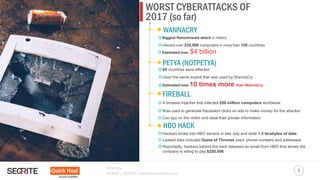
The document discusses significant trends and predictions in cybersecurity for 2017, focusing on ransomware, phishing attacks, and new types of malware. It highlights that ransomware is increasingly targeting backup data and employing tactics such as countdown timers to pressure victims, while phishing attacks have surged, particularly those aimed at social media and SaaS companies. Notably, the document also details major cyberattacks of 2017, including WannaCry and Petya, emphasizing the growing threats faced by users and organizations due to inadequate system updates.