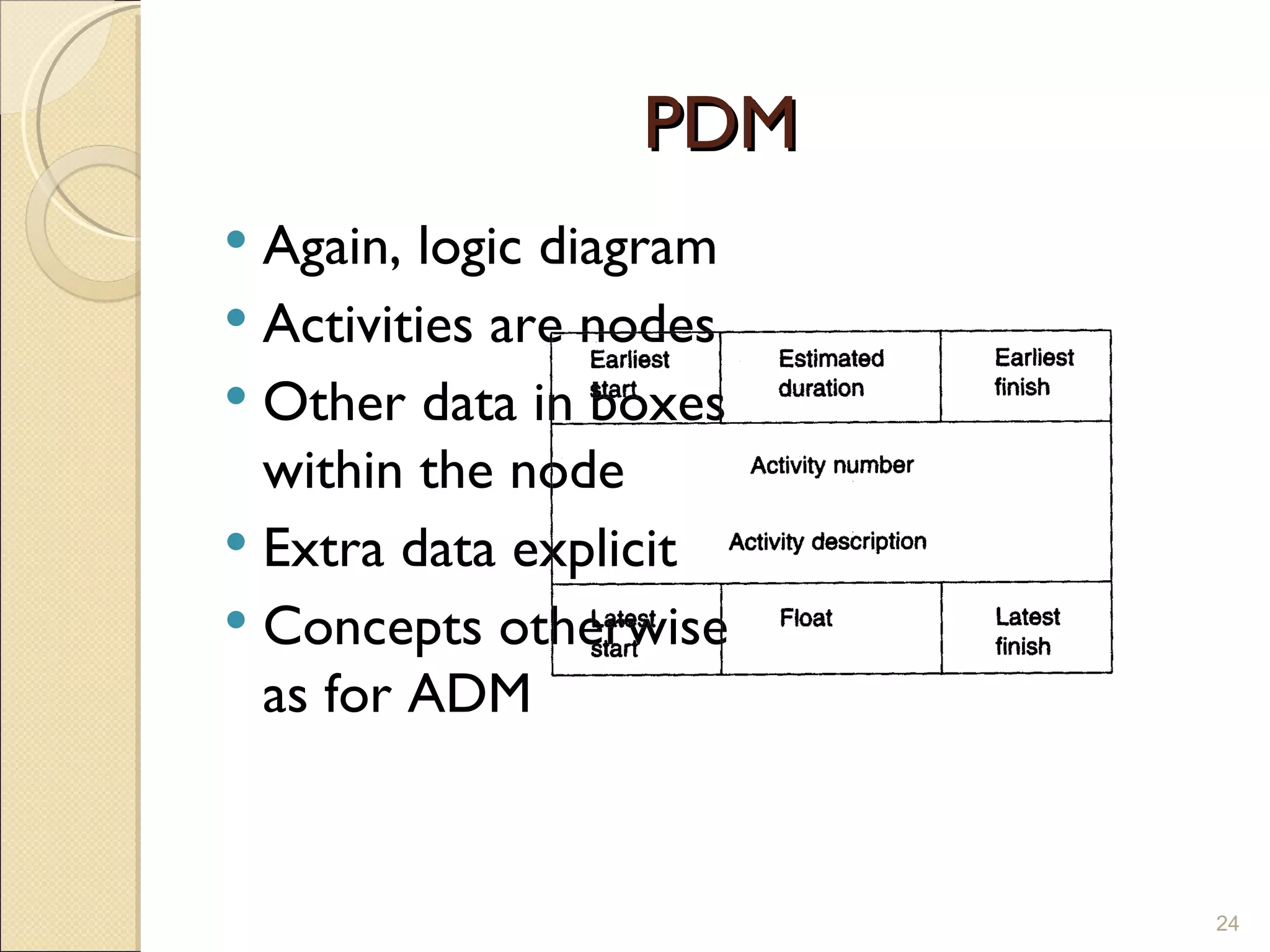
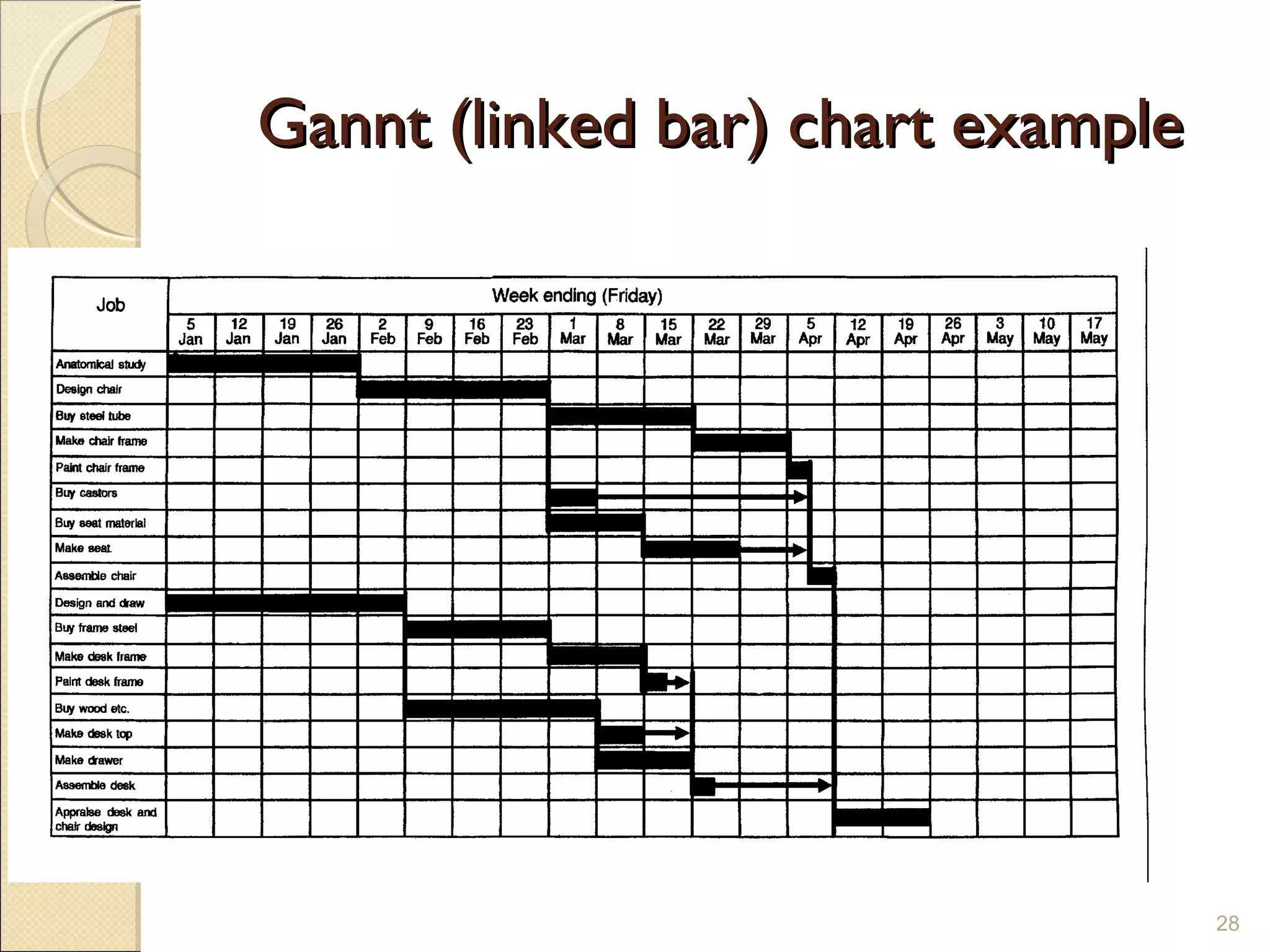
The document discusses project management tools and methodology. It covers what project management is, the types of projects, and key aspects of project management including planning, analysis tools like network analysis, scheduling, monitoring, managing costs and quality. It emphasizes the importance of clear objectives, realistic planning and schedules, and honesty in monitoring and reporting progress.