Carbohydrate metabolism
- 1. CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM Wilhelmina Annie Mensah Dept. Of Med. Bchem. UGMS , Ghana
- 2. Key words • Dextrins - mixture of short, branched and unbranched oligosaccharides • Fascilitated diffusion • ATP • NAD
- 3. Lecture Content 1. Digestion 1.1. Absorption 1.2.1 Glucose transporters 1.2.Disorders of carbohydrate digestion 2. Glycolysis Energy investment stage Energy generation stage Key notes of various steps Fate of pyruvate Regenration of NAD+ lactic acidosis Regulation of glycolysis Inhibition 3. Conversion of pyruvate to acetyl co A
- 4. Digestion is a process by which large complex organic molecules of food are disintegrated into small absorbable forms Enzymes break the α (1-4)glycosidic bonds in polysaccharides Humans lack the enzymes that break β (1-4 ) and α (1-6) glycosidic bonds present in cellulose and branched amylopectin and glycogen . 1.1. Digestion
- 5. Products or substrate Substrates or product Substrates Enzyme Enzyme products Enzyme 2- Duodenum 1- Mouth 3- Ileum 1.1.Digestion
- 6. 1.2.1. Glucose Transporters (carriers) : responsible for the absorption of most of the products of digestion A. Na+ -independent facilitated diffusion transport system Down a concentration gradient ( No energy required) Family of 14 glucose transporters (GLUT -1 to GLUT 14 ) Characteristics 1. Tissue specificity, examples – GLUT -1 –- Erythrocytes and blood-brain barrier – GLUT – 2 –liver, kidney and B-cells of pancreas – GLUT -3 ---Neurons – GLUT- 4 -- Adipose tissues 1.2. Absorption
- 7. 1.2.1. Glucose transporters A. Na+ -independent facilitated diffusion transport system Characteristics 2. Specialized function isoforms –GLUT -1 , GLUT -3, GLUT- 4 are involved uptake of glucose from blood –GLUT – 2 --- transport glucose into or out of cells –GLUT – 5 – uptake of fructose in small intestines and testes 1.2.Carbohydarate Absorption
- 8. 1.2.1. Glucose transporters B. Sodium –monosaccharide co-transport system Against a concentration gradient (Requires energy) Sodium dependent glucose transporter (SGLT) The glucose or galactose is coupled to the conc gradient of Na+ and transported into the cell at the same time. Location Occurs in epithelial of intestines, renal tubules and chorioid plexus. 1.2.Carbohydarate Absorption
- 9. 1.2.1. Transporters Glu and Gal–SGLT -1 Fructose –GLUT-5 Into circulation - GLUT - 2 1.2.Carbohydarate Absorption
- 10. 1. Lactose Intolerance – Genetic deficiency of lactase activity causes non- utilization of lactose – Lactose accumulates in the large intestines and draws water by osmosis causing – Symptoms like • Osmotic diarrhoea • Bacteria fermentation producing CO2 and H2 which gives abdominal cramps and flatulence – Treatment : Withdrawal or reduce milk consumption 1.3. Disorders of carbohydrate digestion
- 11. 2. Congenital Sucrase-Isomaltase deficiency – Genetic deficiency of of surcrase and isomaltase activity causes non- utilization of lactose 3. Disacchariduria – It is due to deficiency of disaccharidases – It is characterized by excretion of large amounts of disaccharide in urine. 1.3. Disorders of carbohydrate digestion
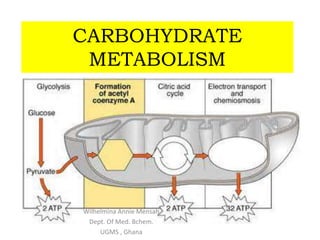
- 12. 2. Glycolysis( Embden-Meyerhof pathway)
- 13. 2. Glycolysis( Embden-Meyerhof pathway) Site - cytoplasm of the cell Source of glucose: from the digestion of dietary carbohydrates enter liver Purpose : converts glucose to 2 pyruvate molecules Produces ATP in tissues that lack mitochondria Two stages (10 steps) – Energy ( 2ATP) investment phase – Energy generation phase (4ATP, 2NADH+) Conditions Aerobic : Pyruvate – CO2 Anaerobic(fermentation) : pyruvate – lactate
- 14. 2.1. Glycolysis( Embden-Meyerhof pathway) 1. Energy ( 2ATP) investment phase 1 2 3 4 5
- 15. 2.2. Glycolysis( Embden-Meyerhof pathway) – 2. Energy generation phase (4ATP, 2NADH) 5 6 7 10 9 8
- 17. Key Notes Step 1 Can also be catalysed by liver glucokinase under conditions of high glucose conc such as after a high meal Phosphorylation of glucose is important to prevent glucose from being transported out of the cell Step 3 Rate limiting and Commited step of glycolysis PFK is a important regulatory enzyme PFK is regulated by high ATP and F6P 2.3 Glycolysis( Embden-Meyerhof pathway)
- 18. Key Notes Step 6 Phosphorylation of G3P is by inorganic phosphate (Pi ) not ATP Step 7 and 10 sbstrate level phosphorylation : enzyme transfer a high energy Phosphate from a substrate to ADP to form ATP 2.3. Glycolysis( Embden-Meyerhof pathway)
- 19. Glycolysis energetics – Net ATP Produced • Net reaction for glycolysis 1 NADH = 3 ATPS 2NADH = 6 ATPS + 2 ATP Total number of ATPs = 8 2.4. Glycolysis( Embden-Meyerhof pathway)
- 20. 2.5. Glycolysis( Embden-Meyerhof pathway) 5 Fates of Pyruvate Lactate Acetyle- CoA Ethanol Oxaloacetate Alanine
- 21. Regeneration of NAD+ Essential because accumulation of NADH can stop glycolysis Ways of regeneration Aerobic conditions - Electron transport system Anaerobic conditions: formation of alcohol Anaerobic conditions - Formation of lactate under regenerates NAD+ 2.6. Glycolysis( Embden-Meyerhof pathway)
- 22. LACTIC ACIDOSIS : Accumulation of lactic acid in the muscles Causes: Lack of O2 in the tissues • Vigorous exercise • Collapsed circulation • Myocardial infarction • Uncontrolled hemorrage • Shock Causing Aenarobic glycolysis; Pyruvate to Lactate to regenerate NAD+ 1.4. Glycolysis( Embden-Meyerhof pathway)
- 23. Glycolysis in Cancerous cells High rate of glycolysis than other cells Experience hypoxia (limited oxygen supply), initial lack an extensive capillary network to supply the tumor with oxygen. Depend on anaerobic glycolysis for much of their ATP production until capillaries are formed Convert glucose to pyruvate and then to lactate as they recycle NADH 1.4. Glycolysis( Embden-Meyerhof pathway)
- 24. 1.4. Glycolysis( Embden-Meyerhof pathway) Regulation of glycolysis Allosteric regulation Up regulation F16B on pyruvate kinase AMP on PFK1 F26B on PFK1 Down regulation G6P on hexokinase Citrate on PFK1 ATP on PFK1
- 25. 1.4. Glycolysis( Embden-Meyerhof pathway) Regulation of glycolysis Hormonal control • Insulin increases rate of glycolysis by increasing concentration of glucokinase, phosphofructokinase-1 pyruvate kinase
- 26. 1.4. Glycolysis( Embden-Meyerhof pathway) Inhibitors of Glycolysis 1.Glyceraldehyde -3-phosphate dehydrogenase inhibitors (step 2) They combine with-SH of active site and makes enzyme inactive Iodoacetate, arsenate heavy metals like Hg2+, Ag+. 2.Enolase ( step 9): inibited by fluoride.
- 27. Quick reminder 1. Digestion 1.1. Absorption 1.2.1 Glucose transporters 1.2.Disorders of carbohydrate digestion 2. Glycolysis Energy investment stage Energy generation stage Key notes of various steps Fate of pyruvate Regenration of NAD+ lactic acidosis Regulation of glycolysis Inhibition 3. Conversion of pyruvate to acetyl co A
- 28. 2.Glycolysis( Embden-Meyerhof pathway- Quick Reminder)
- 29. Quick Reminder
- 30. 3. Conversion of pyruvate to acetyl Co A Players – Coenzyme A – NAD+ – TPP – Lipoamide/lipoate – FAD – Pyrvate dehydrogenase
- 31. 3. Conversion of pyruvate to acetyl Co A Site : Mitochondria Matrix Energetics : 2 NADH = 6 ATP
- 32. 3. Conversion of pyruvate to acetyl Co A Regulation
- 33. Role of B Enzymes 3. Conversion of pyruvate to acetyl Co A
- 34. 4 . Citric Acid Cycle (TCA or Kreb Cycle)
- 35. Site : Mitochondrial matrix Purpose – Conversion of 2 acetyl-CoA to CO22 – Generates reducing equivalents (NADH, FADH2) and GTP to be oxidized in the respiratory chain to generate ATP Stages : 8 steps 4. Citric Acid Cycle (TCA or Kreb Cycle)
- 36. Regulation 4. Citric Acid Cycle (TCA or Kreb Cycle) citrate Acetyl Co A Citrate synthase ATP Isocitrate Isocitrate dehydrogenase ATP, NADH ADP Succinyl CO A α- ketoglutarate α- ketoglutarate dehydrogenase ATP, NADH
- 37. 4. Citric Acid Cycle (TCA or Kreb Cycle) Energetics : 2 Acetyl CoA from 2 Pyruvate 1 NADH =3 ATP 1FADH= 2 ATP 1 GTP = 1 ATP × 2 = 24
- 38. ATP generation during oxidation of Glucose • However, the amount depends on shuttle used for the transfer of reducing equivalents from cytosol to mitochondria. 4. Energetics
- 40. Quick Reminder
- 42. Glycogen structure it makes up 6% of the body weight Made of α D- glucose molecules Straight chains made of α (1-4) glycosidic bonds Branches made of α (1-6) glycosidic bonds
- 43. 5.Glycogenolysis and Glycogenesis Glycogenesis: is the synthesis of glycogen from glucose due to sufficient ATP produced Glycogenolysis : the breakdown of glycogen to produce glucose (ATP) in a state of fasting or glucose depletion
- 44. 5.Glycogenesis Glycogenesis: is the synthesis of glycogen from glucose due to sufficient ATP produced Site : Liver and skeletal muscles Purpose : to serve as a ready source of glucose for glycolysis because Fat can not be oxidized under anaerobic condition. Acetyl-CoA of fat oxidation can not be converted to glucose. Skeletal muscle is unable to mobilize fat rapidly.
- 45. 5.Glycogenesis Hexokinase/glucokinase Glucose Glucose -6-P UTP PPi Phosphogluco mutase Glucose -1-P ATP ADP UDP- Glu- pyrophosphorylase 2Pi UDP-Glucose Glycogen primer Glcn UDP Glycogen synthase Glycogen
- 46. • Glycogenin
- 47. 5.Glycogenolysis Glycogenolysis: is the conversion of glycogen to glucose Site : Liver and skeletal muscles during fast and excercise Purpose : to serve as a ready source of glucose for glycolysis because Fat can not be oxidized under anaerobic condition. Acetyl-CoA of fat oxidation can not be converted to glucose. Skeletal muscle is unable to mobilize fat rapidly.
- 48. Pi 5.Glycogenolysis Phosphorylase Glycogen( Glucose)n Glucose -1-P Phosphogluco mutase Glucose -6-P Glucose 6-phosphatase Glucose Glucose Glycolysis Transferase & Debranching enzyme Pi Muscle Liver, kidney, intestines
- 49. P P P P P P P P phosphorylase Transferase activity of Debranching enzyme -1,6 glucosidase activity of Debranching enzyme
- 50. Glycogen storage diseases Causes : absence of major enzymes in glycogen metabolism Presentation : accumulation of abnormal amount glycogen in the liver or muscles Symptoms Liver enlargement due to increased liver glycogen Exercise intolenrant Liver cirrhosis Hypoglycemia Cardiac and respiratory failure Death
- 51. Disease Enzyme defect Type I (von Gierke’s ) Glucose 6-phosphatase Type II (Pome’s) Lysosomal glucosidase Type III (Cori’s) Debranching enzyme Type IV (Andersen’s) Branching enzyme Type V (McArdle’s) Muscle phosphorylase Type VI (Her’s) Liver phosphorylase Type VII Musle phosphofructokinase Type VIII Liver phosphofructokinase Glycogen storage diseases
- 52. 5.Control of Glycogen Metabolism
- 53. Guconeogenesis • The synthesis of glucose from non-carbohydrate sources in the liver and kidney • Begins in the mitochondria and ends in the cytosol • Notable precursors are Pyruvate Glycerol Lactate Amino acids
- 54. Pathway Gluconeogenesis - glycolysis going backwards - 3 places differ- control points in glycolysis - 4 new enzymes (eukaryotes) - importance of near equilibrium reactions - ATP energy, NADH reducing equivalents consumed #3 #10 #1 **Gluconeogenesis Net Reaction:** 2 Pyruvate + 4 ATP + 2 GTP + 2 NADH + 2 H+ + 6 H2O Glucose + 4 ADP + 2 GDP+ 2 NAD+ + 6 Pi Glycolysis Net Reaction: Glucose + 2 ADP + 2 NAD+ + 2 Pi 2 Pyruvate + 2 ATP + 2 NADH + 2 H+ + 2 H2O
- 55. Gluconeogenesis 6 ATP needed total 4 needed to overcome barrier of production of 2 mol of PEP
- 56. Gluconeogenesis: The Irreversible Steps Pyruvate PEP; reversing the pyruvate kinase step of glycolysis. 4 subunits Biotin Allosteric + acetyl CoA Transcriptional regulation + glucagon (fasting) - Insulin (fed state) Indicates CAC Backed-up No allosteric reg Hormonal induction
- 57. Gluconeogenesis No ATP needed since Fru-1,6-bisP not high energy intermediate
- 58. Fru-1,6-biP Fru-6-P; reversing the PFK-1 step of glycolysis. Large – DG and irreversible Allosteric modulation - AMP - 2,6-Fru bisP (opposing effect in glycolysis)
- 61. • Cori cycle: Synthesis from lactate Guconeogenesis
