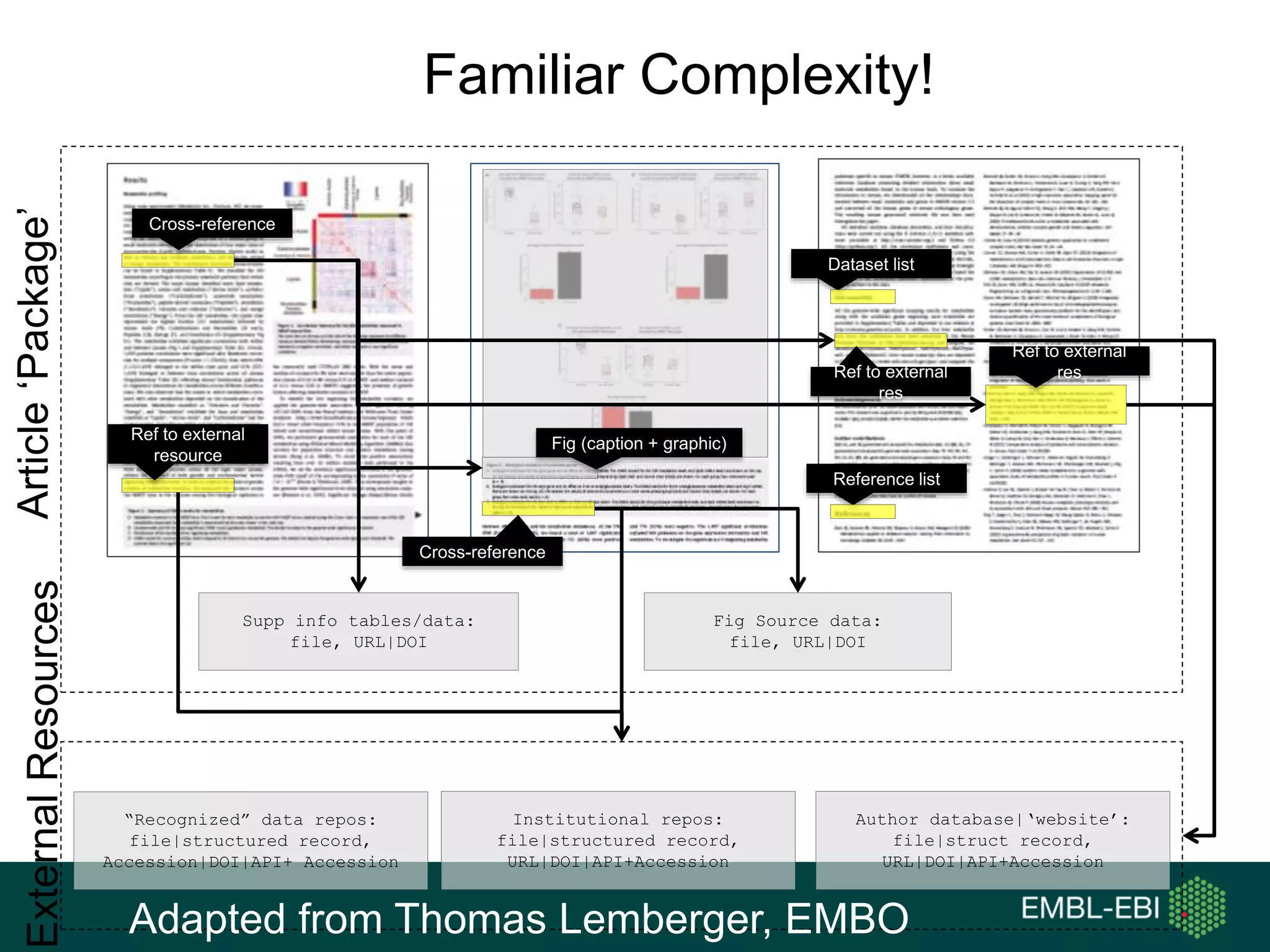
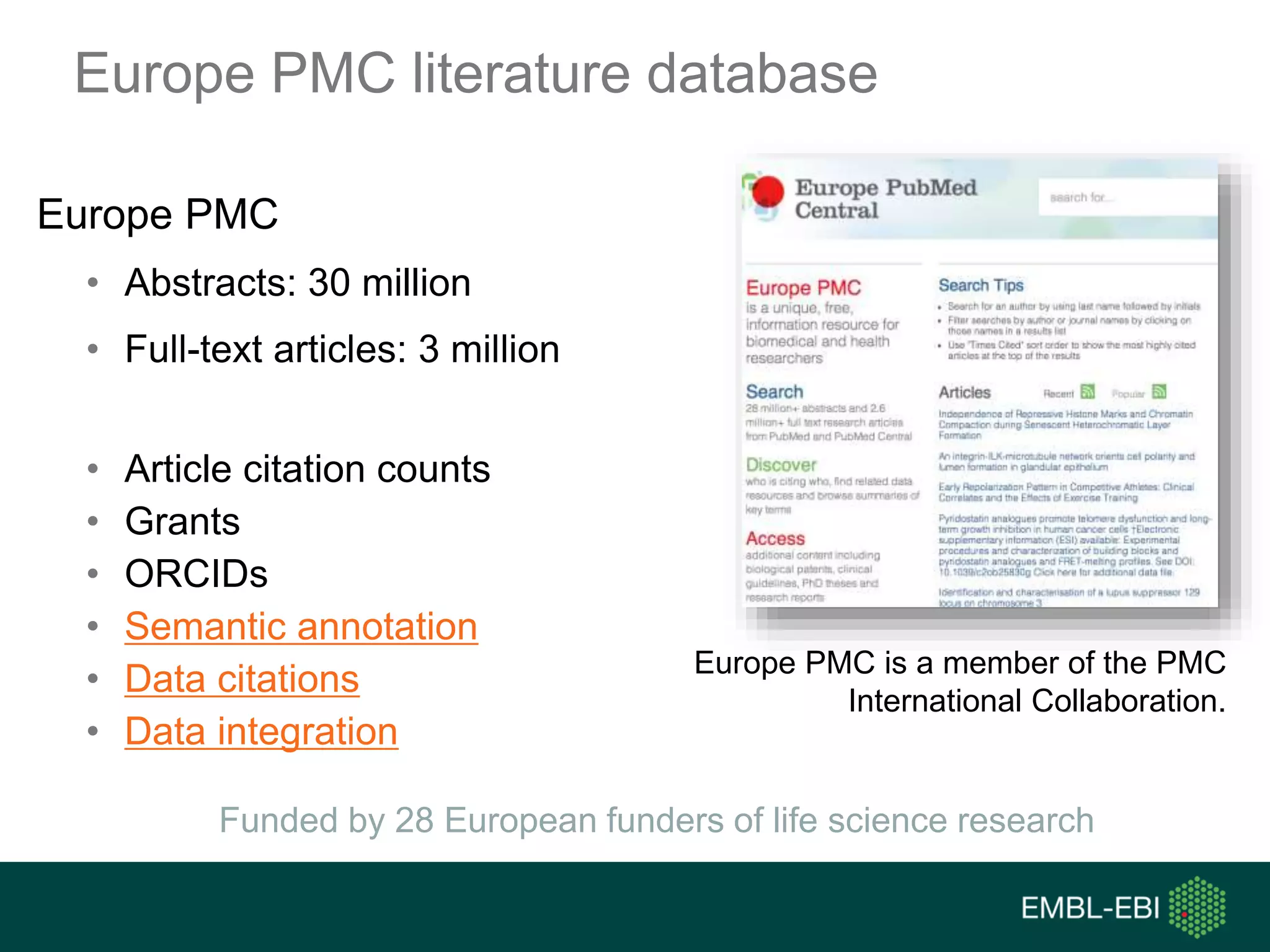
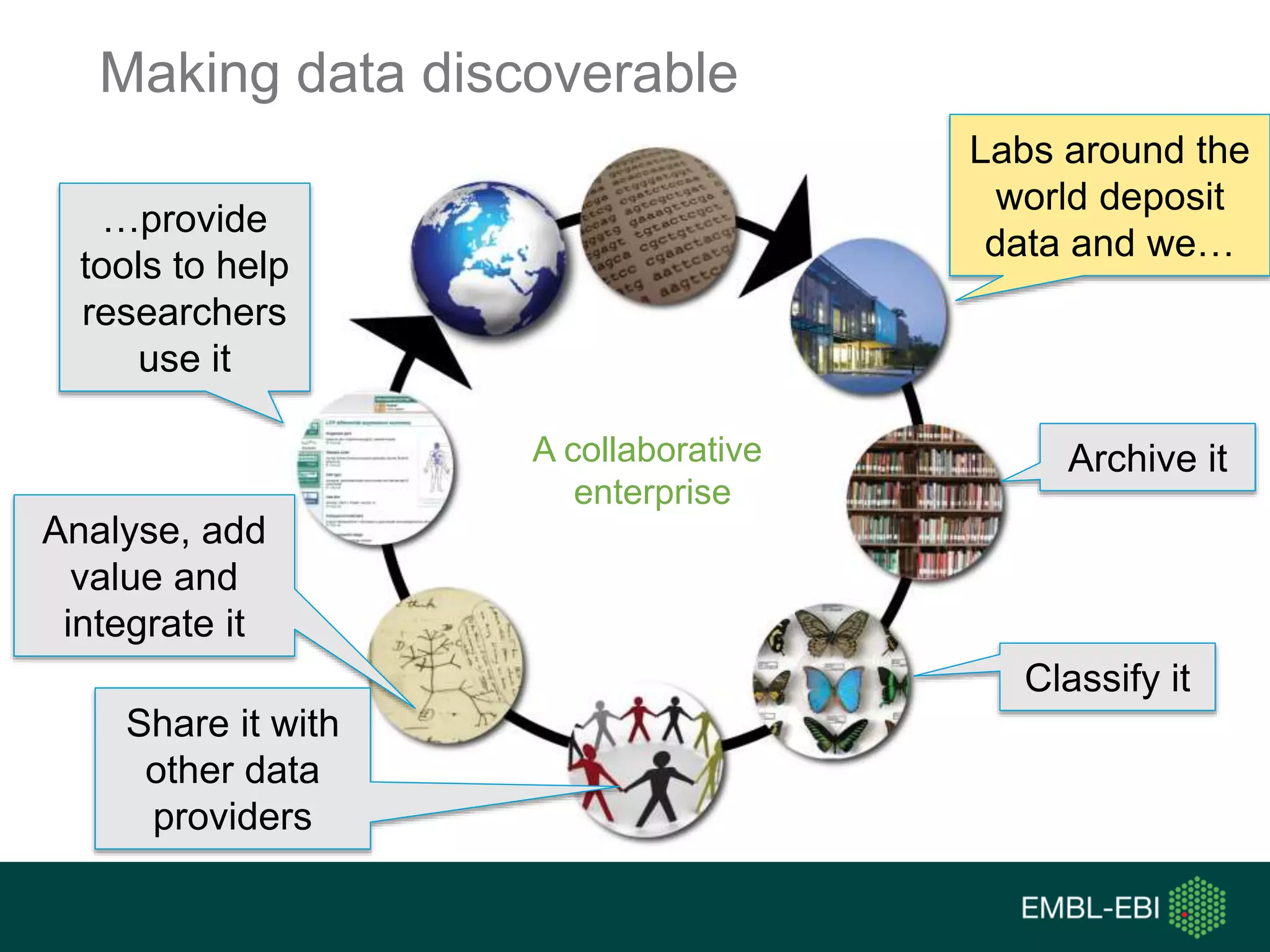
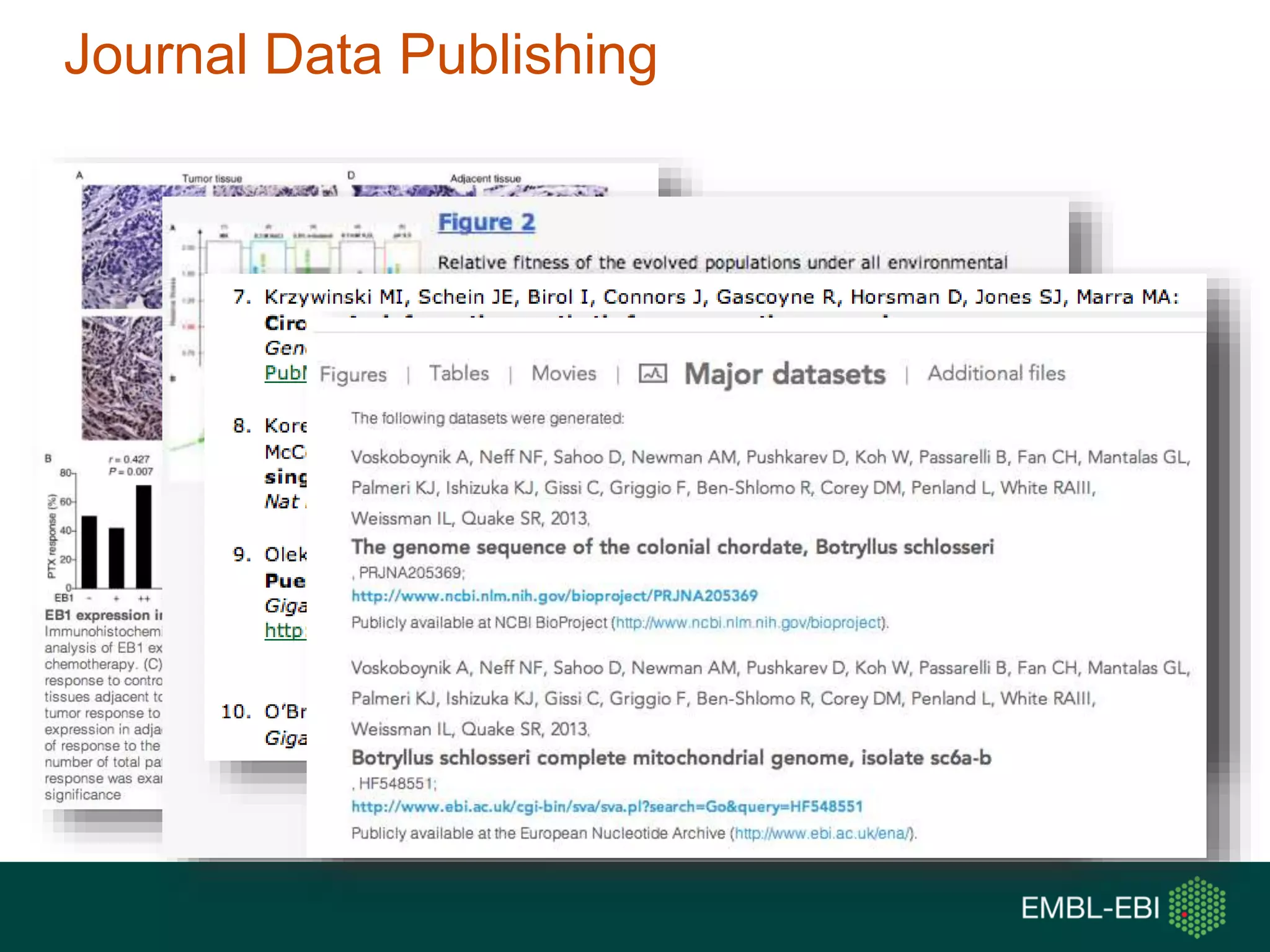
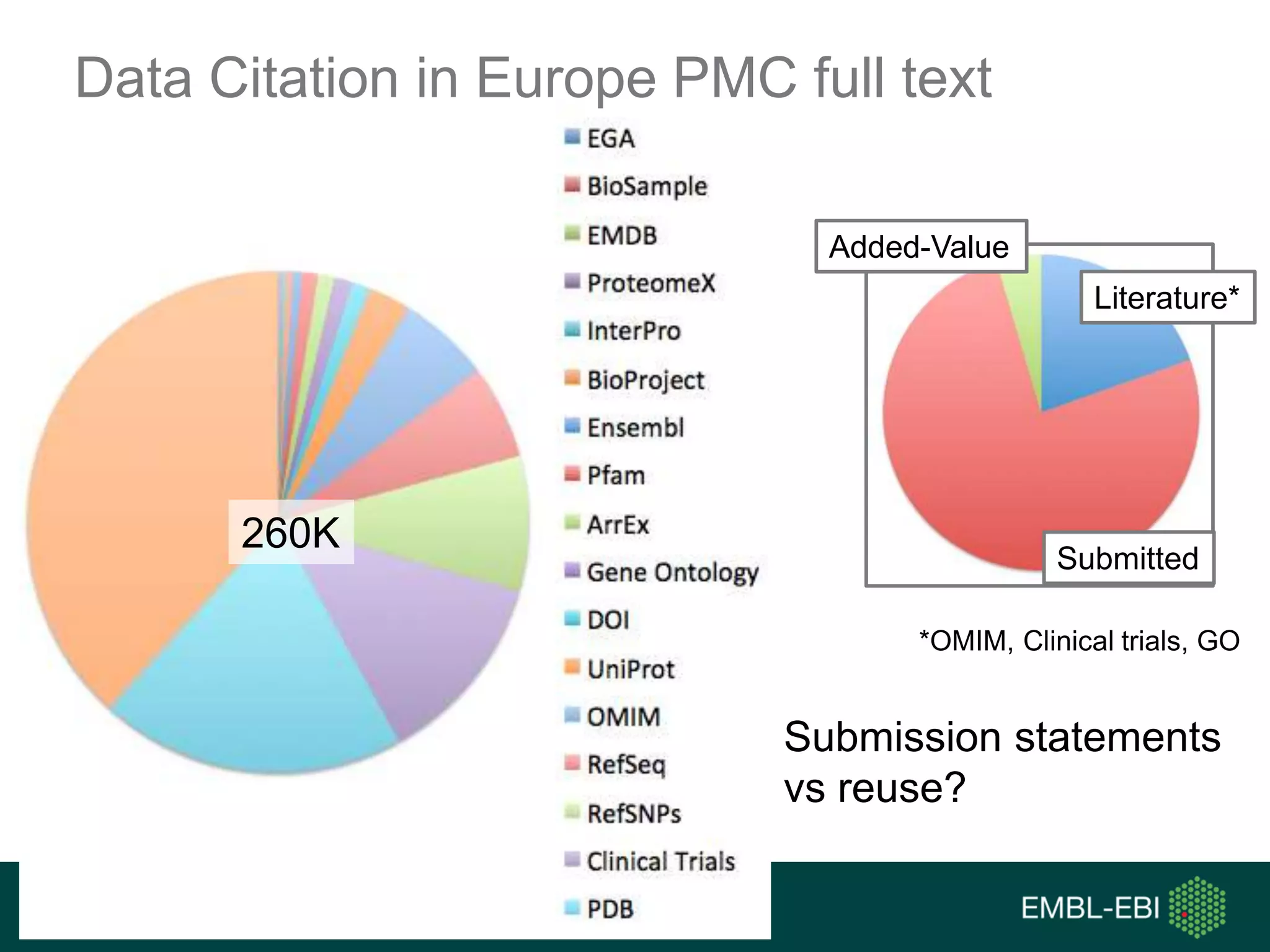
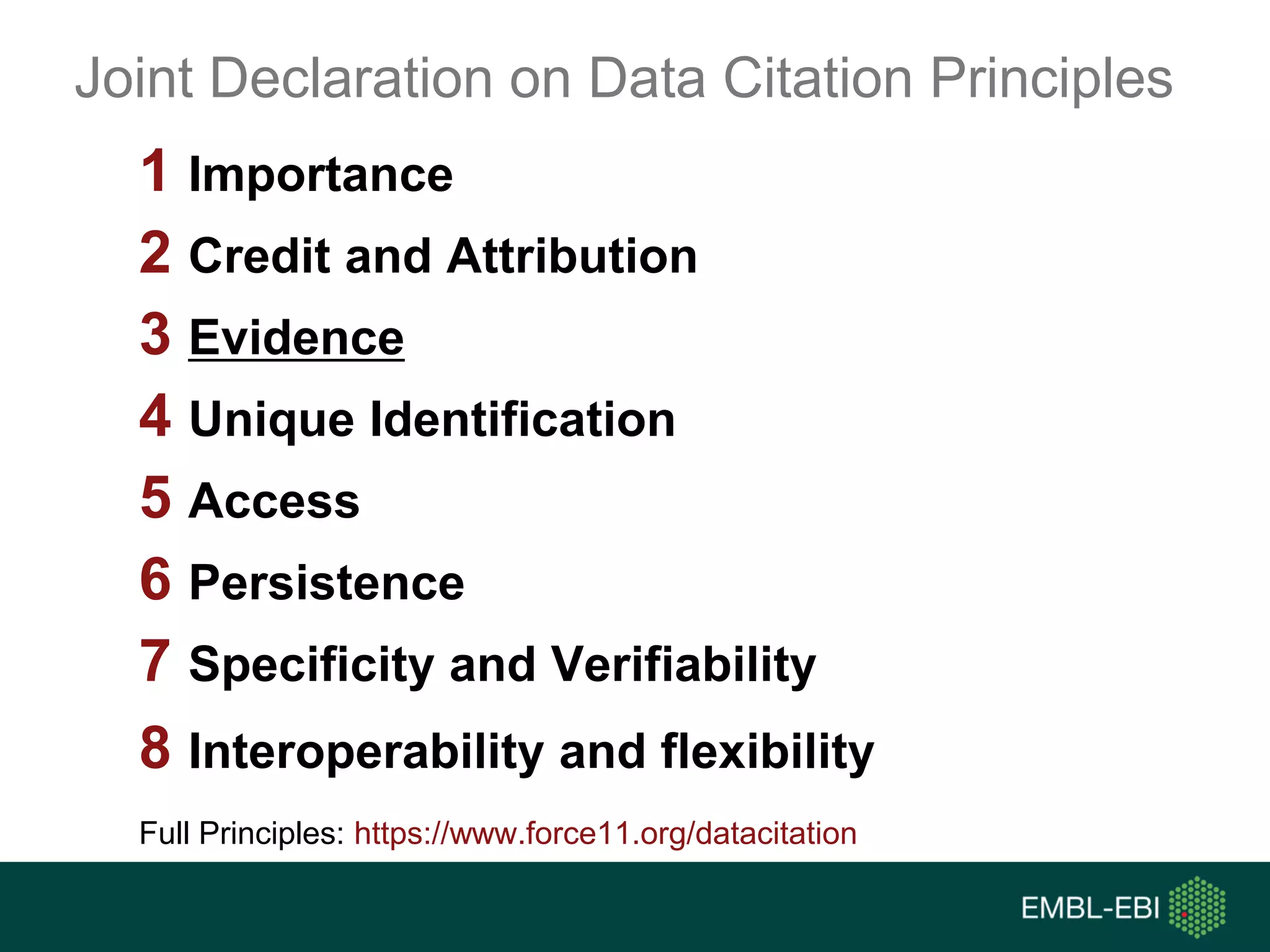
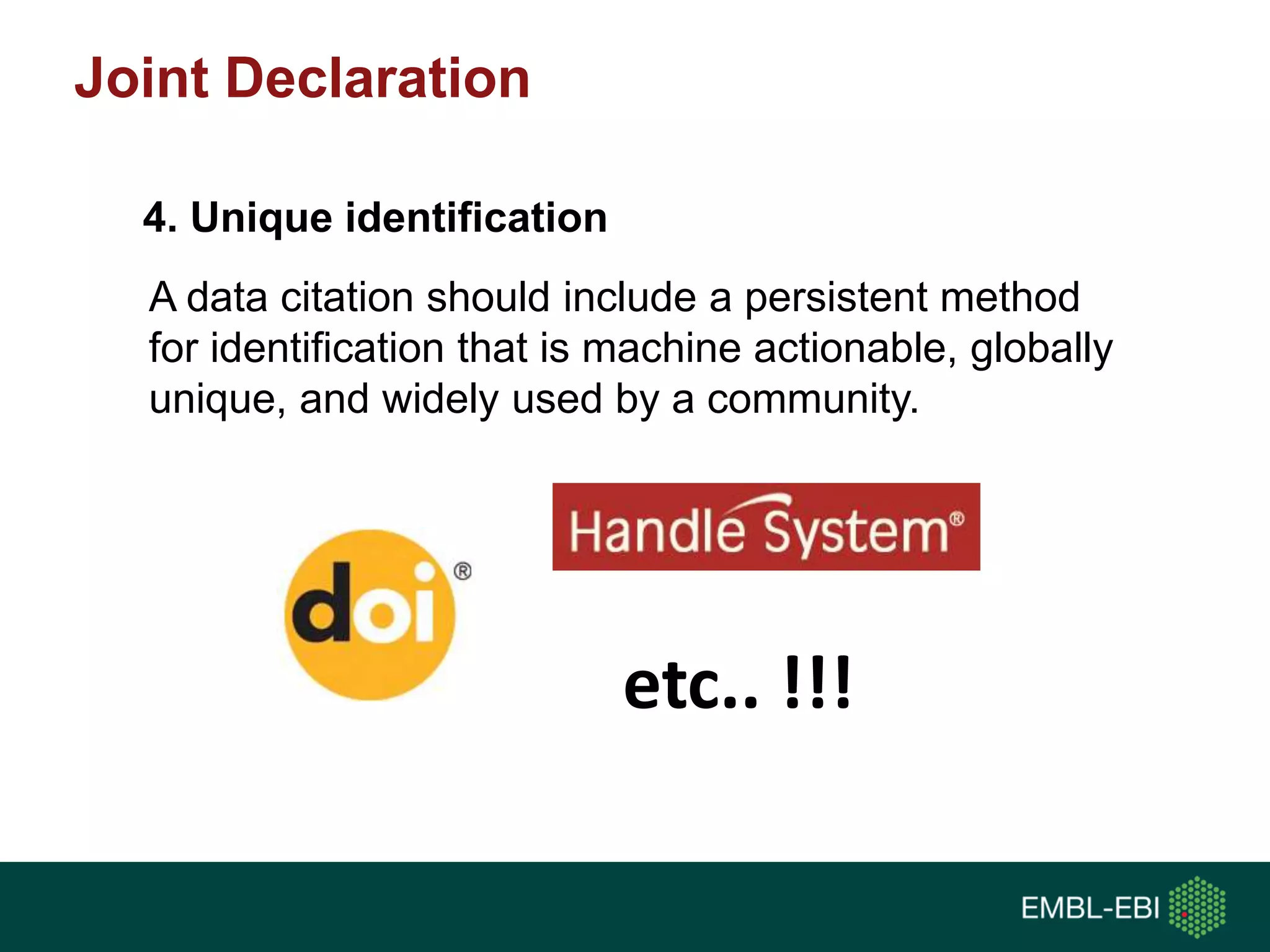
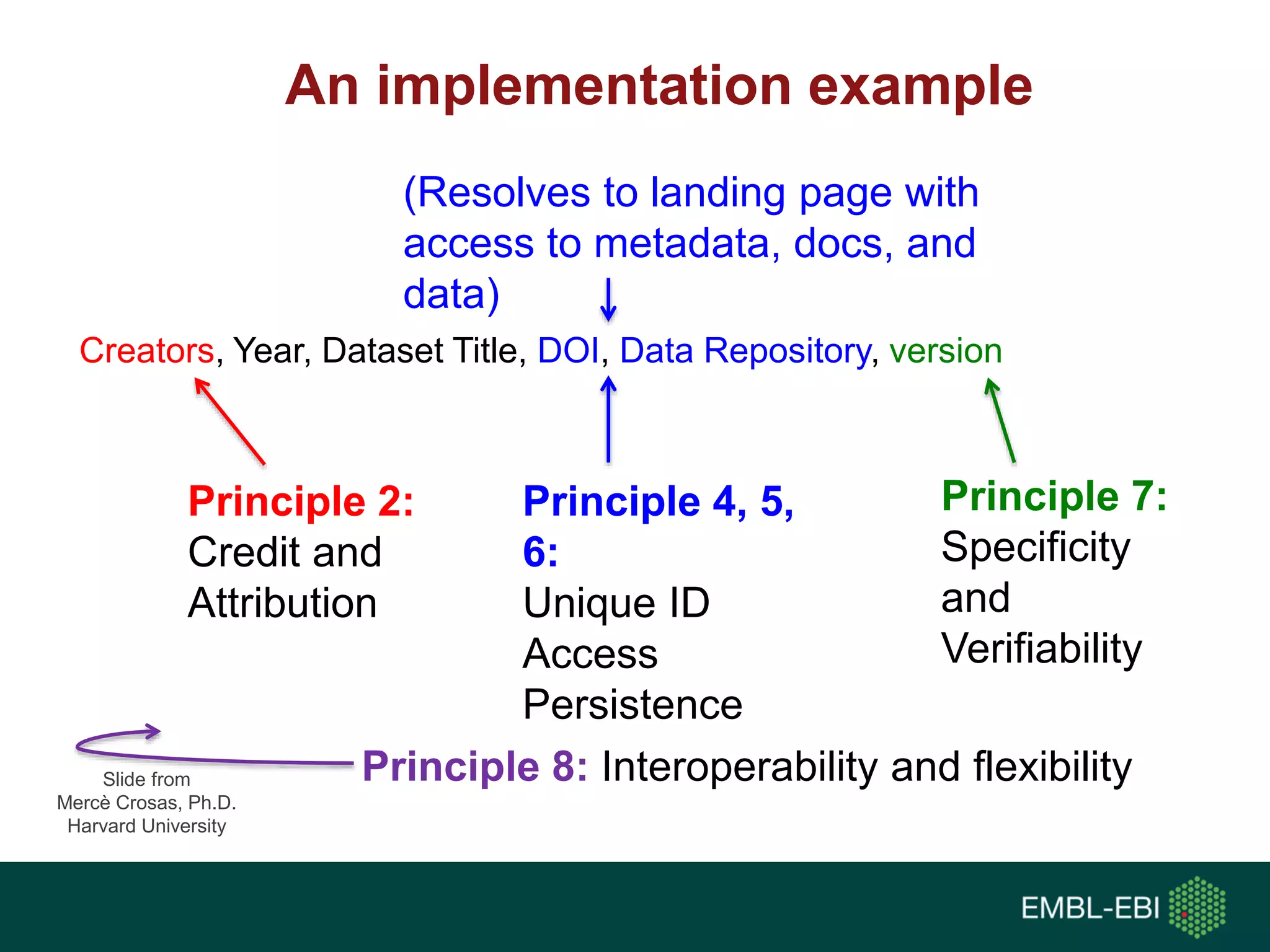
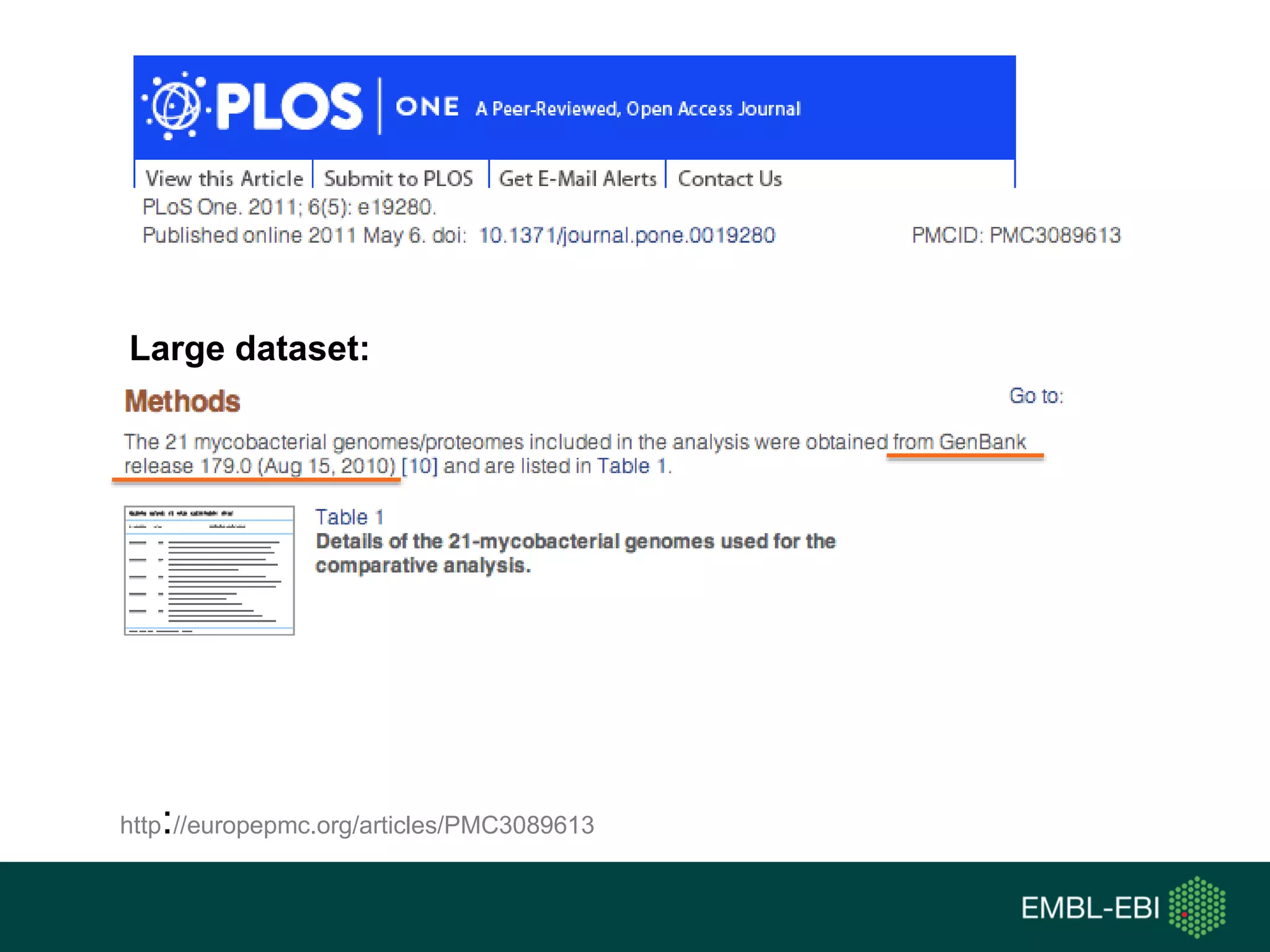
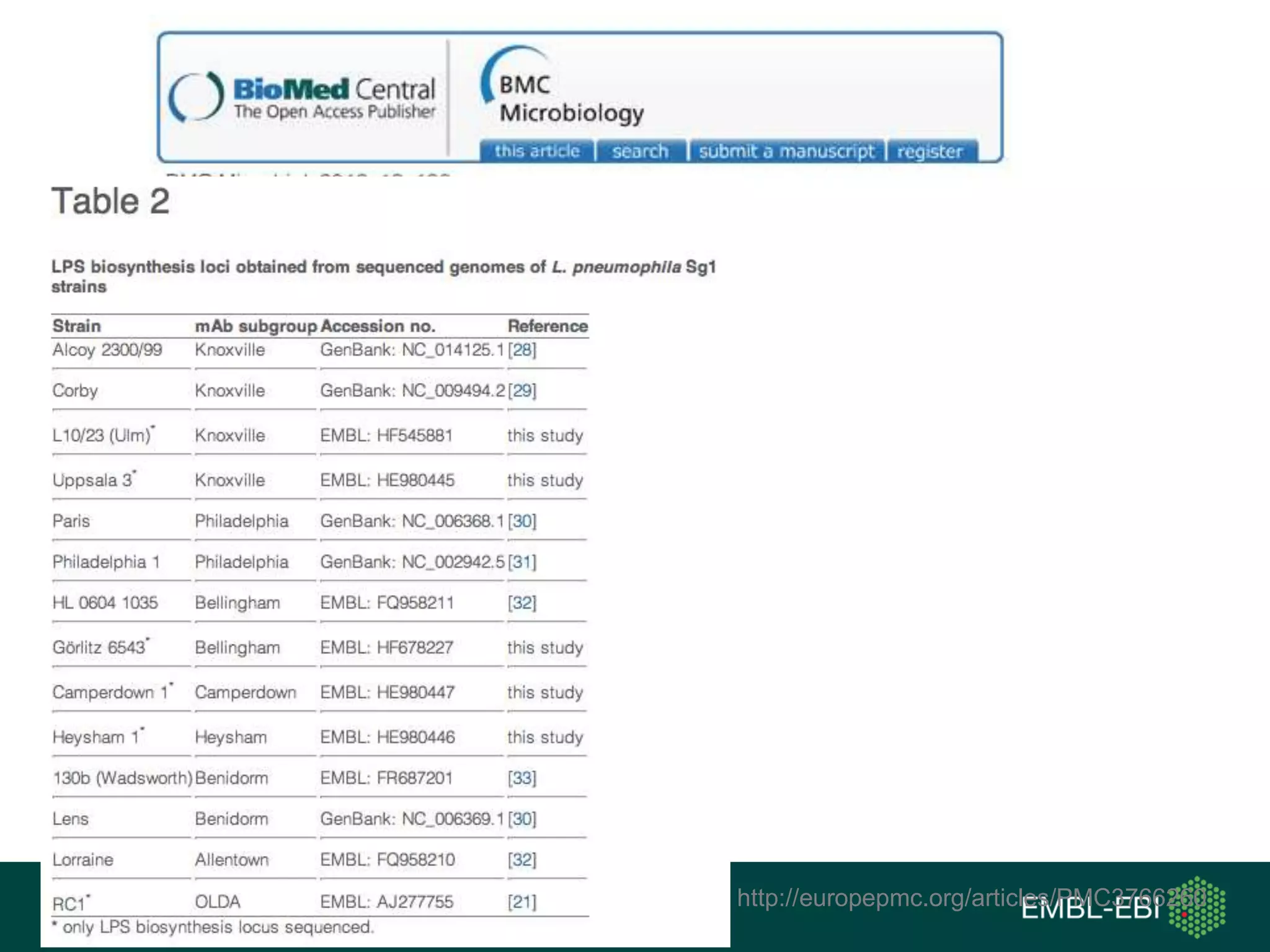
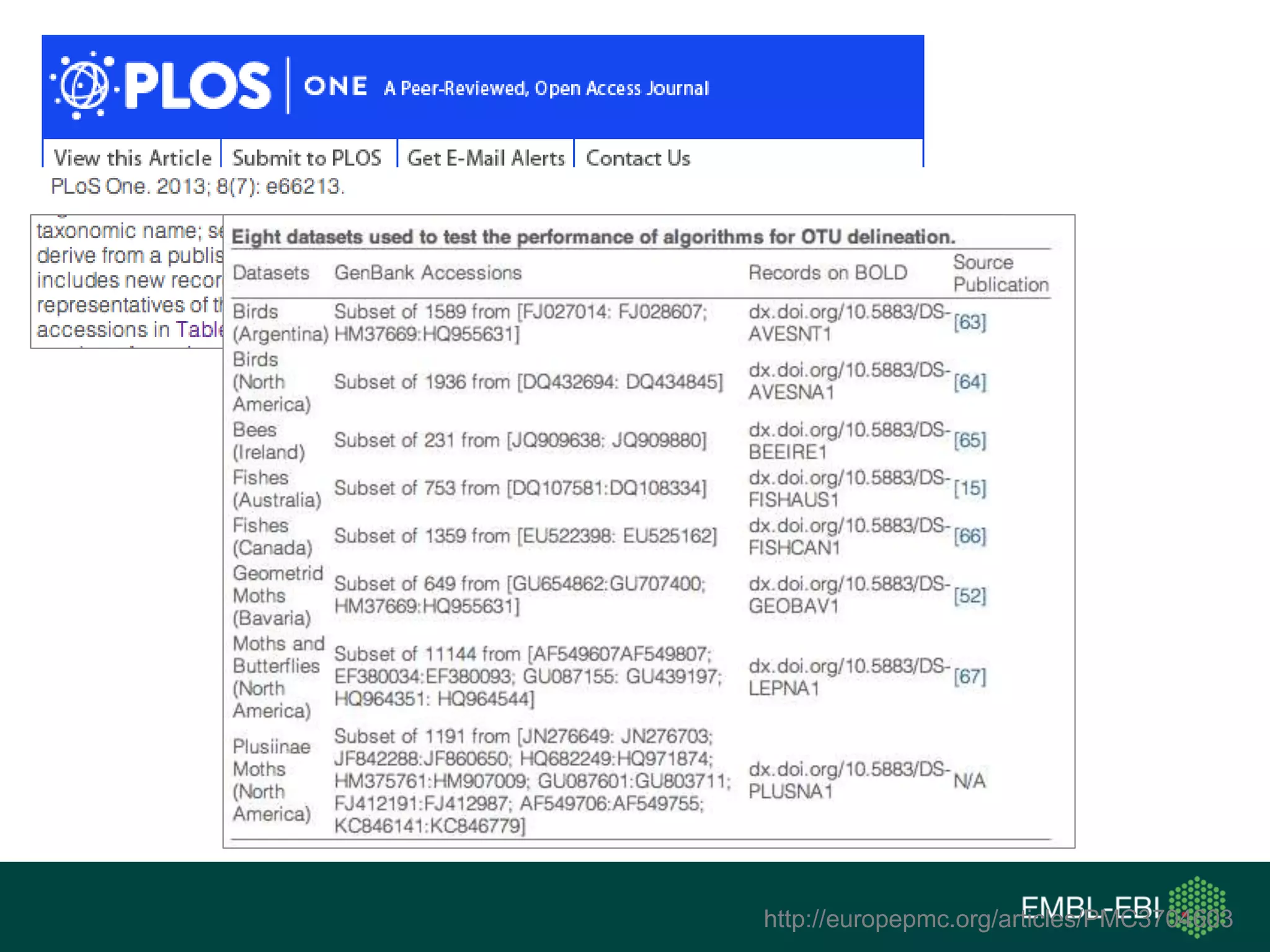
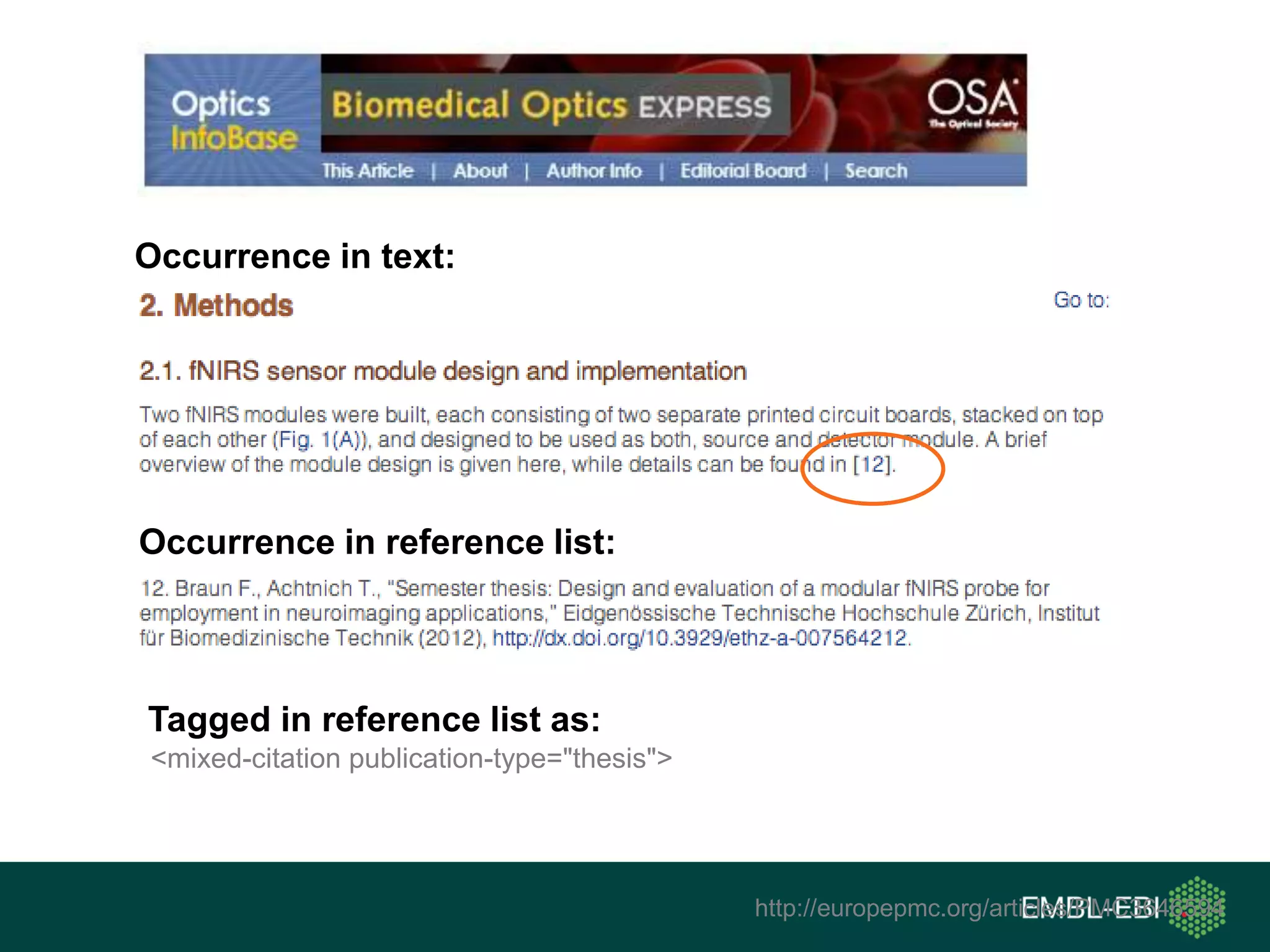
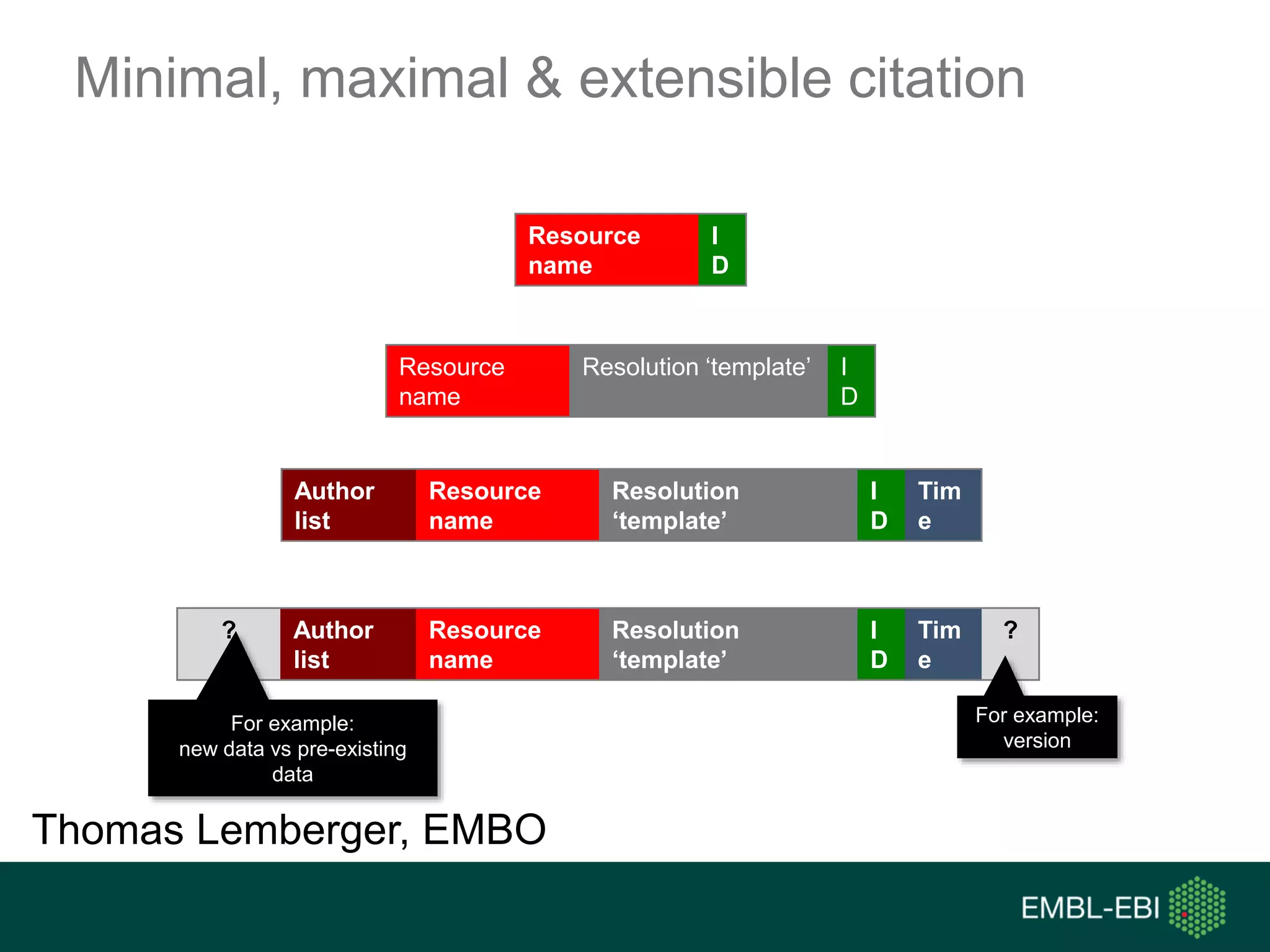
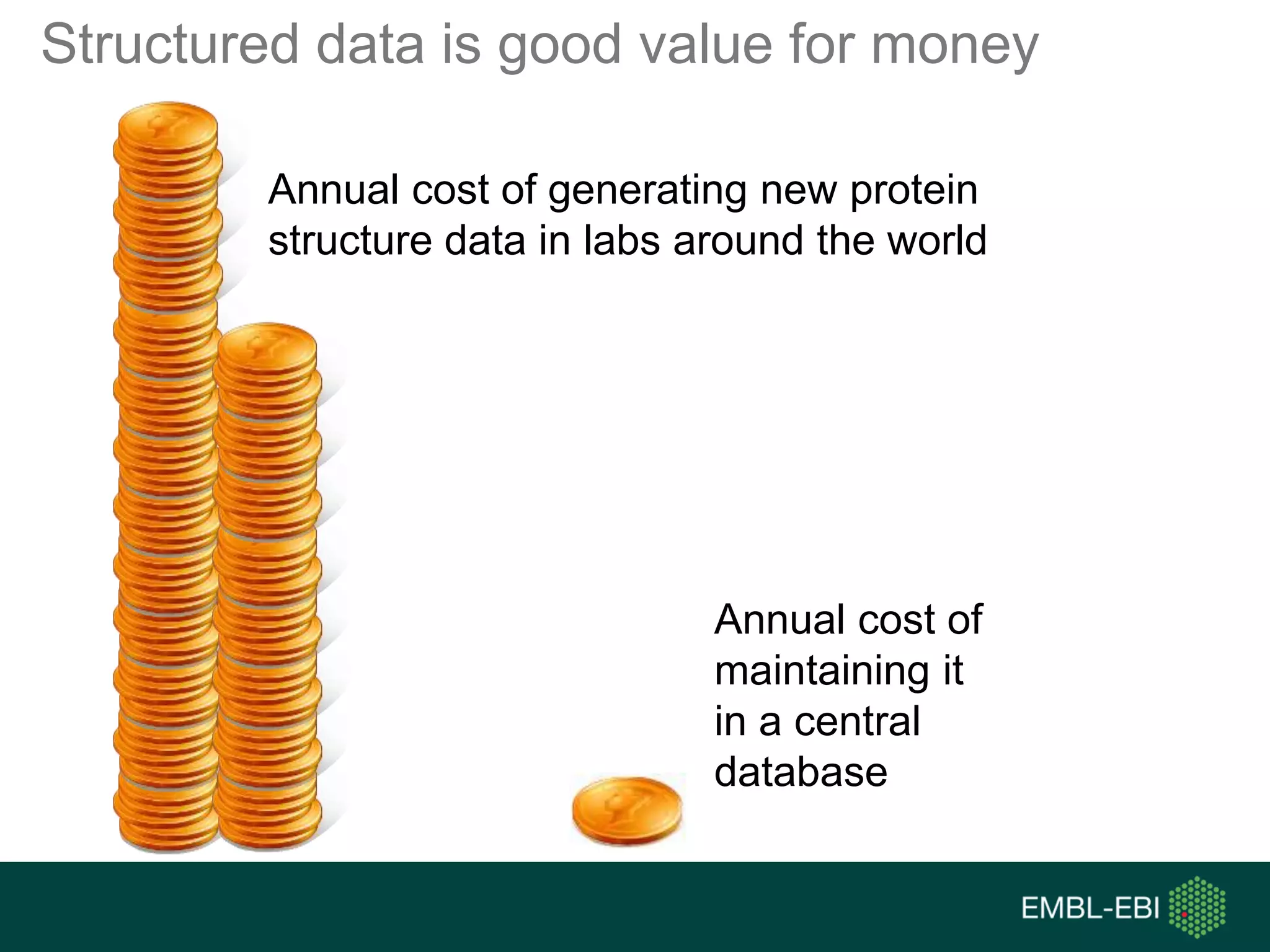
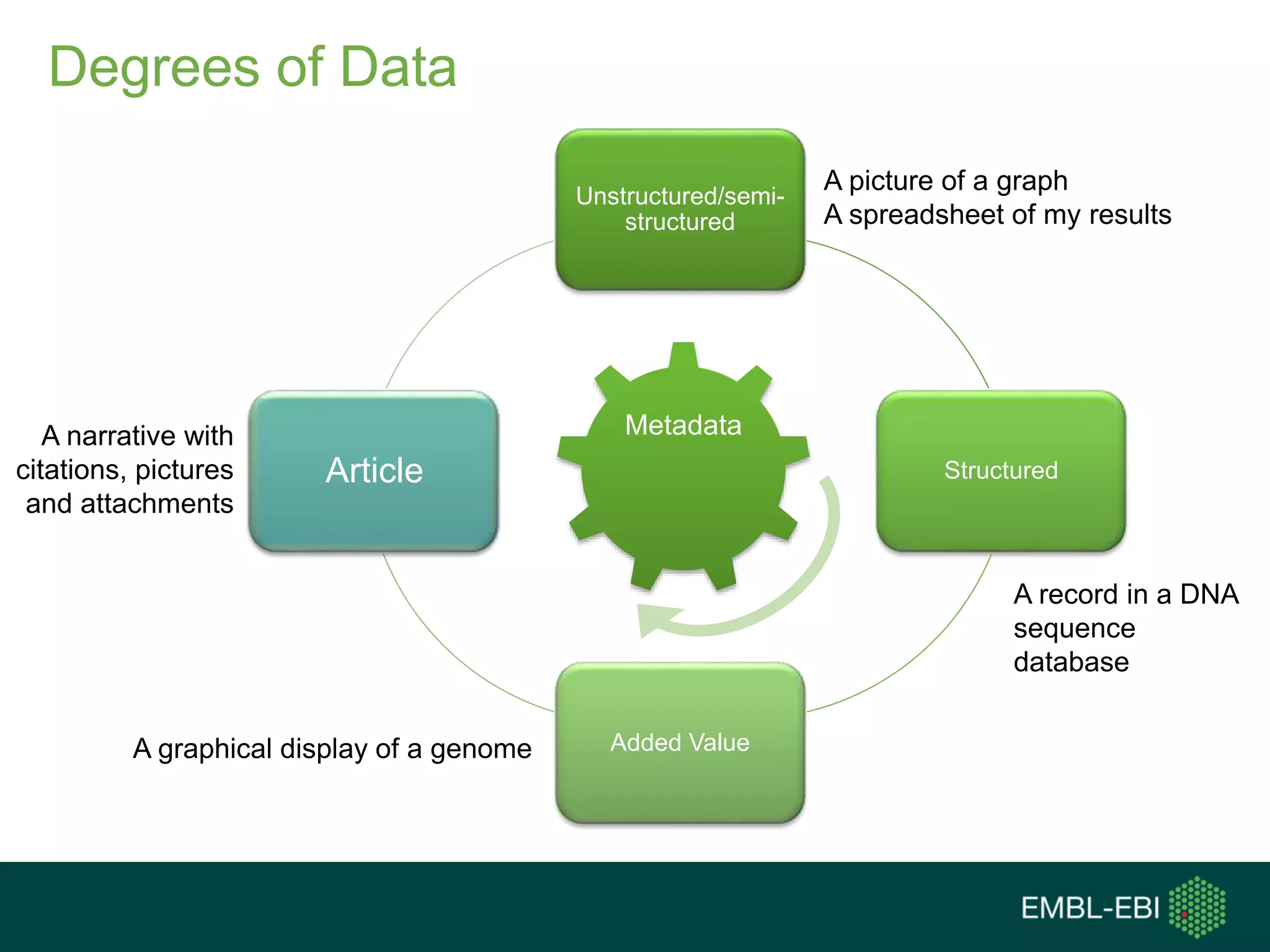
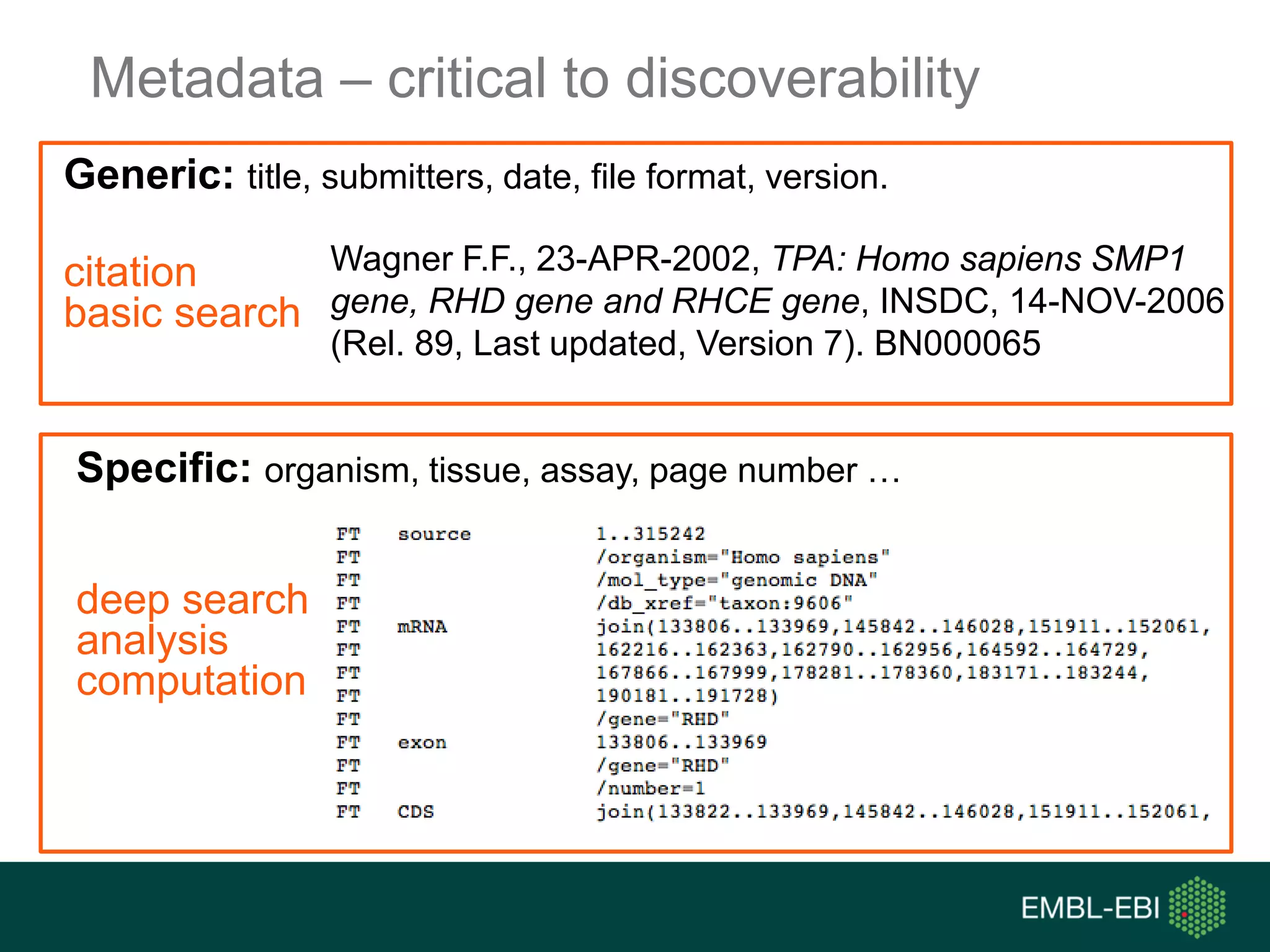
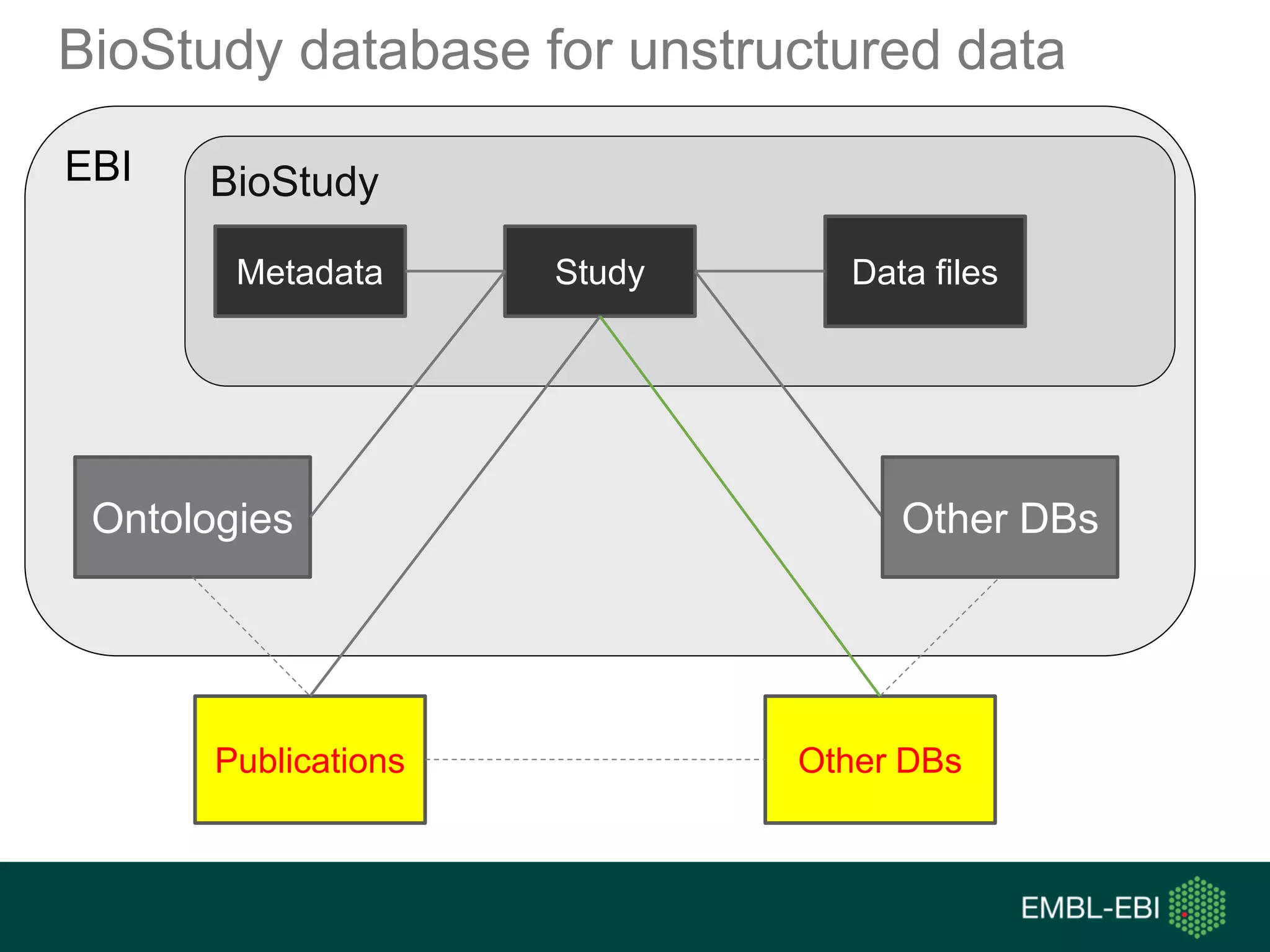
The document discusses the principles and challenges of data citation in research literature, emphasizing that data should be considered legitimate and citable products of research. It highlights key principles such as importance, credit and attribution, unique identification, and accessibility that facilitate reliable data use. Furthermore, it outlines implementation examples and the role of institutions like Europe PMC in promoting structured data practices to enhance discoverability and reproducibility in life sciences.