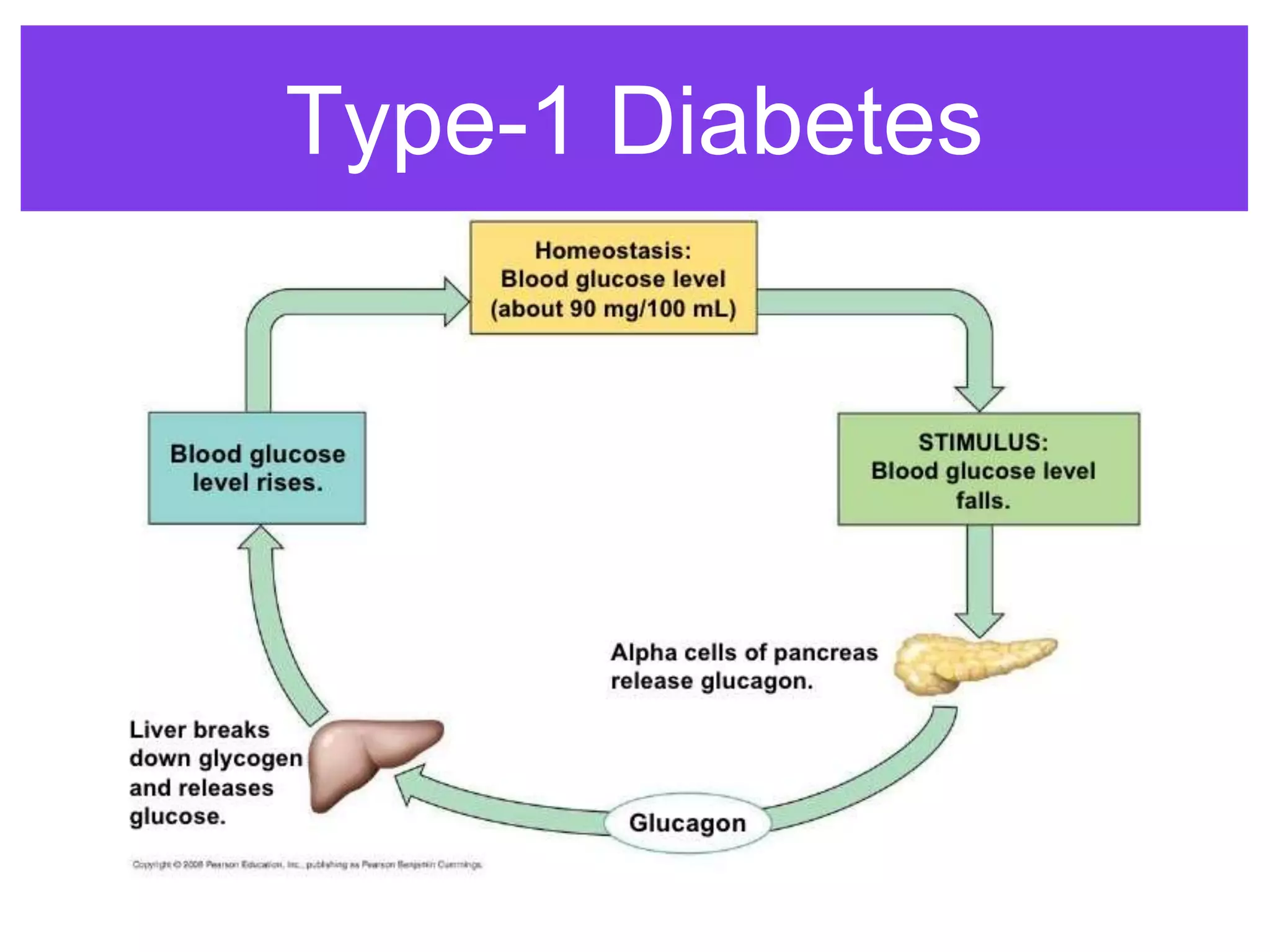
The document discusses the endocrine system and various endocrine diseases. It defines endocrinology as the study of endocrine glands and hormones, and endocrinologists as physicians who diagnose and treat diseases related to these glands. Some common endocrine diseases mentioned include type 1 diabetes, hyperthyroidism, hypothyroidism, low testosterone, growth hormone deficiency, Hashimoto's thyroiditis, and Addison's disease. The document then provides more details on type 1 diabetes, describing its symptoms, the involved glands and hormones of the pancreas and how insulin and glucagon regulate blood glucose, and treatment options of insulin replacement therapy.