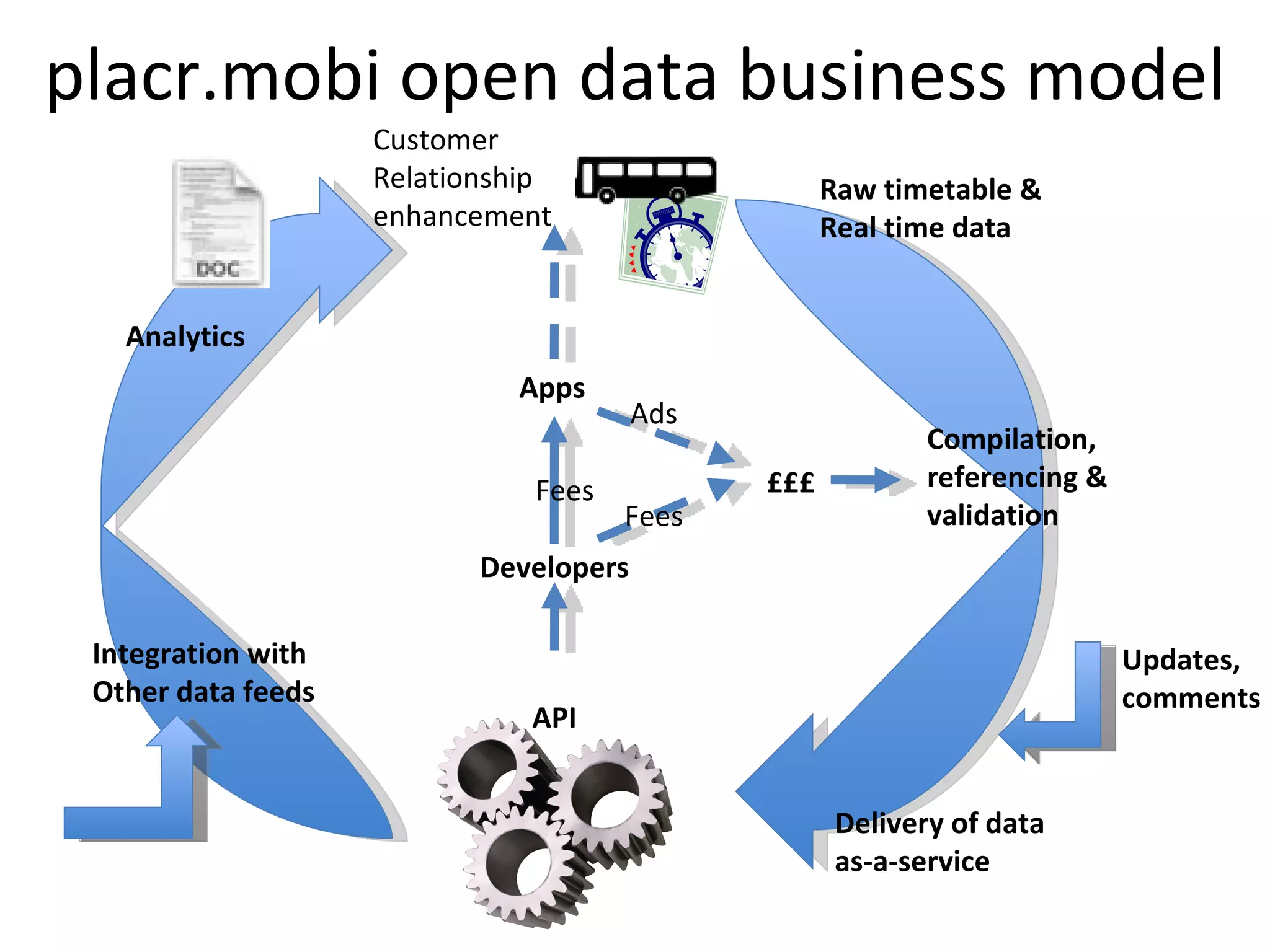
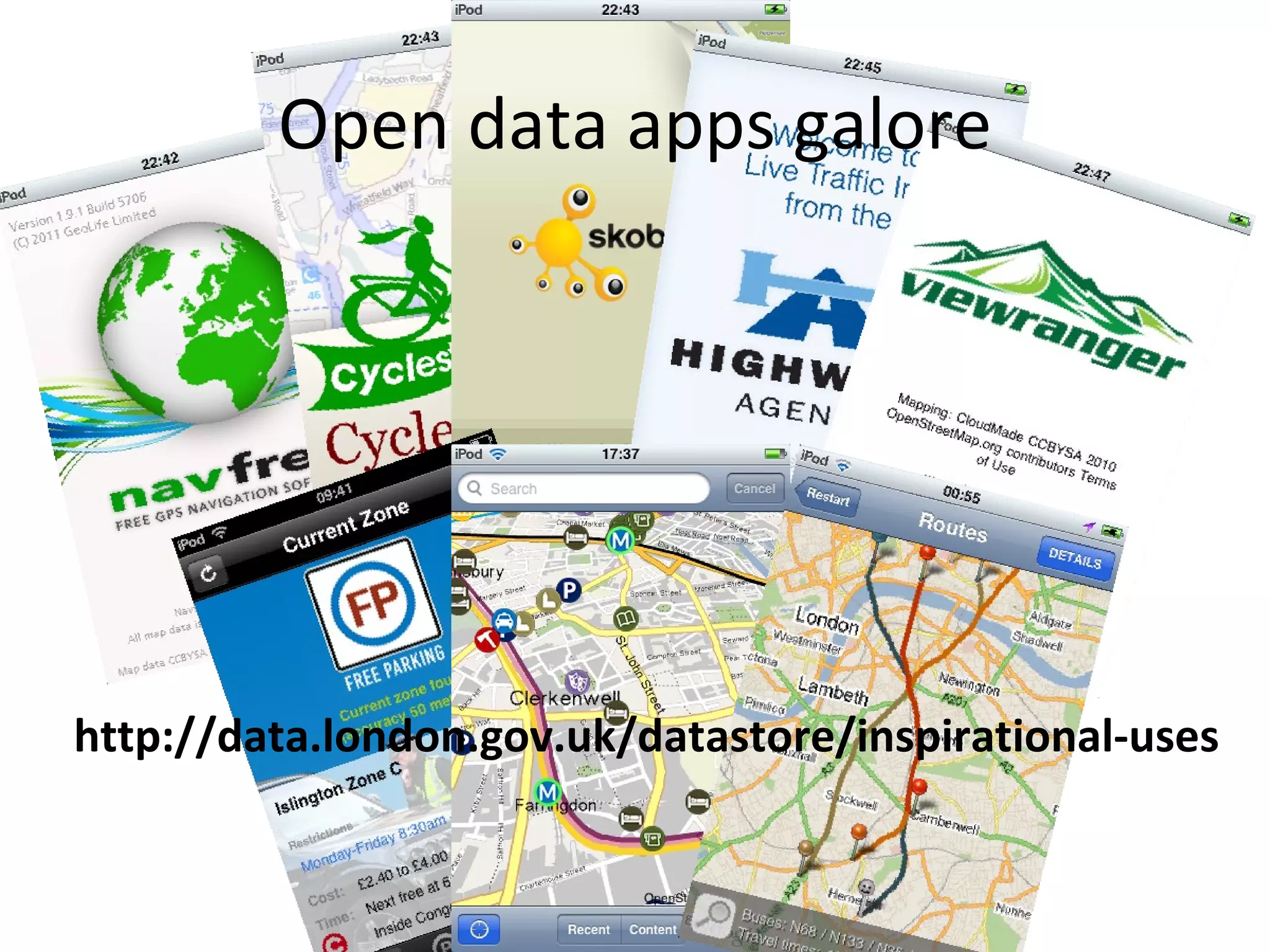
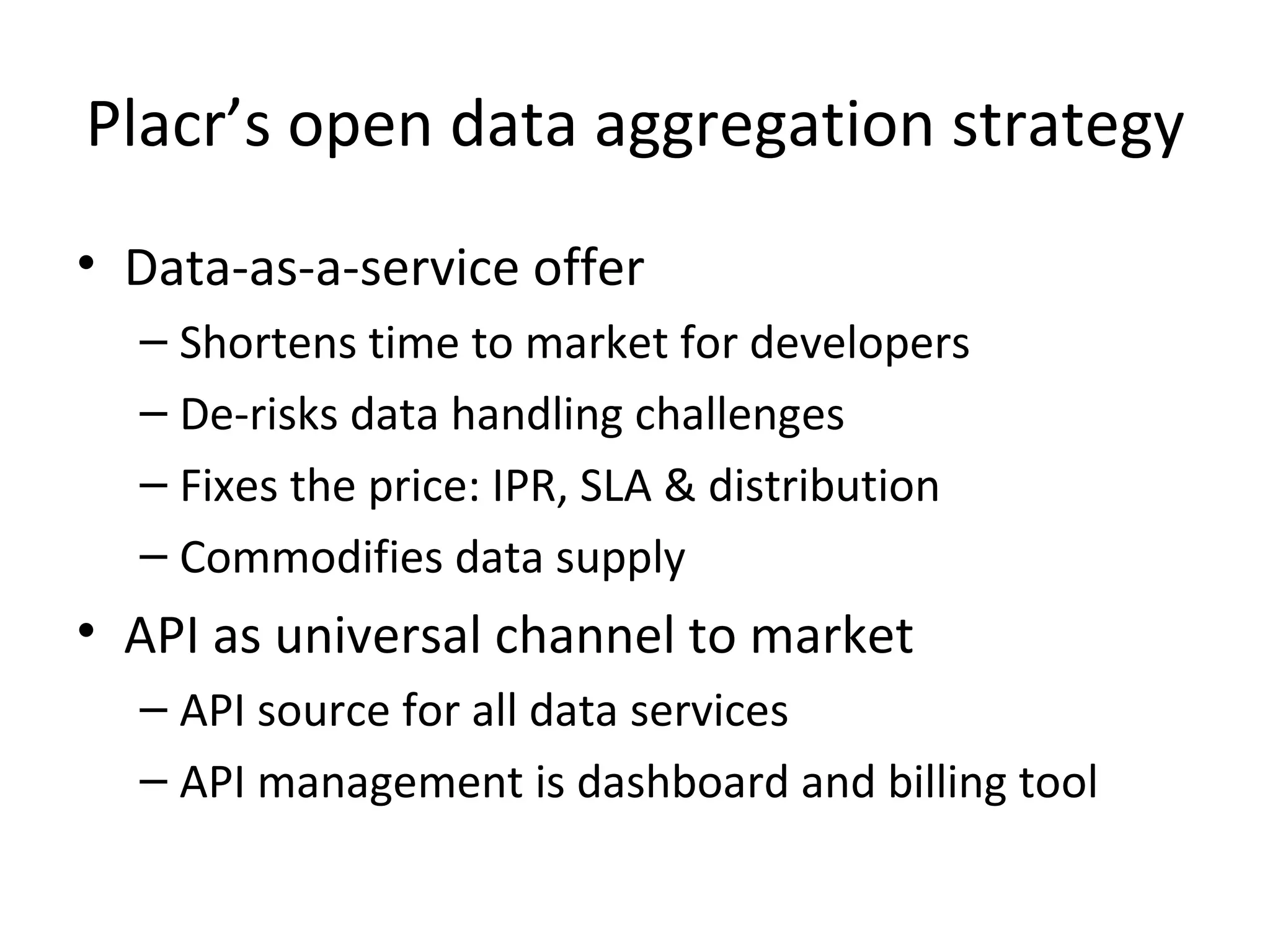
The document discusses business models for open data and strategies for monetization. It outlines some of the economic fundamentals to consider with open data, including differences in licensing terms. It also discusses defining value-add through services like data processing, packaging, and integration. The document provides examples of developing services around open data like APIs, apps, and consulting. It presents Placr's strategy of offering open data as a service to shorten time to market for developers and de-risk challenges of handling data.





![Contact http://www.placr.co.uk/ [email_address] @madprof http://www.slideshare.net/madprof](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/isa-opendata-bizmodels-raper-120228063144-phpapp02/75/Irish-Software-Association-Open-Data-Bisiness-Models-13-2048.jpg)