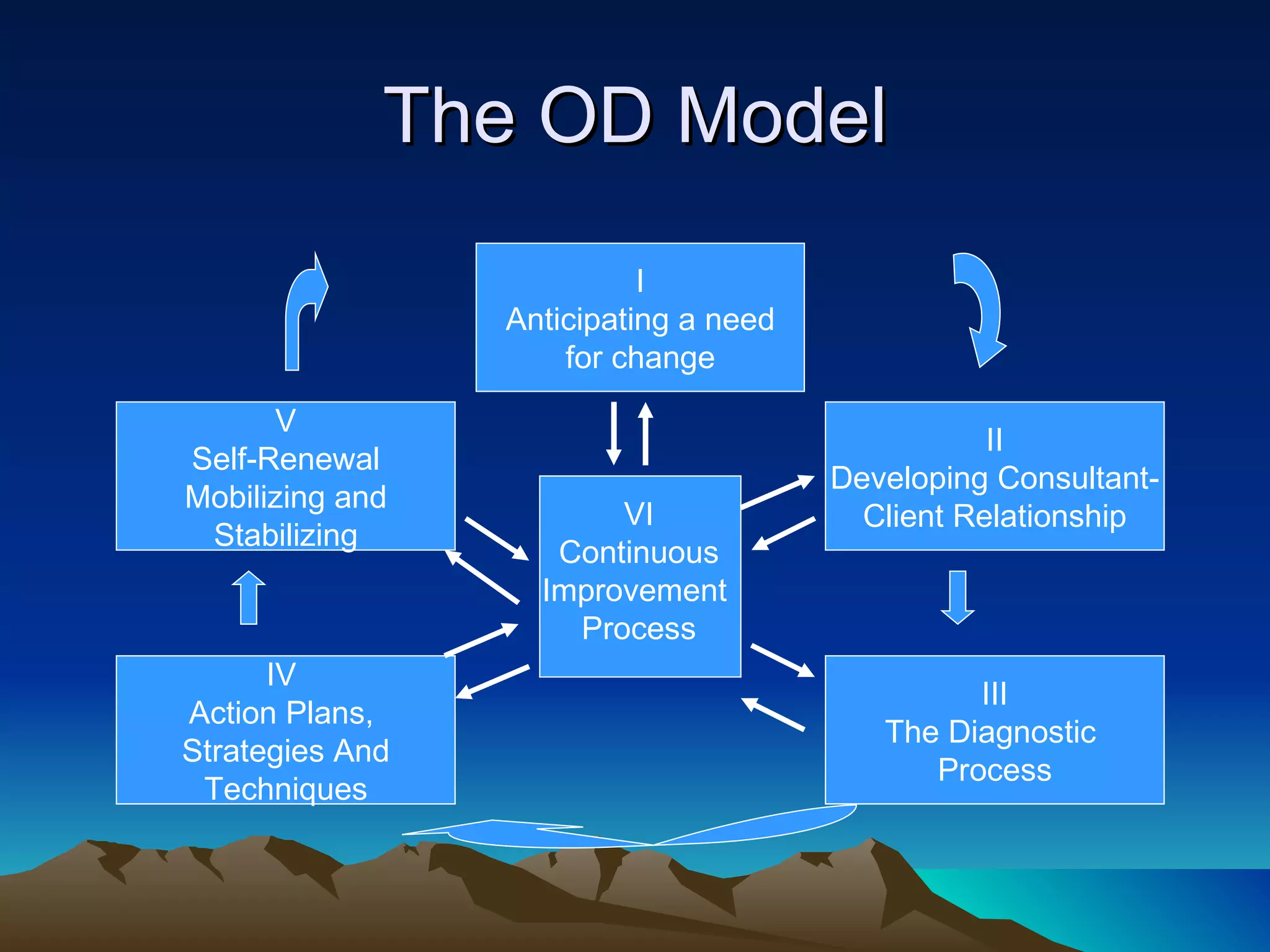
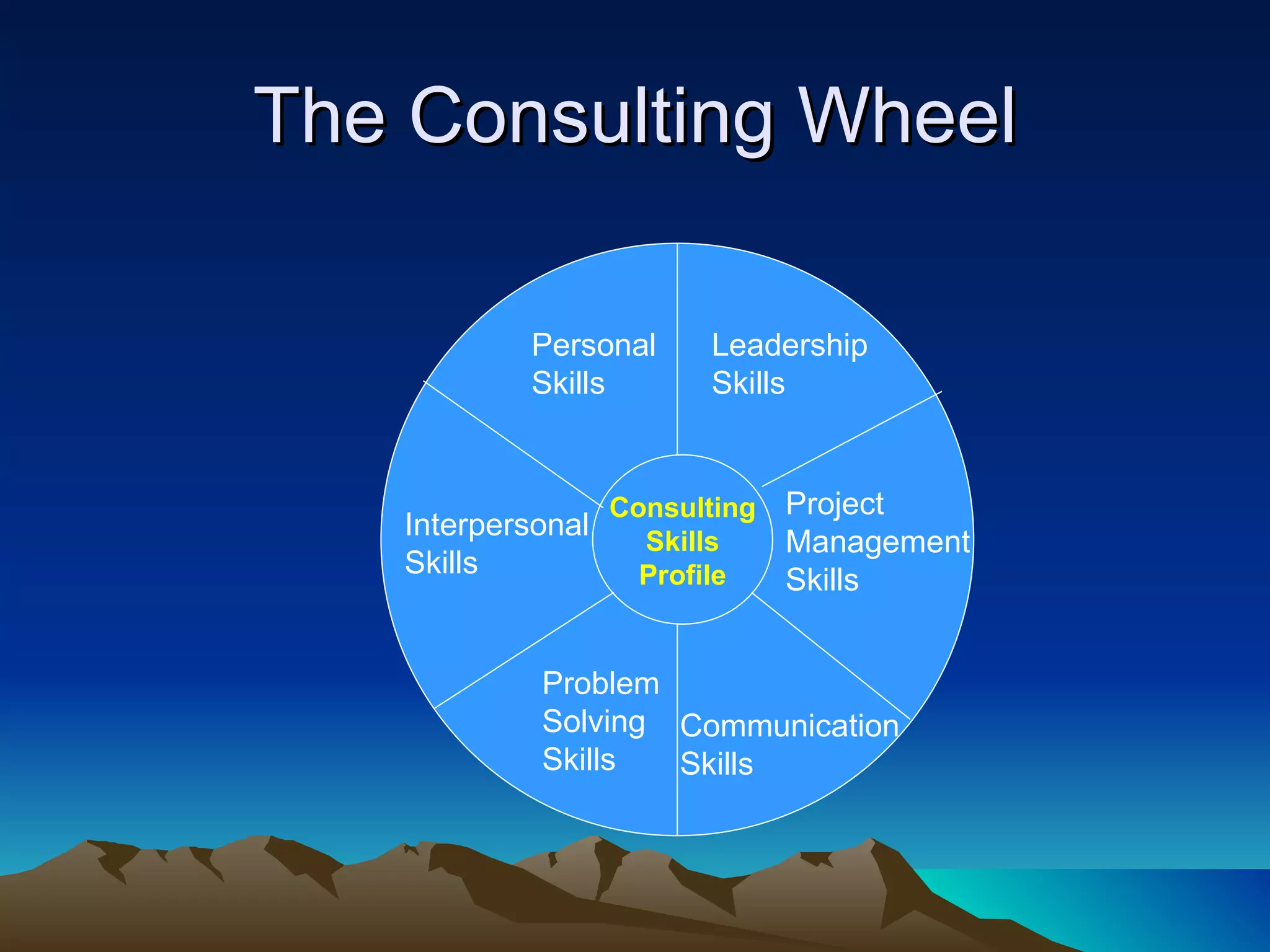
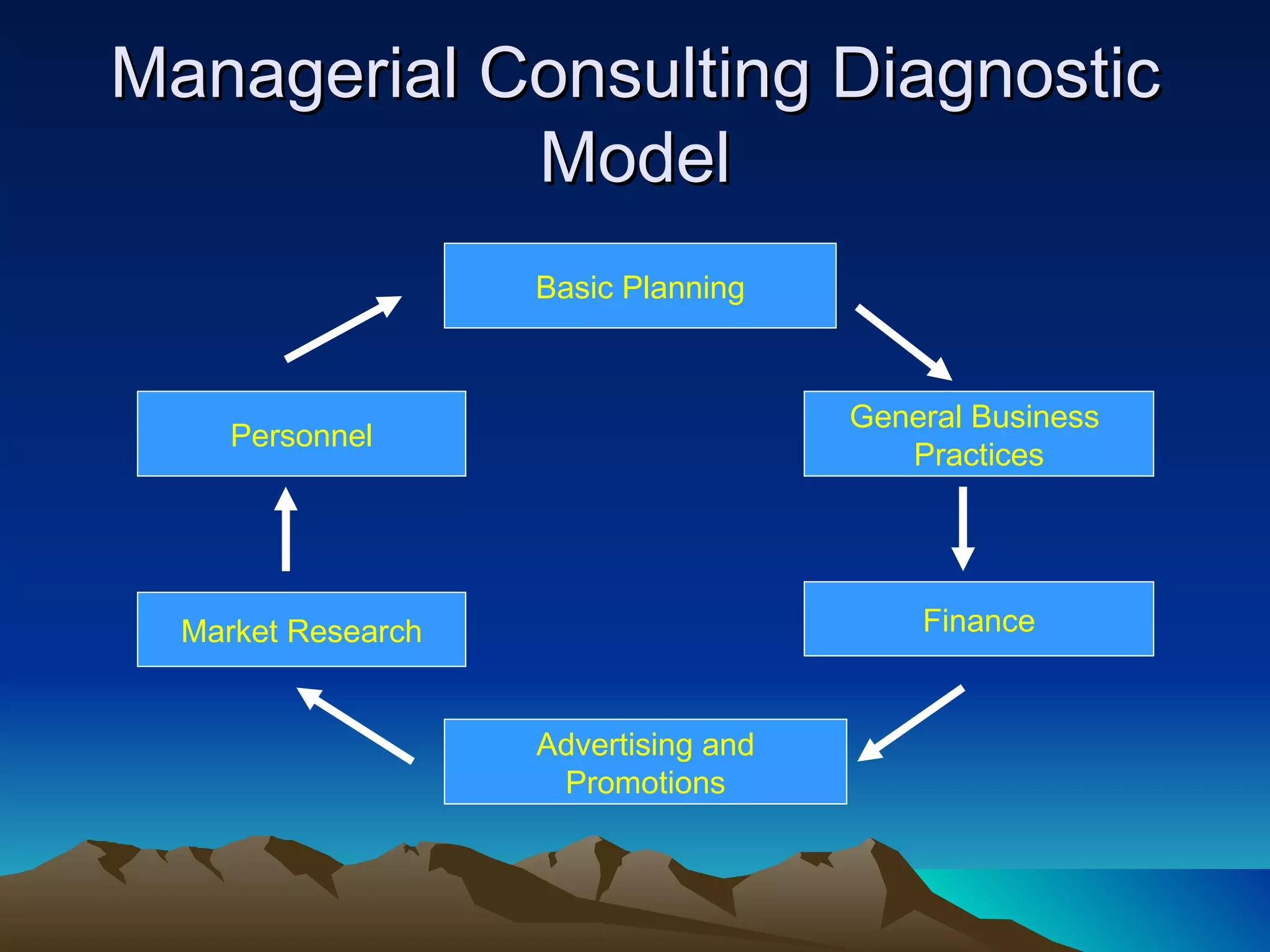
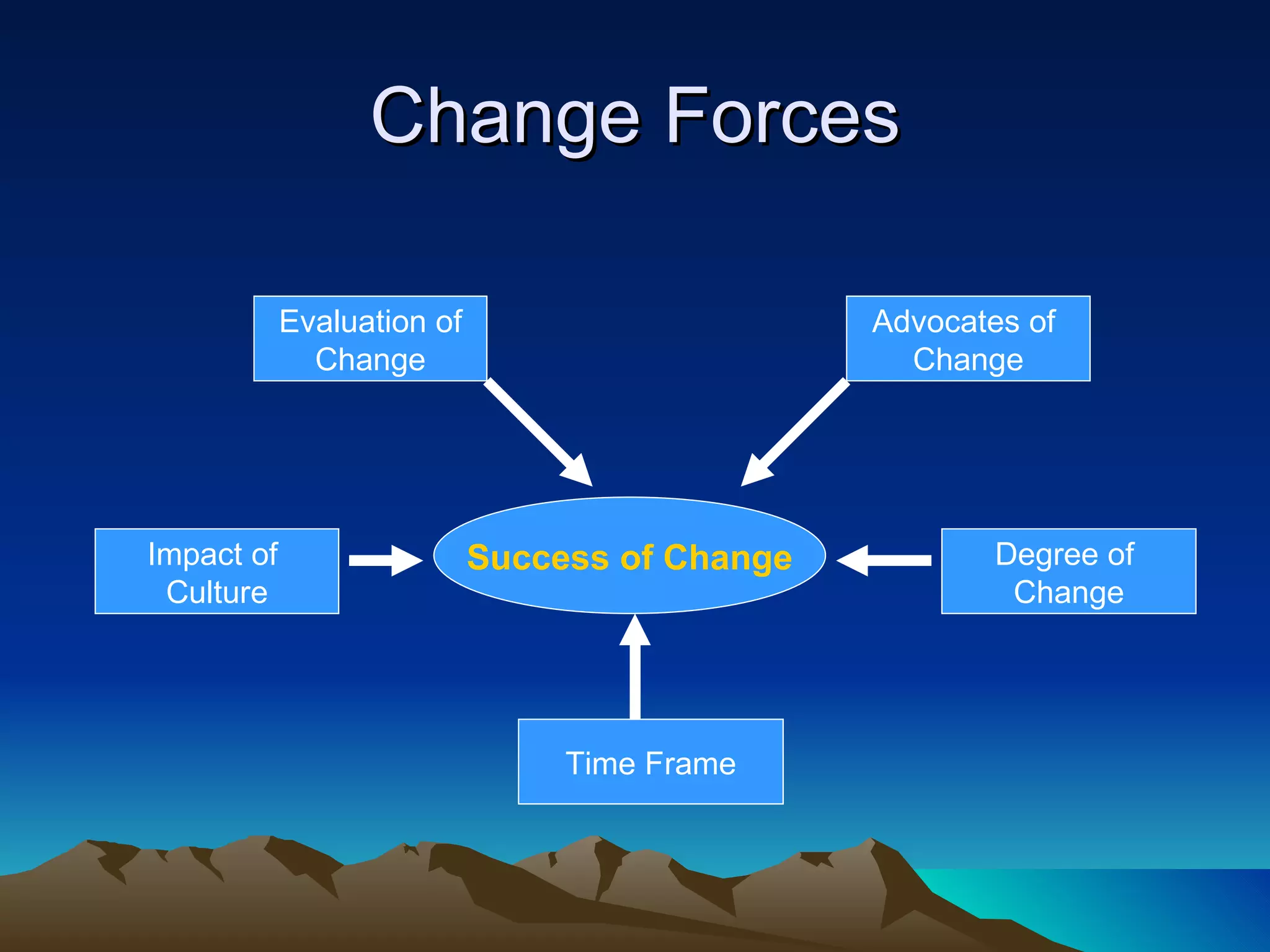
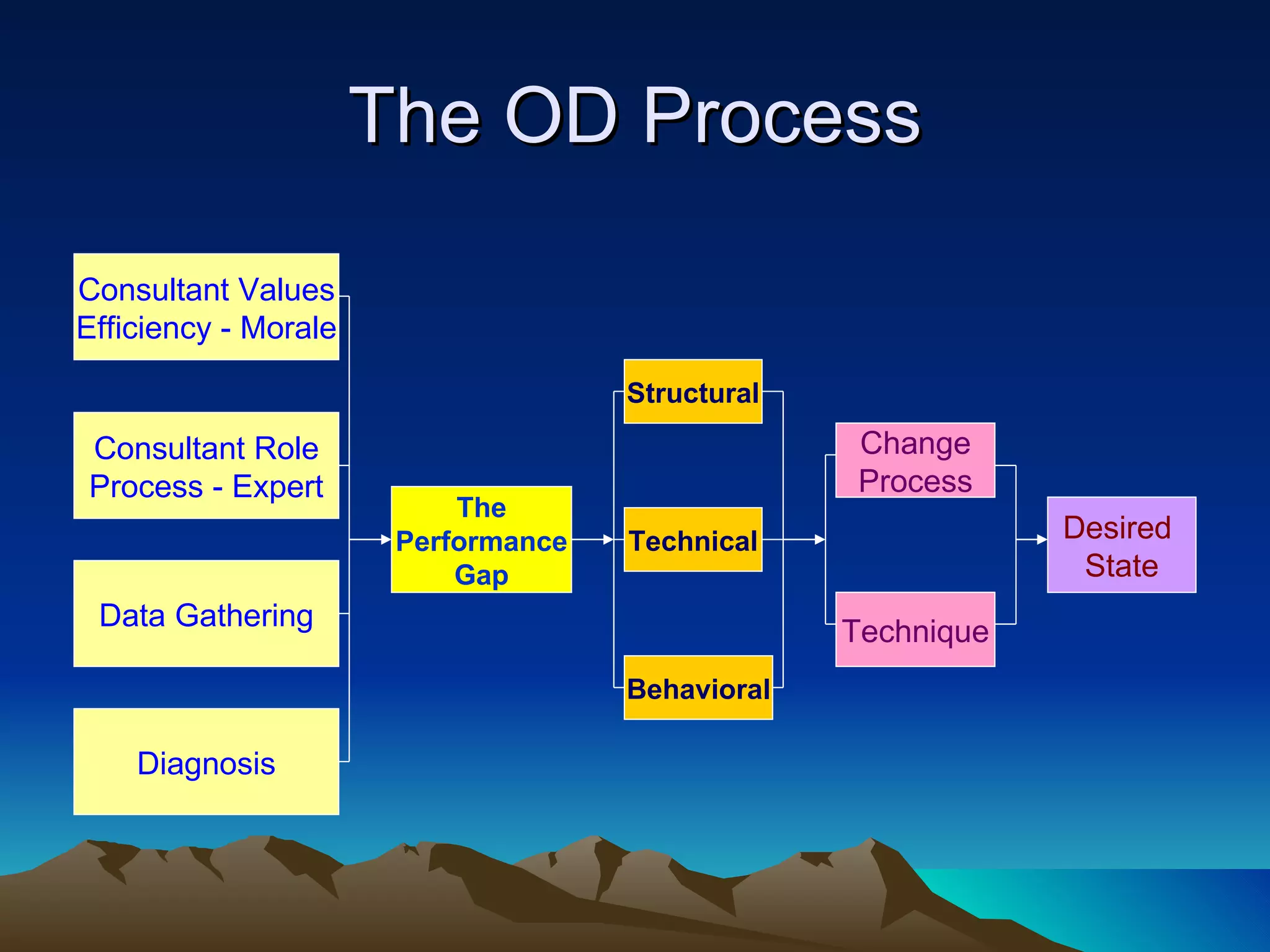
Organizational development (OD) is a planned, systematic process to increase organizational effectiveness. It involves diagnosing the entire organization and implementing changes from the top down. The OD process uses an empowering approach through facilitating vision, learning, and problem solving to collaboratively manage organizational culture. Key themes in OD include meeting employees' social and motivational needs to boost productivity, and rationalizing work processes to optimize output. Common OD interventions include team development, intergroup cooperation, system-wide performance improvements, and strategic transformations.