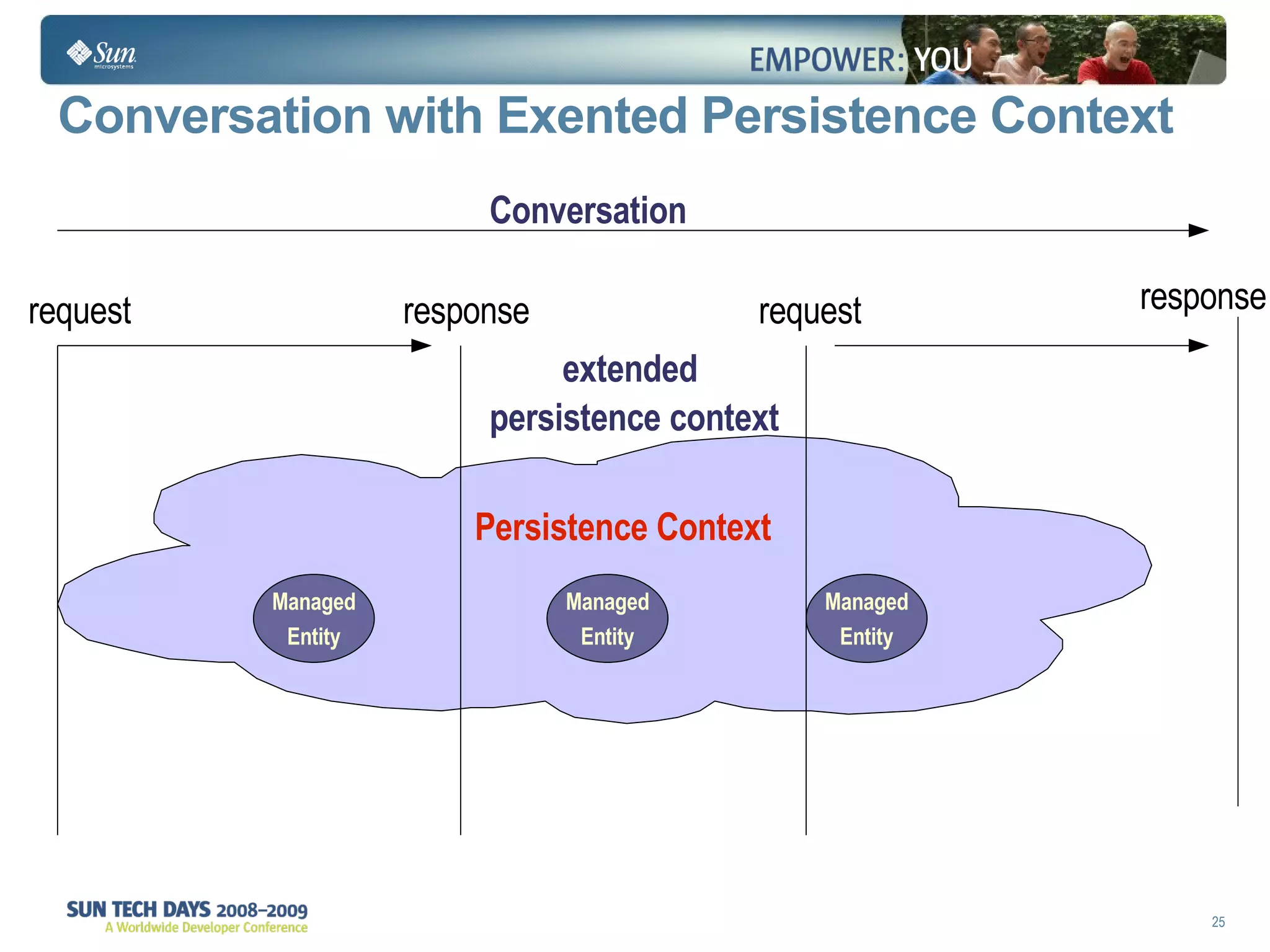
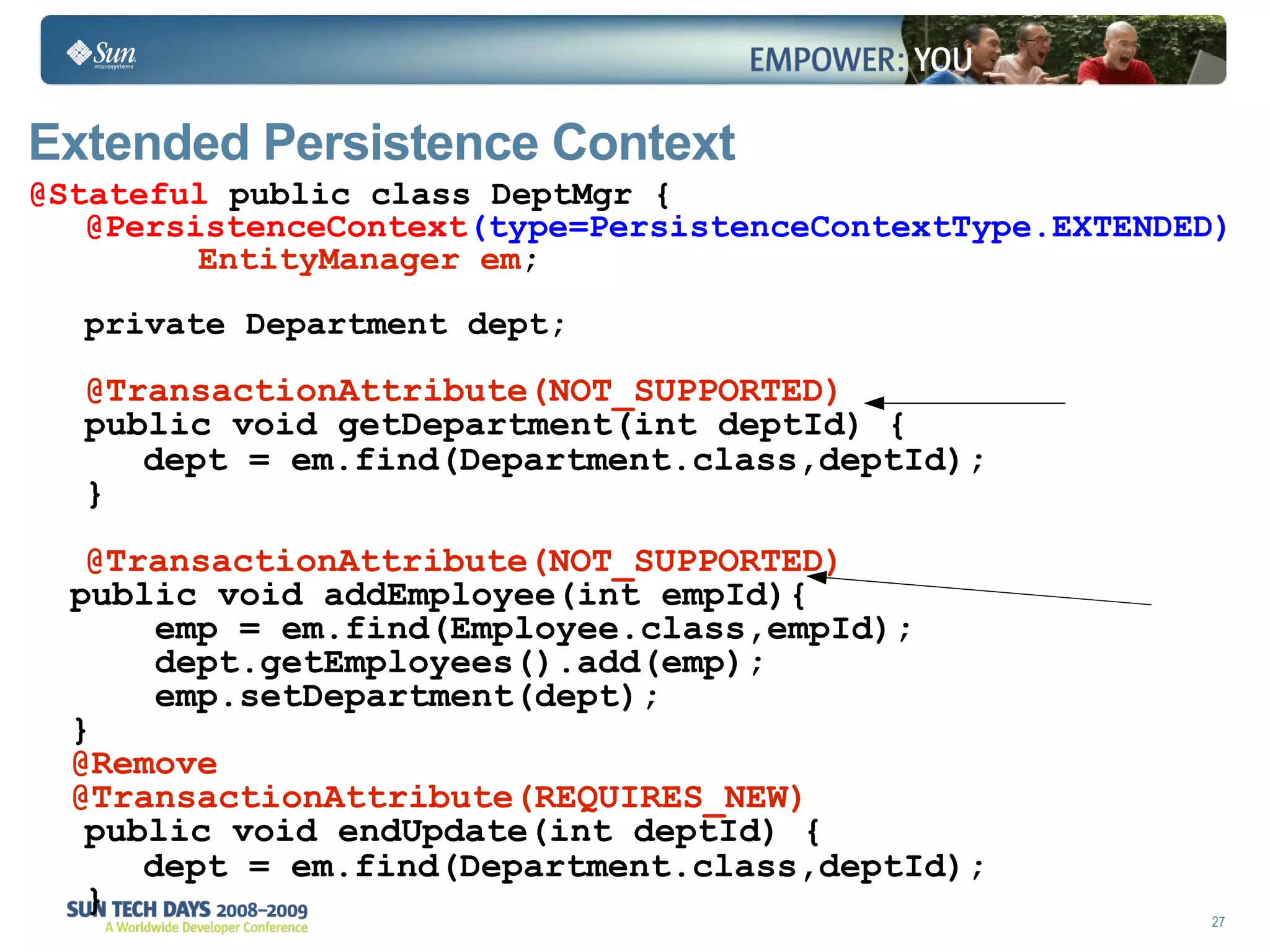
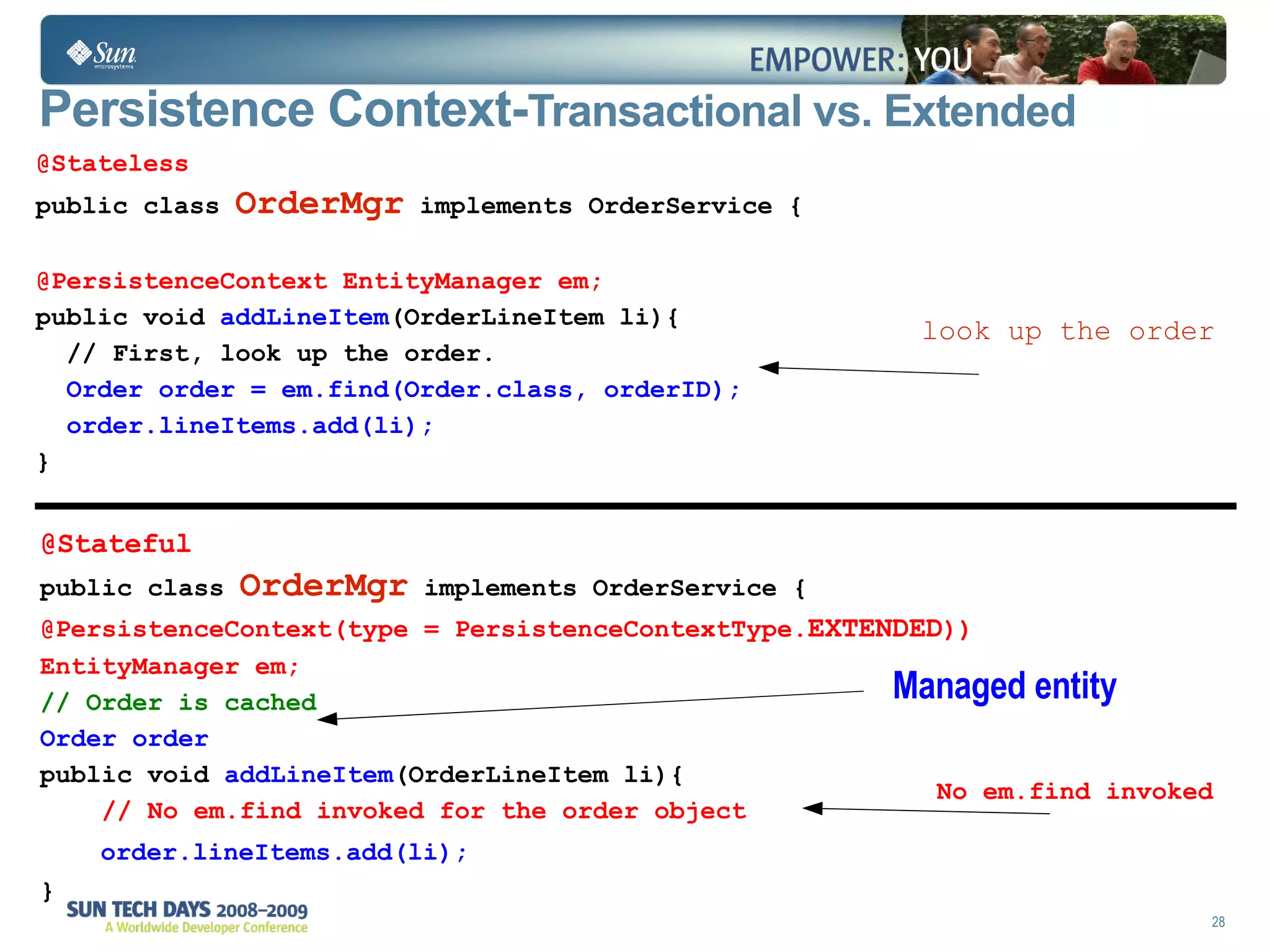
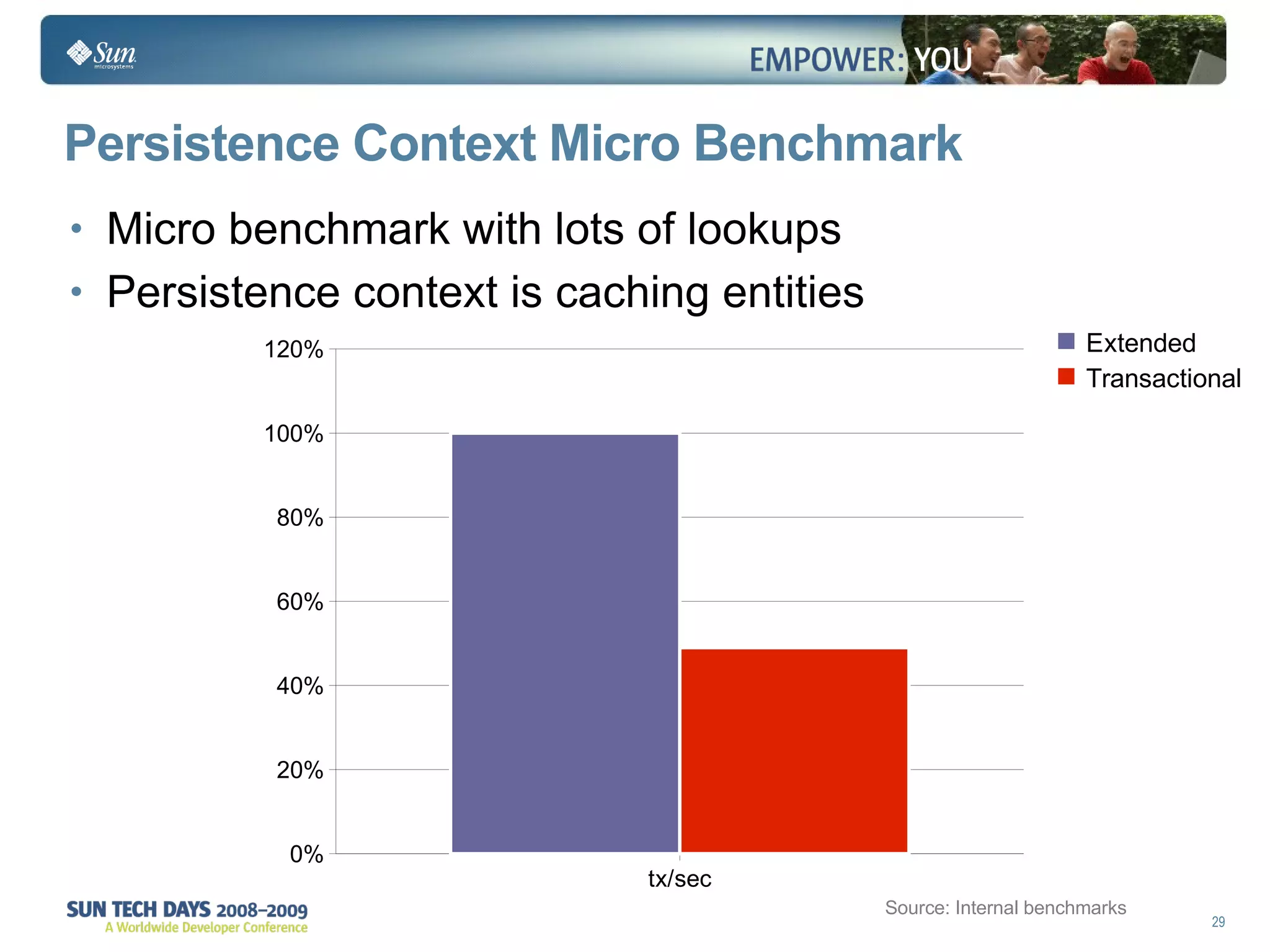
- Extended and transaction scoped persistence contexts determine entity lifetime and caching.
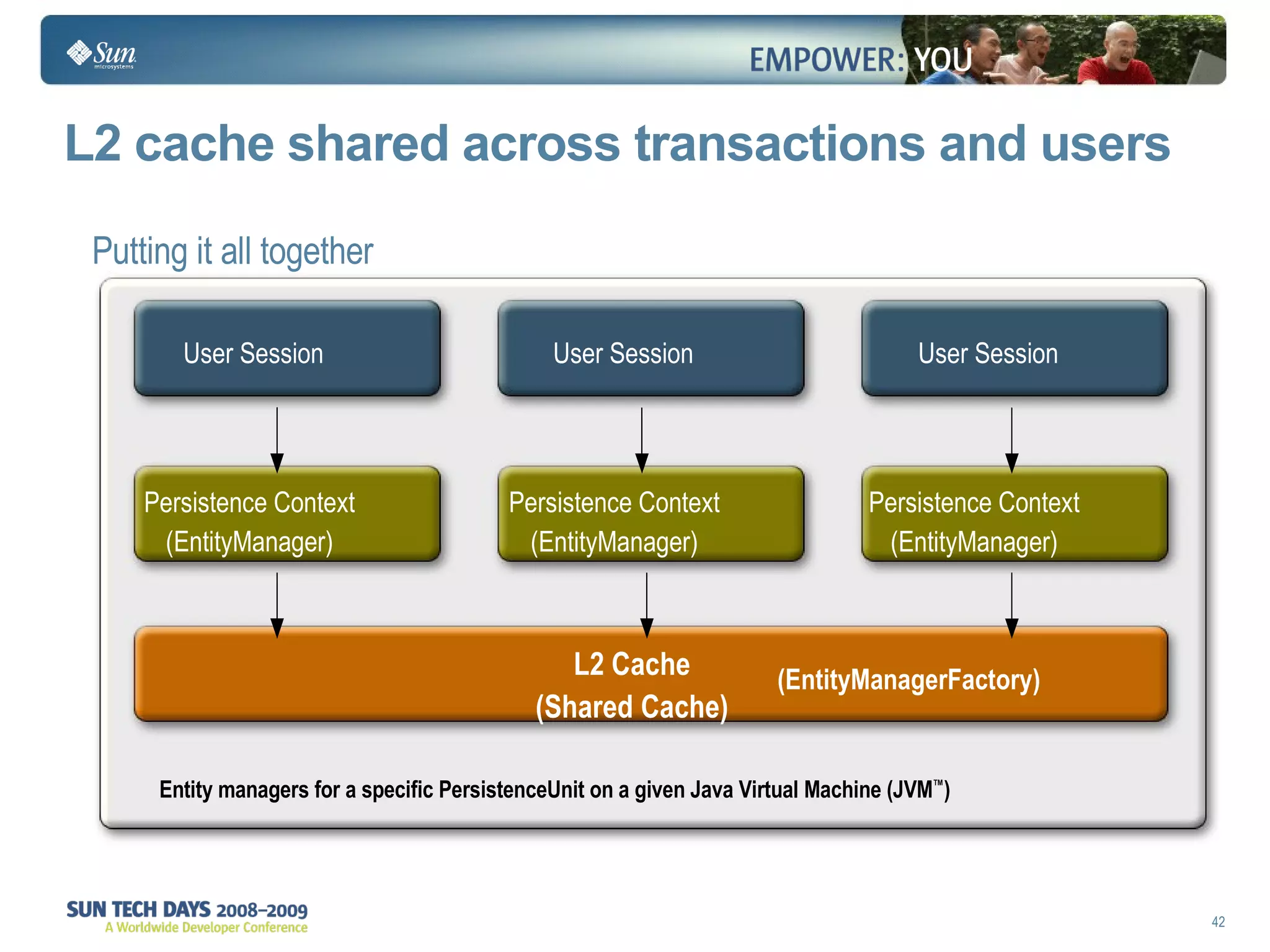
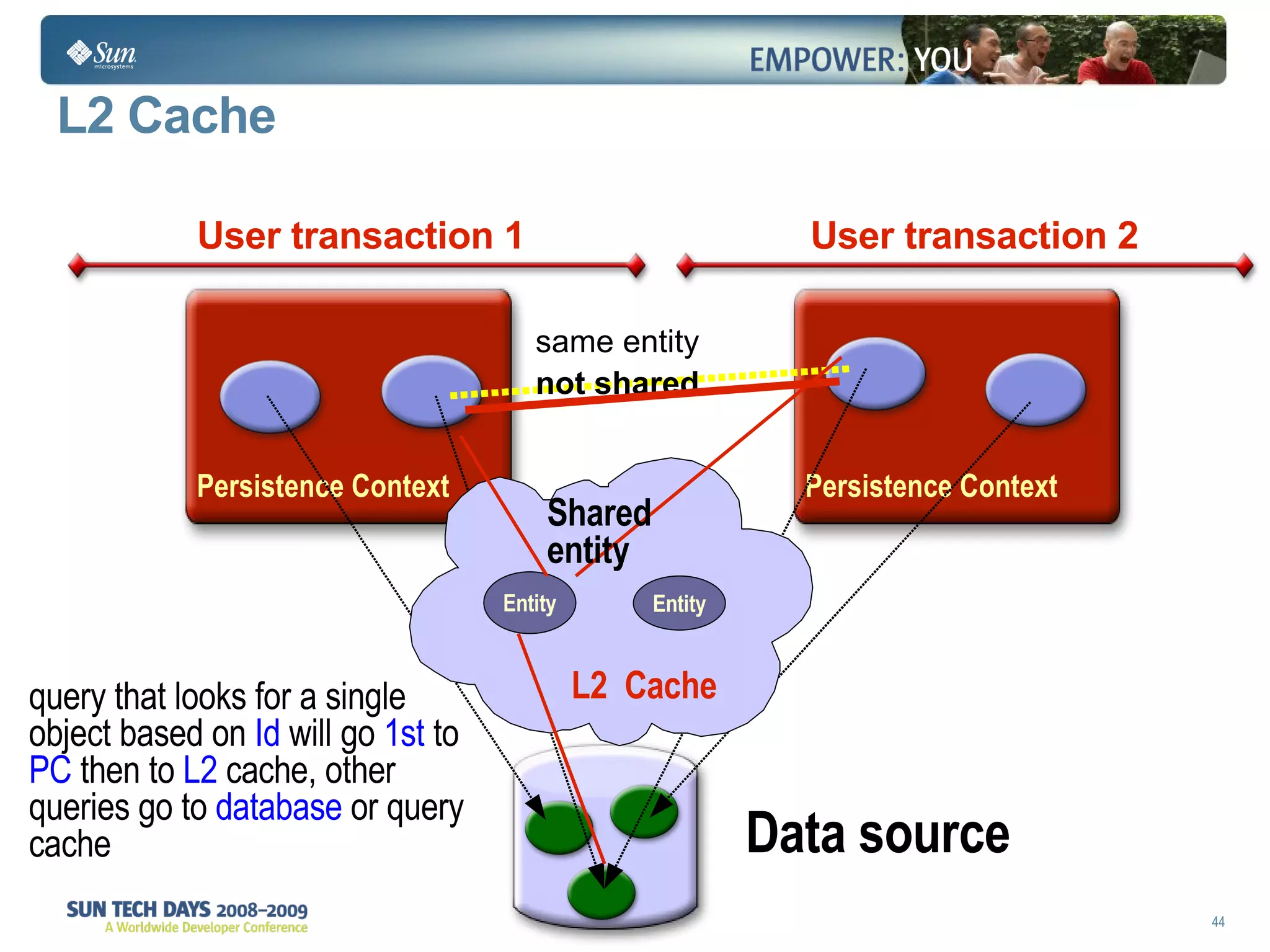
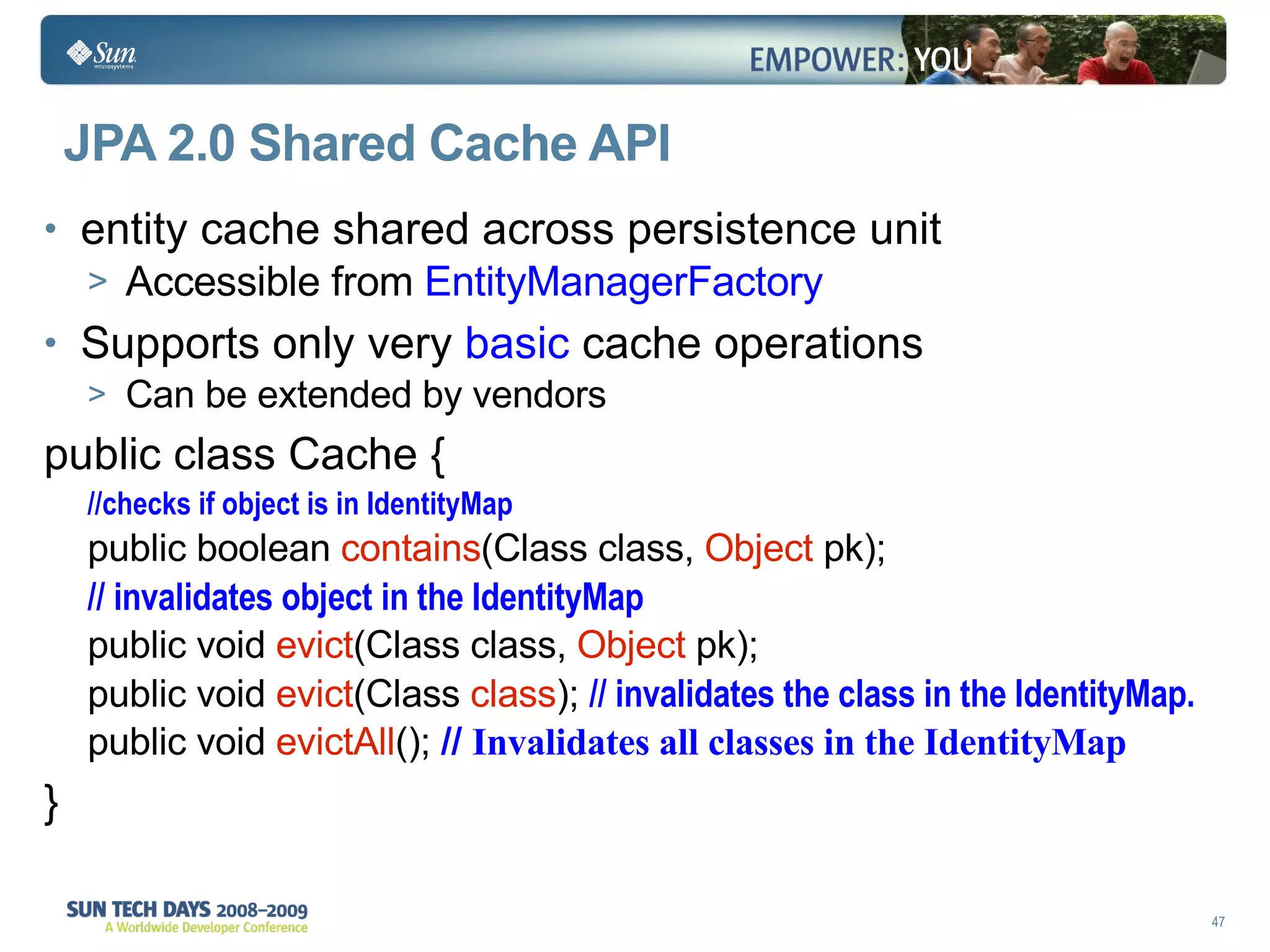
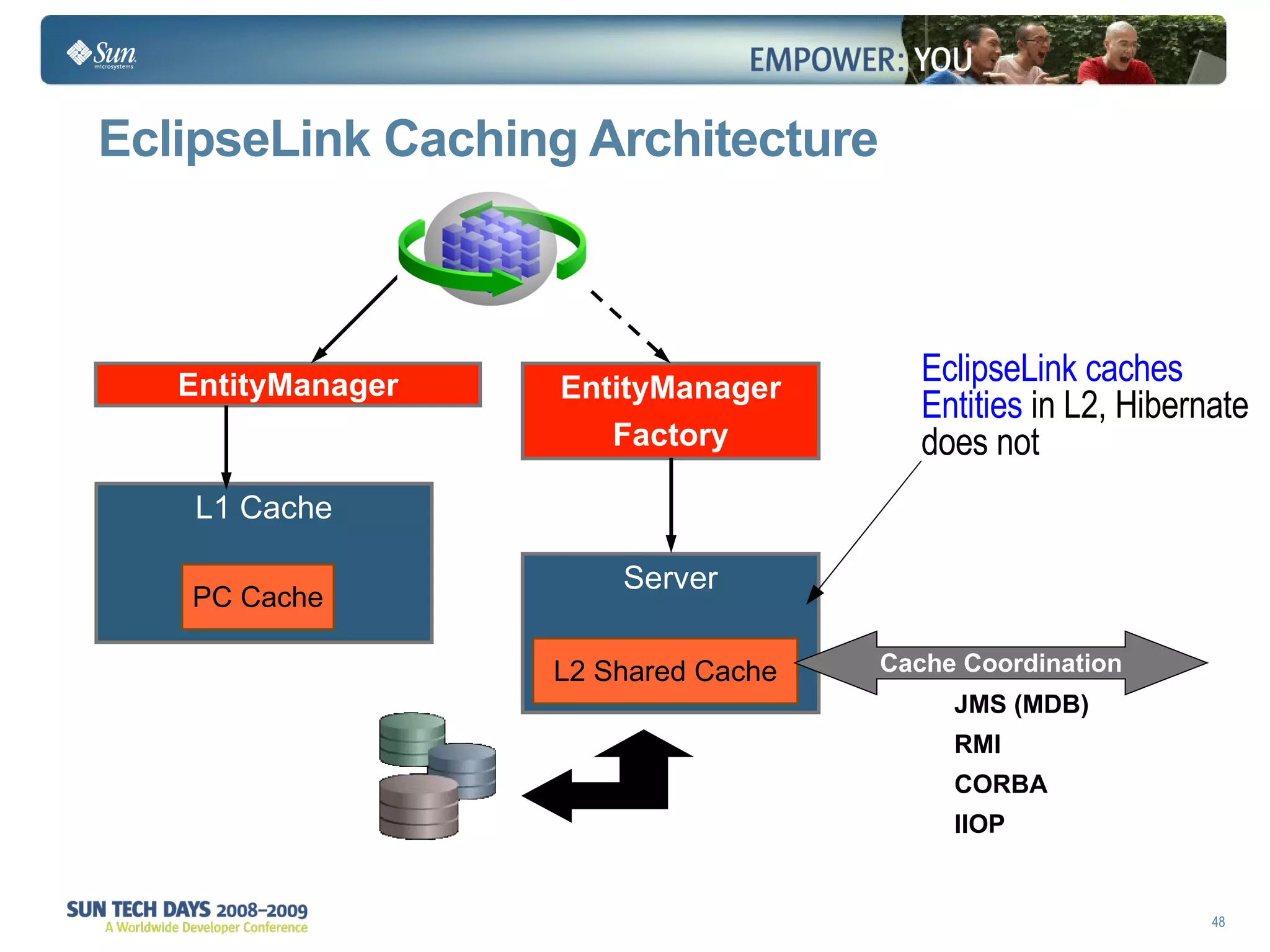
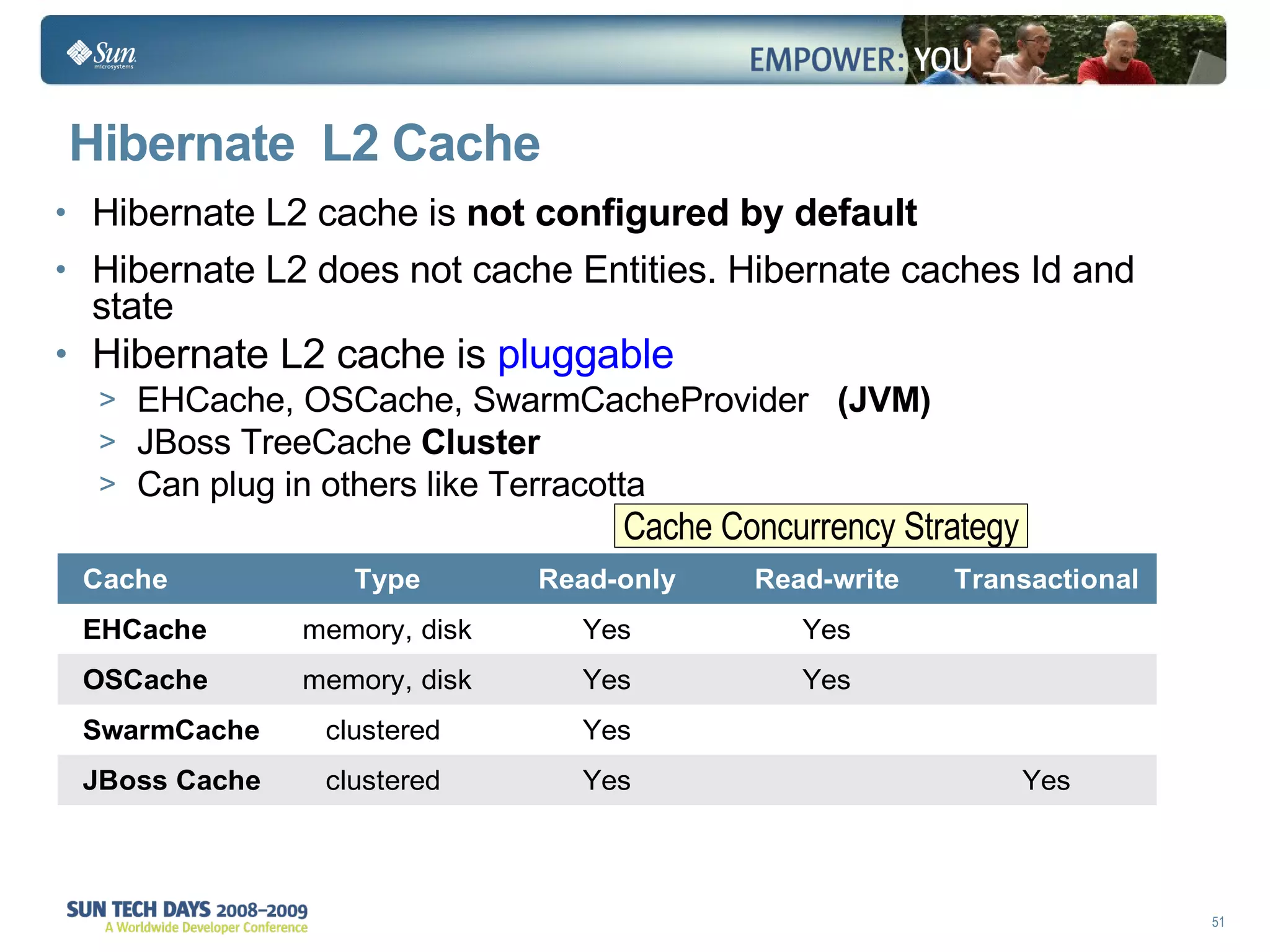
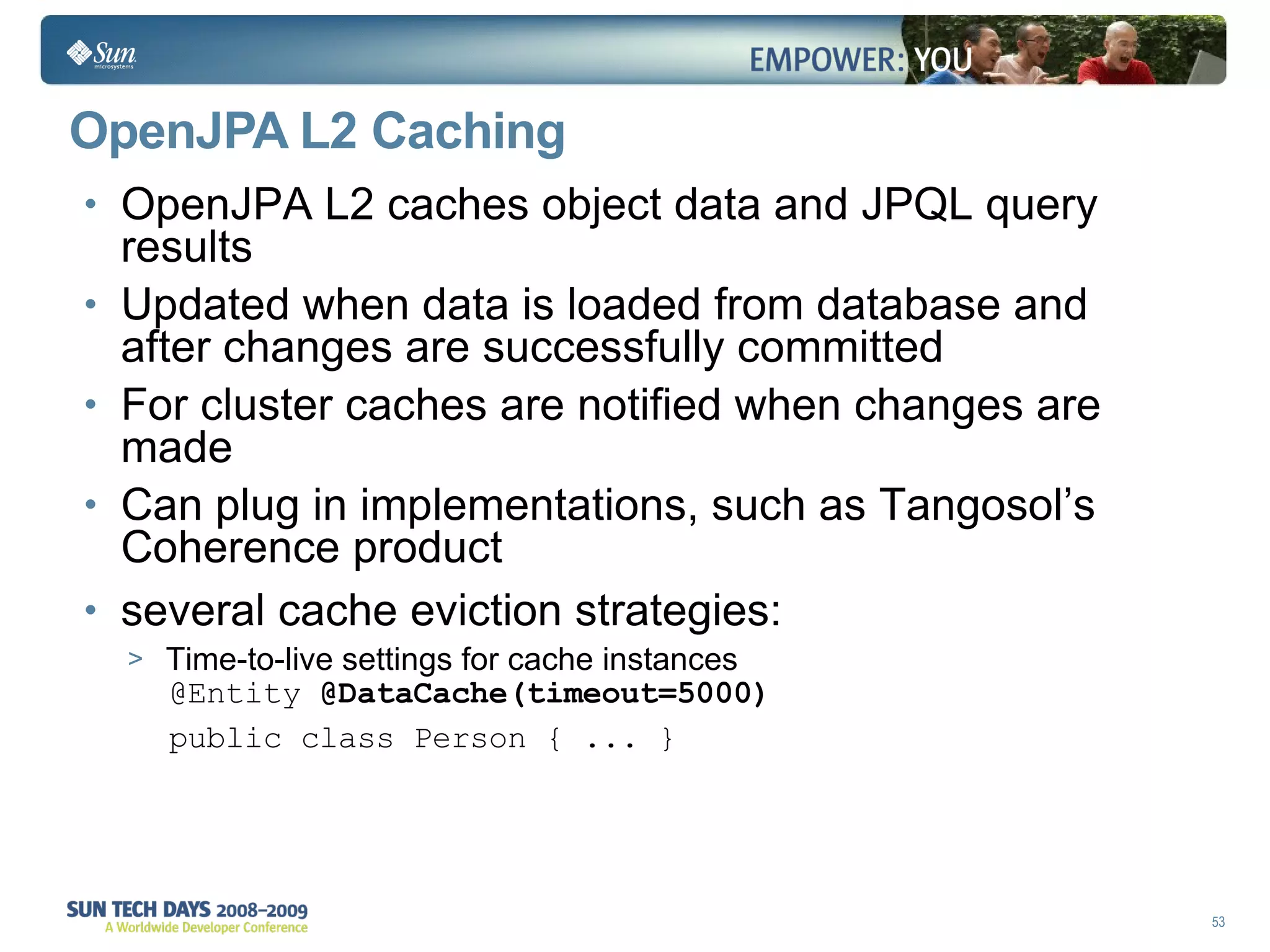
- The second level cache can improve performance by caching entities across contexts.












![Optimistic versus Pessimistic Concurrency Optimistic Concurrency Pros—No database locks held Cons—Requires a version attribute in schema user or app must refresh and retry failed updates Suitable when application has few parallel updates Pessimistic Concurrency Lock the row when data is read in database locks the row upon a select (SELECT . . . FOR UPDATE [NOWAIT]) Pros—Simpler application code Cons—Database locks limits concurrent access to the data = scalability May cause deadlocks Not in JPA 1.0 (vendor specific), supported in JPA 2.0 Suitable when application has many parallel updates](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/td09jpabestpractices2-124040706964-phpapp02/75/JPA-Best-Practices-32-2048.jpg)