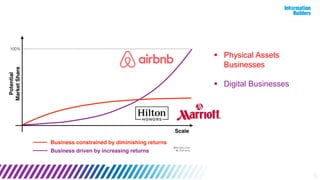
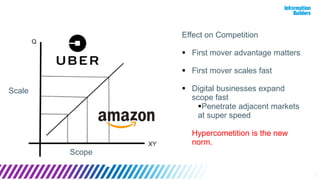
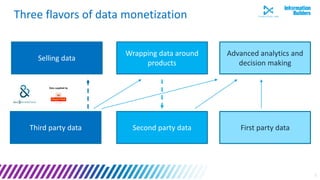
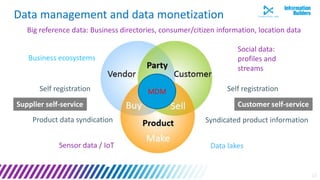
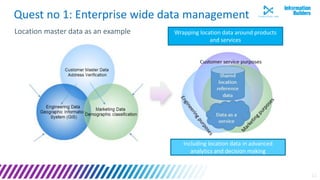
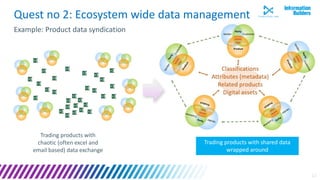
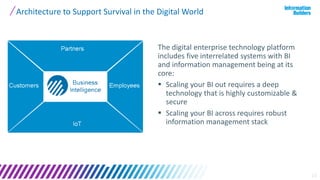
The document discusses a webinar series on data monetization, highlighting historical developments in data collection, management, and technological advancements such as blockchain and IoT. It emphasizes the importance of first mover advantage in digital business, the challenges of self-service BI, and the need for effective data presentation to facilitate decision making. The content outlines various strategies for wrapping data around products and discusses the evolving landscape of data monetization and management.