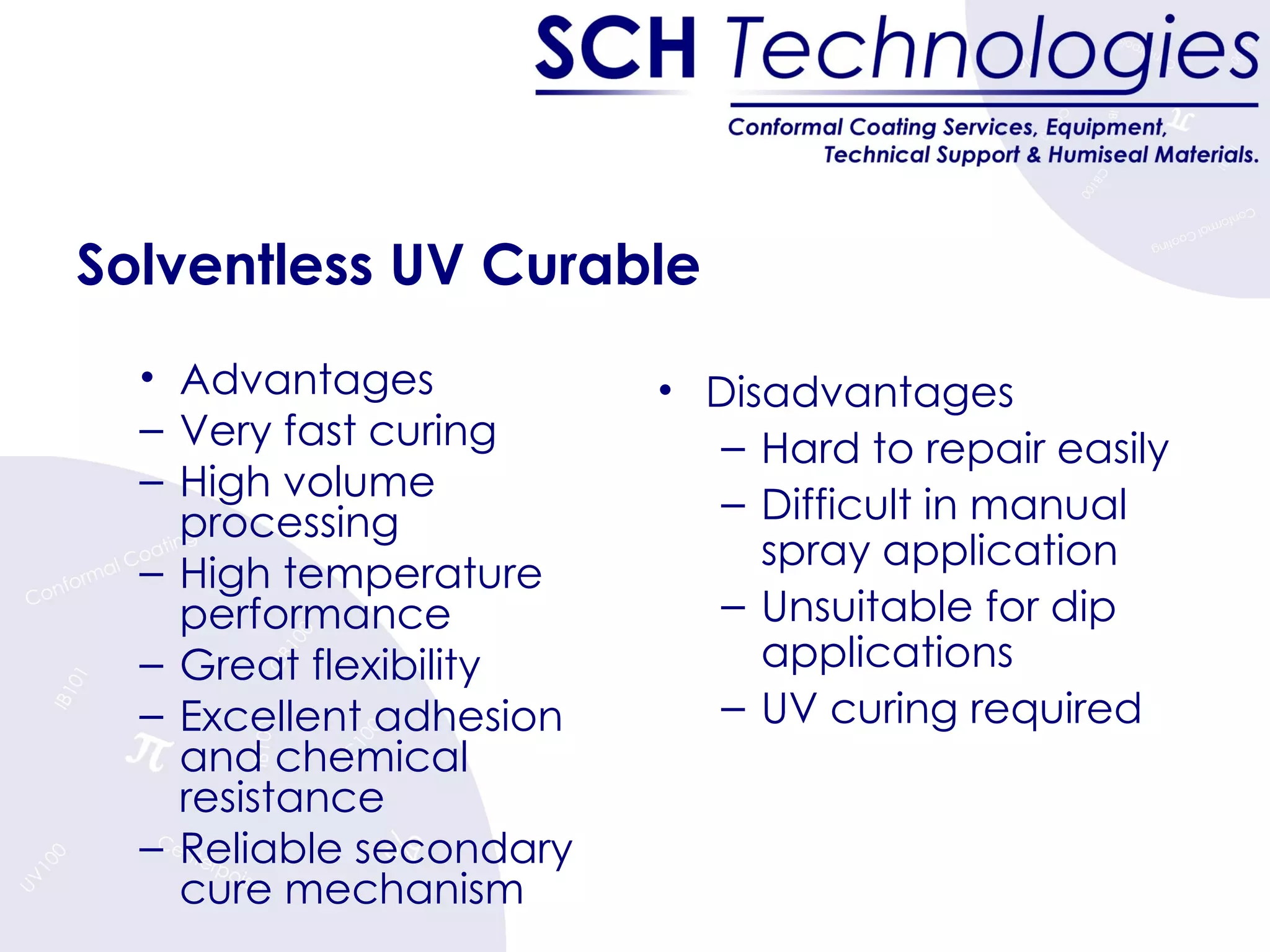
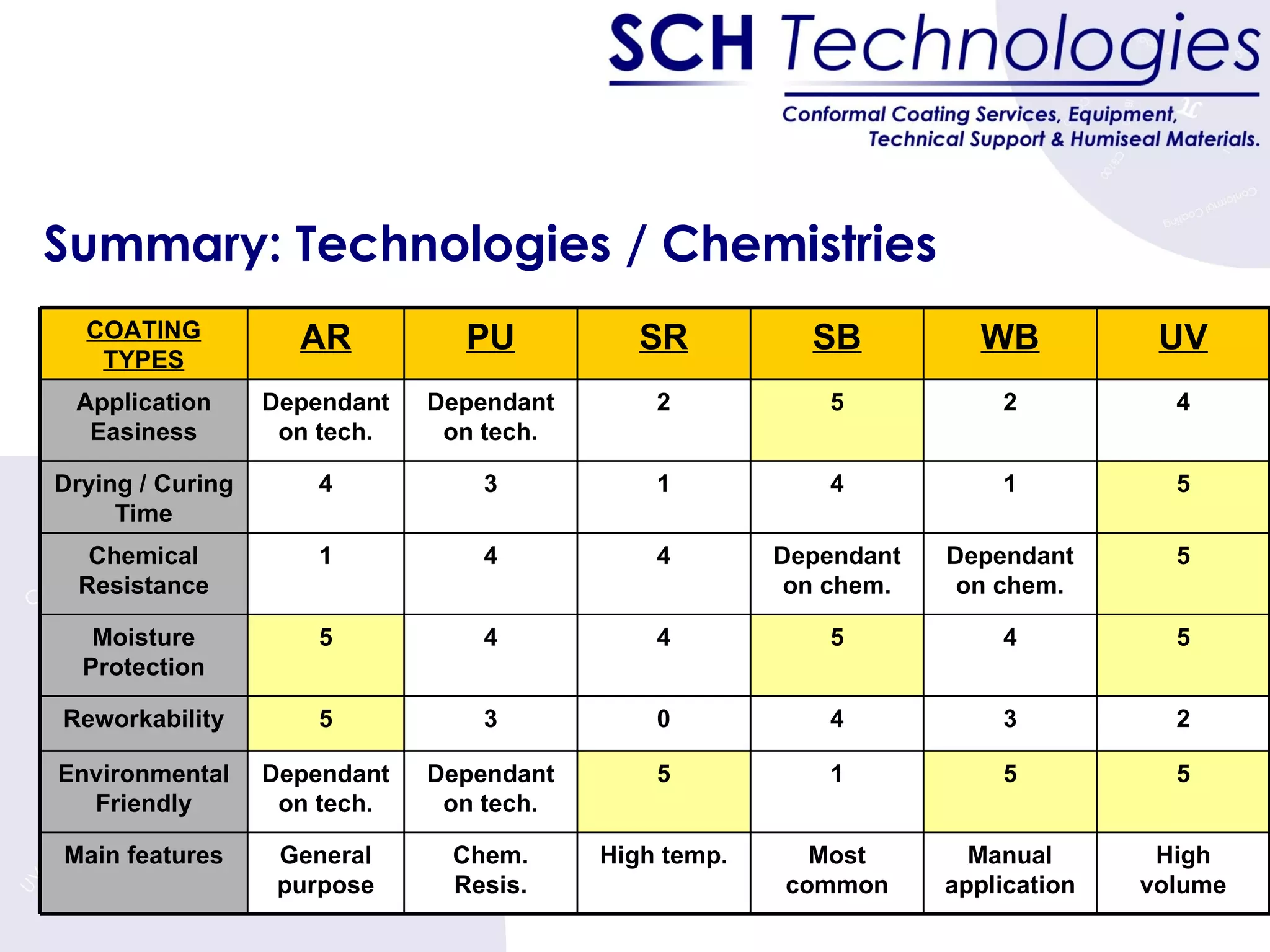
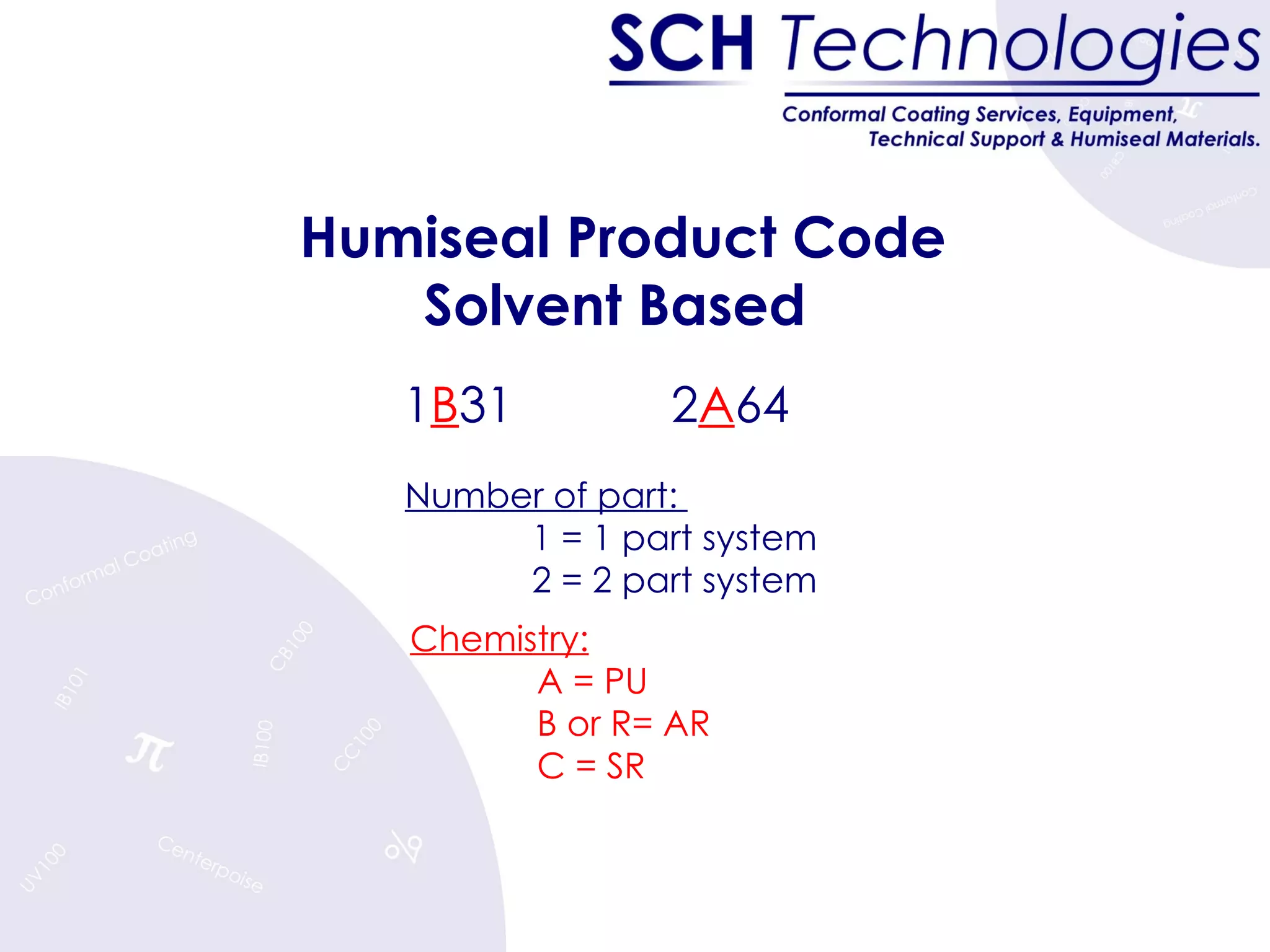
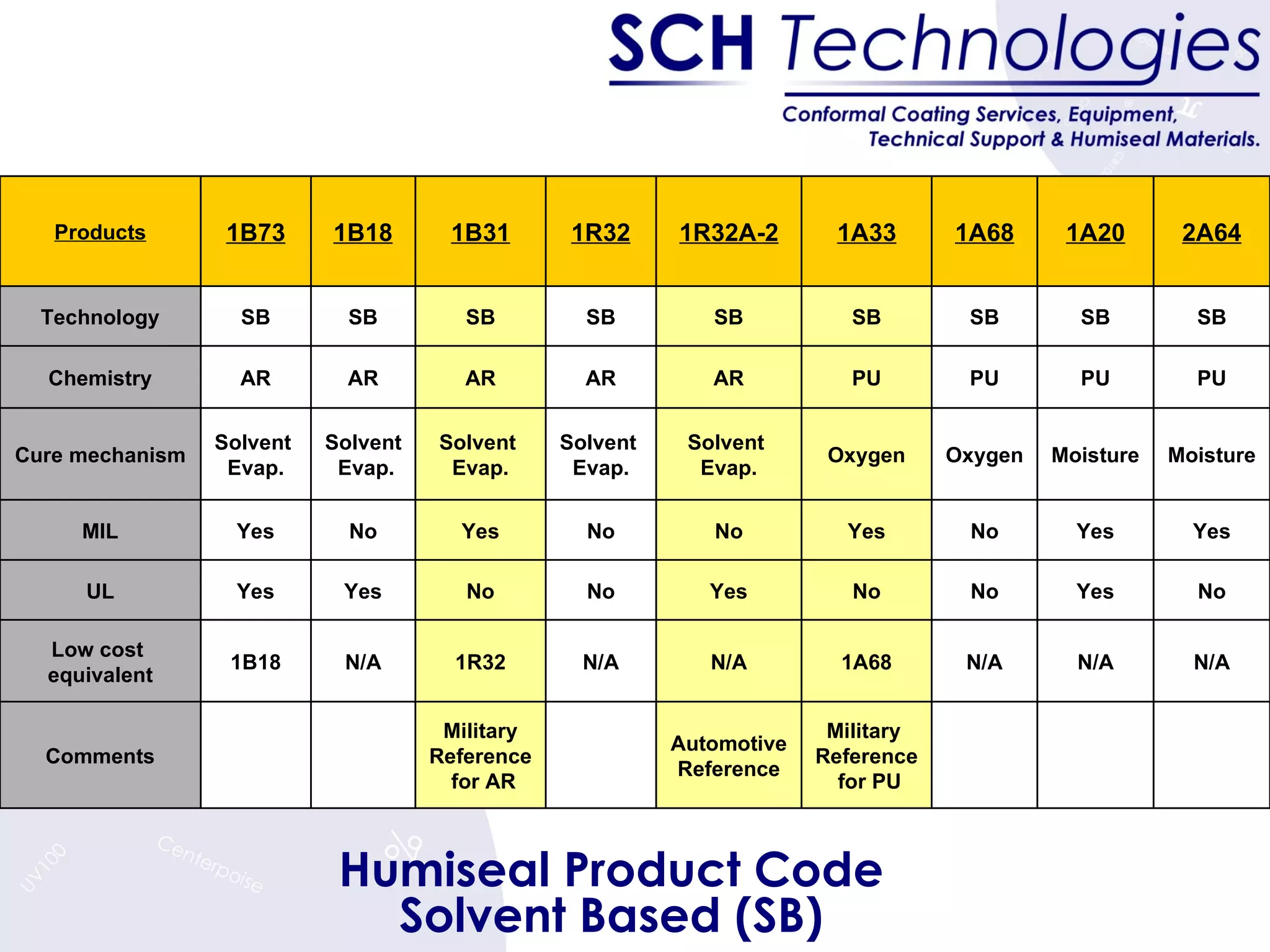
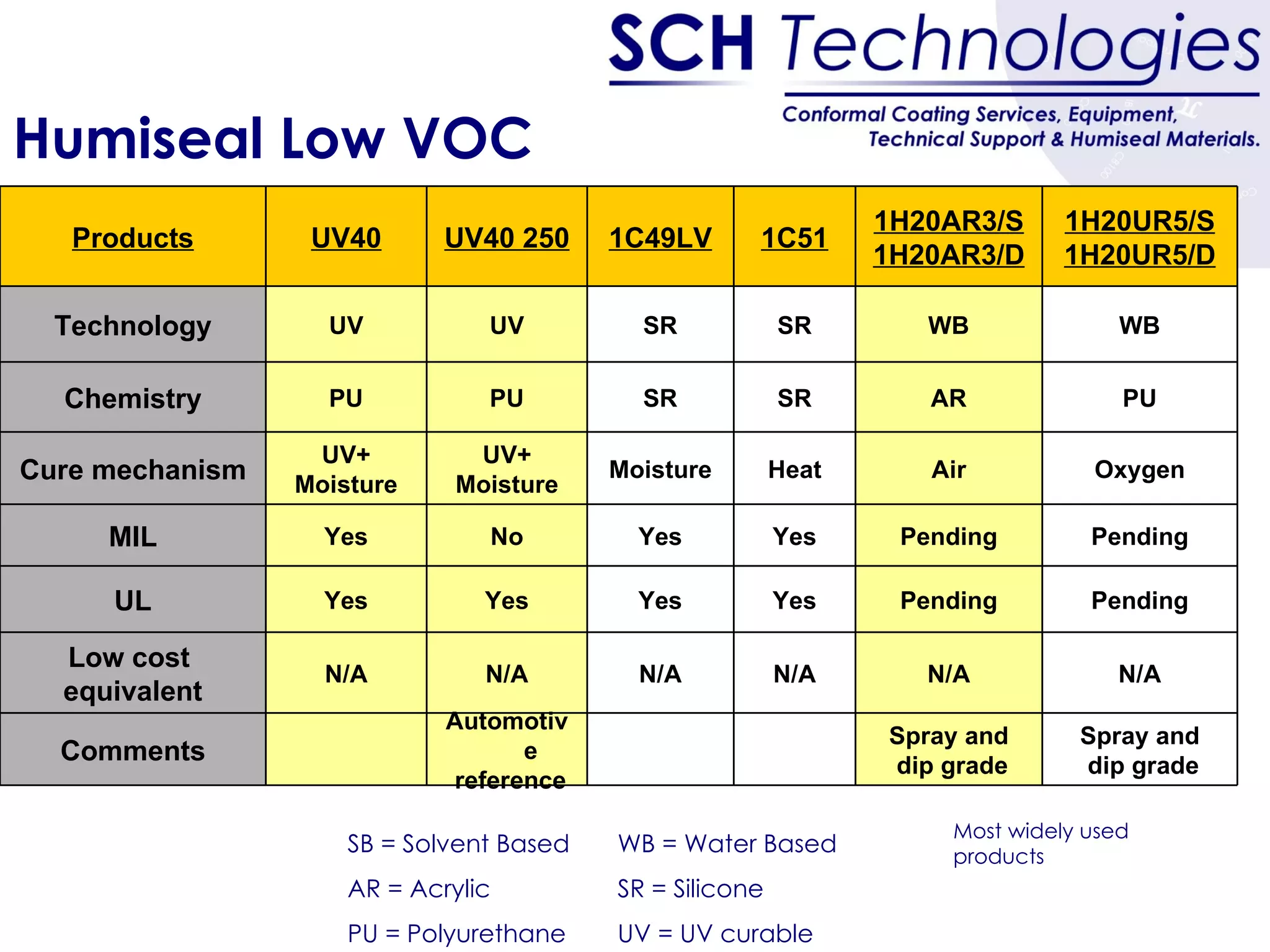
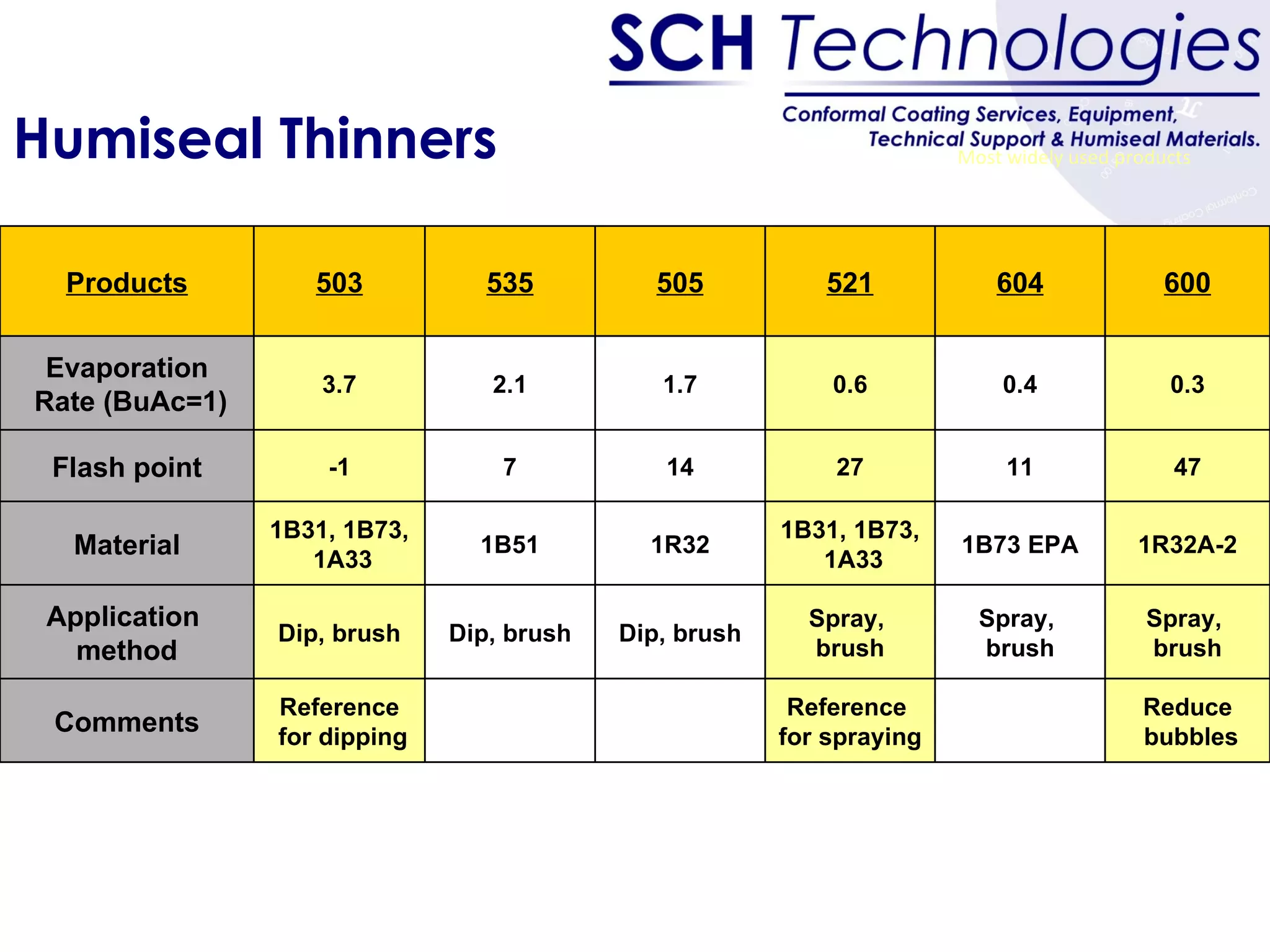
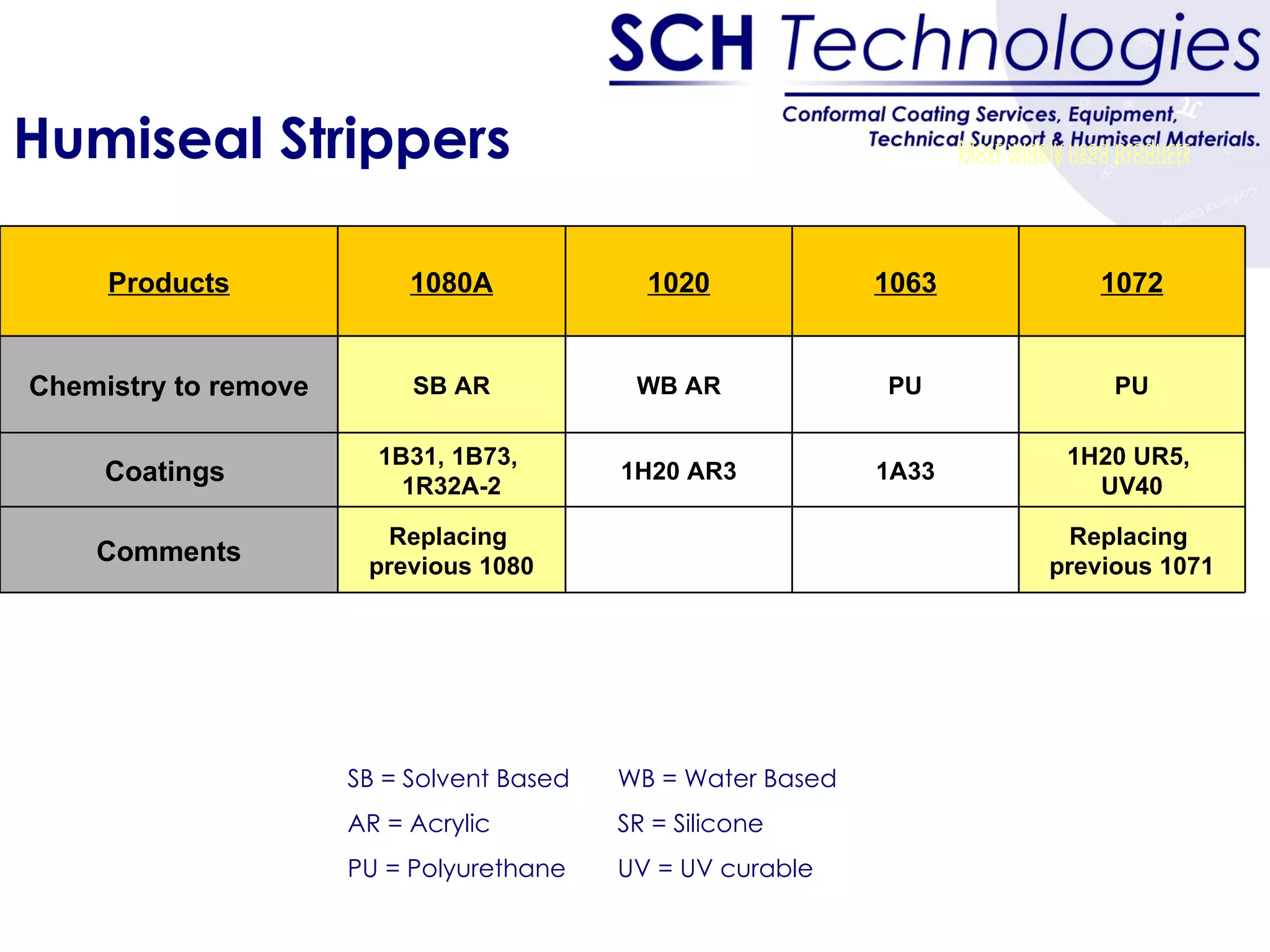
The document discusses different types of conformal coatings, their properties and applications. It defines conformal coating as a thin protective plastic film that conforms to an electronic circuit board. The main types covered are acrylics, polyurethanes, epoxies, silicones and fluorocarbons. Acrylics are most common due to their low cost and ease of application, while silicones are suitable for high temperature uses. Key factors in selecting a coating include chemical resistance, temperature tolerance, and ease of application and repair.