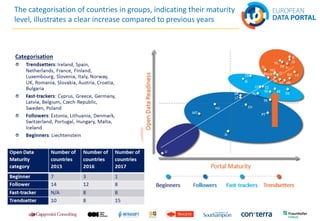
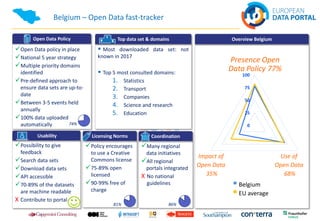
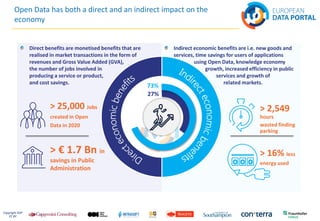
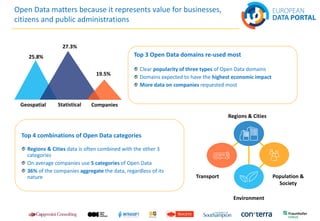
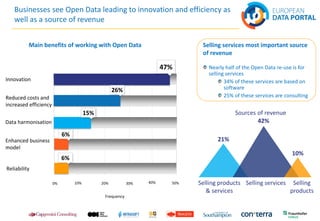
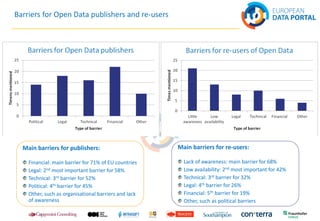
The document discusses best practices in open data across Europe, with a focus on Belgium, outlining the European Data Portal's offerings, including metadata and training for data publishers. It highlights Belgium's progress in open data maturity, the impact of open data on various sectors, and examples of successful implementations in different countries. Furthermore, it addresses barriers faced by publishers and re-users of open data and provides information on recent reports and resources related to open data.