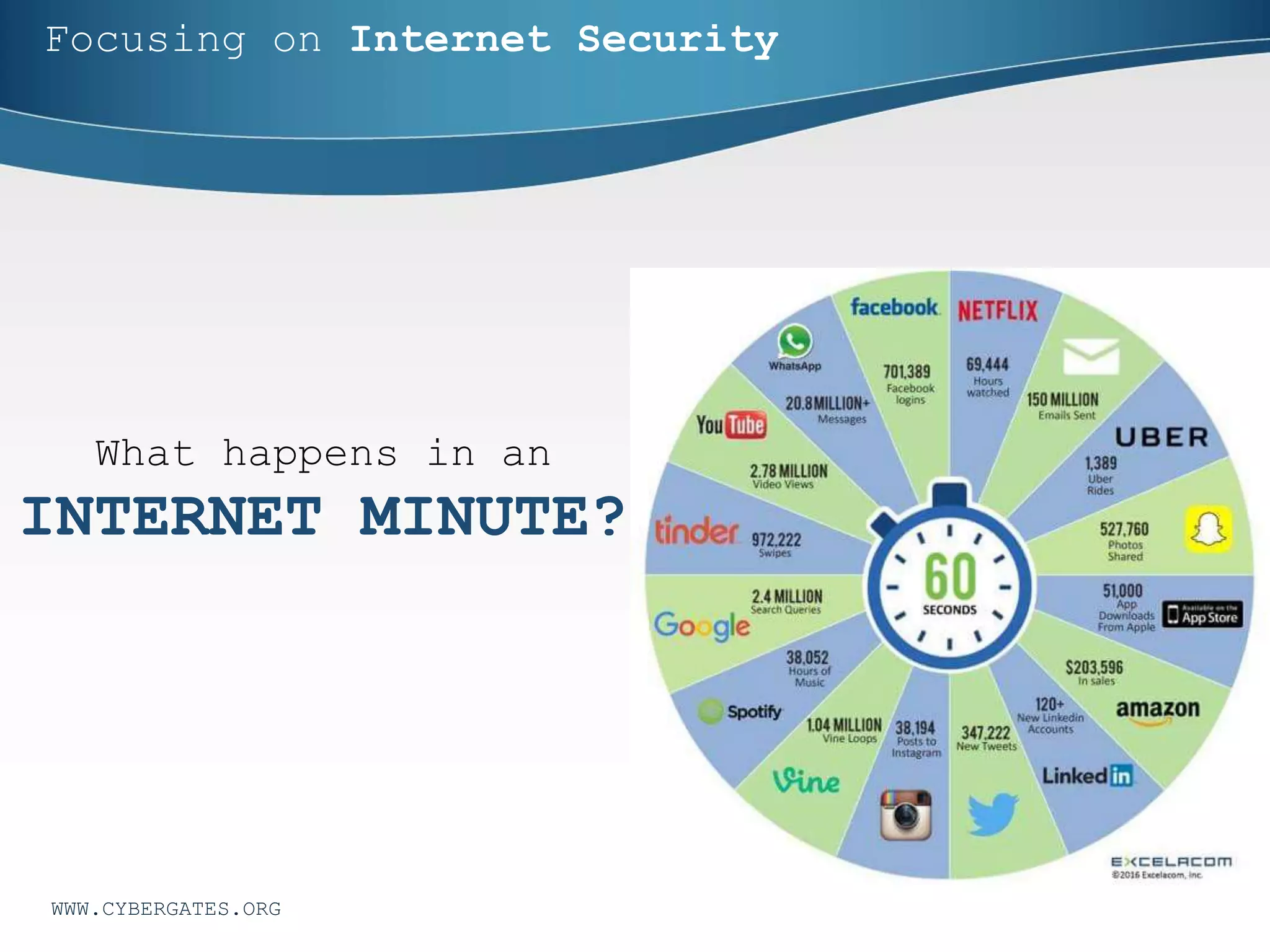
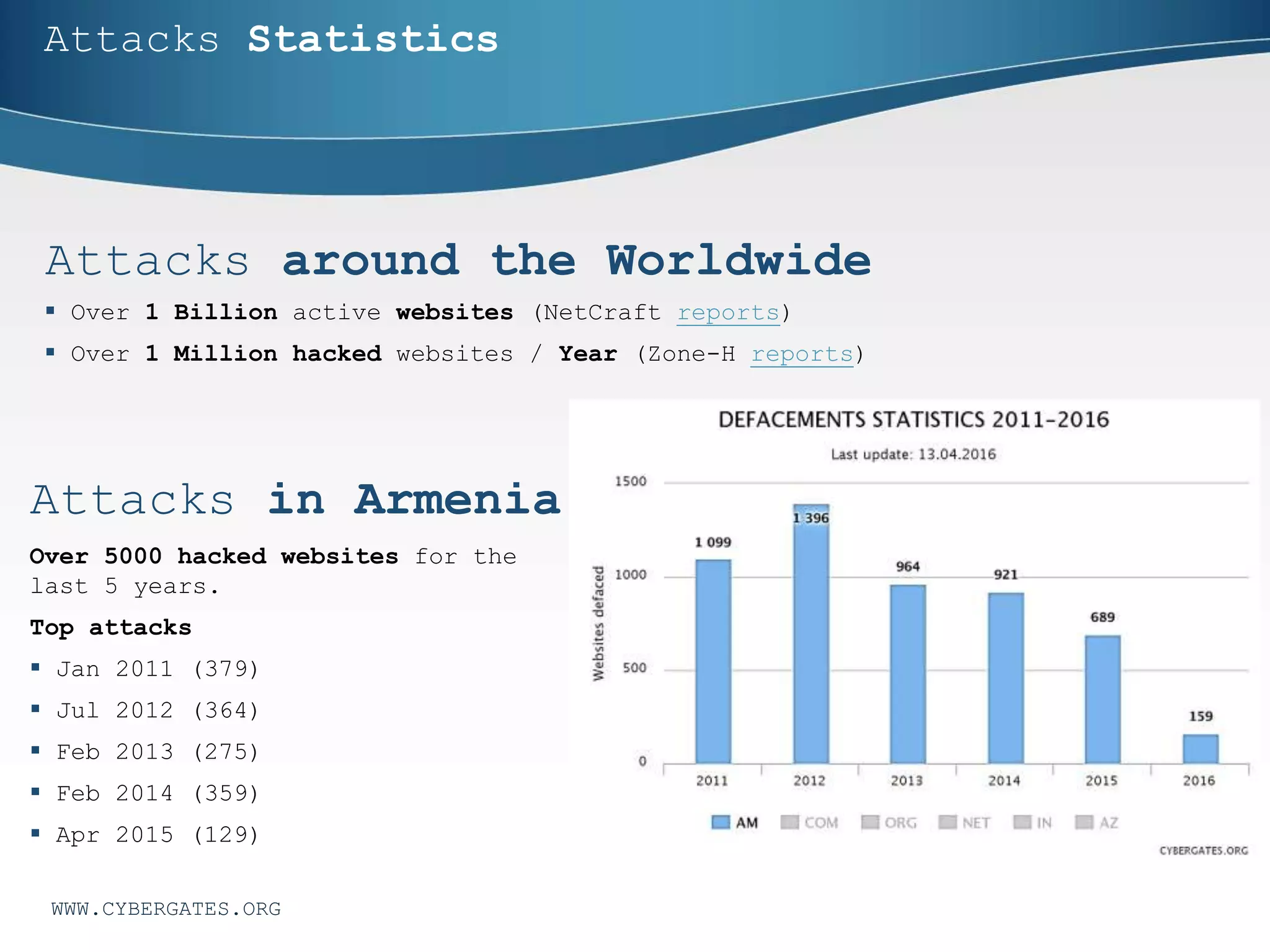
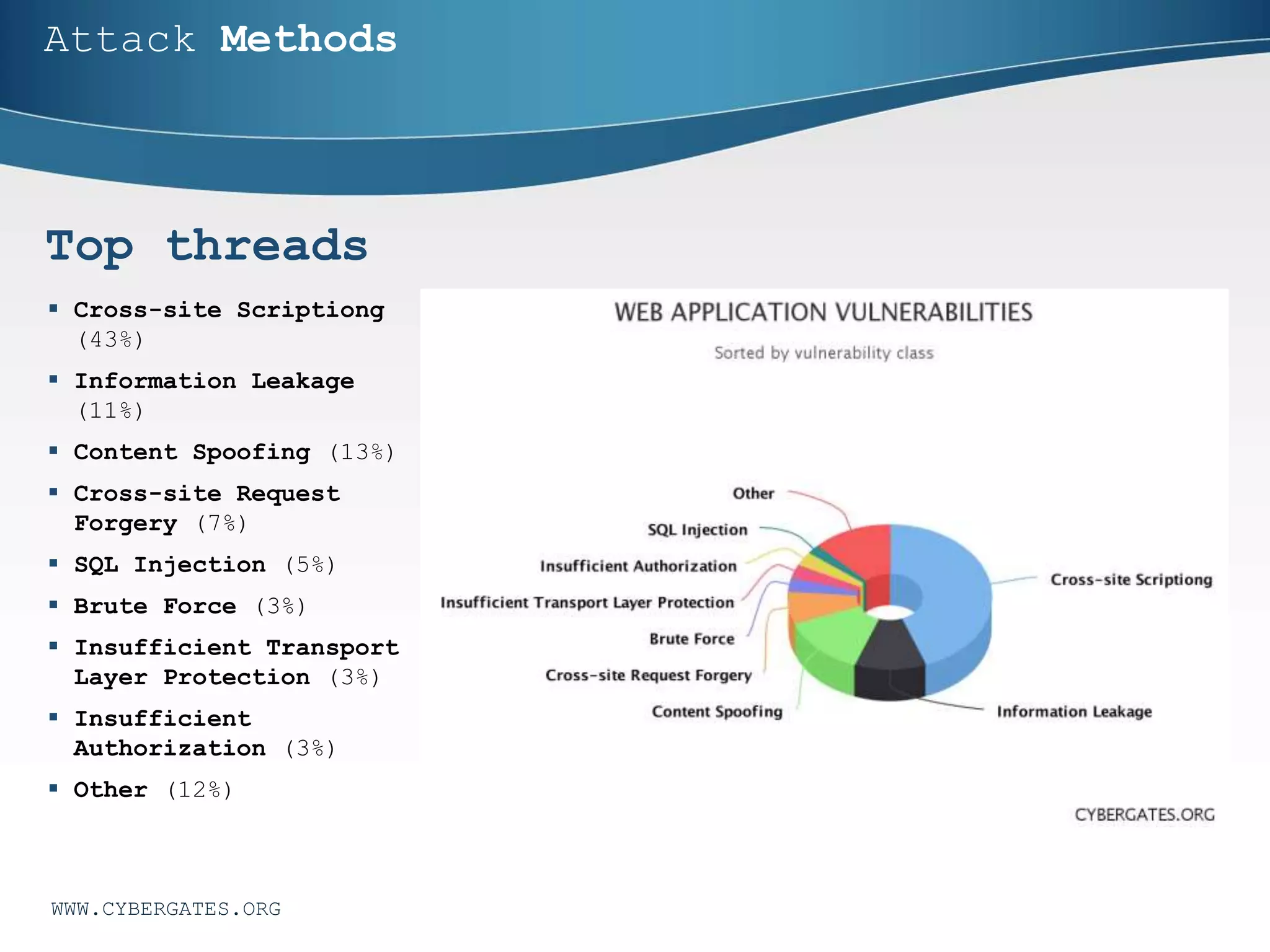
This document discusses cybersecurity challenges and provides an overview of key concepts. It covers the CIA security model of confidentiality, integrity and availability. It also discusses identification, authentication and authorization. Additional sections outline cybersecurity elements like people, processes, technology and policies. Cybersecurity statistics on data breaches and spending are presented. Common security threats like SQL injection, password attacks, phishing and ransomware are analyzed. Approaches for both reacting to and avoiding security problems are proposed. The document promotes the services of Cyber Gates for cyber defense.