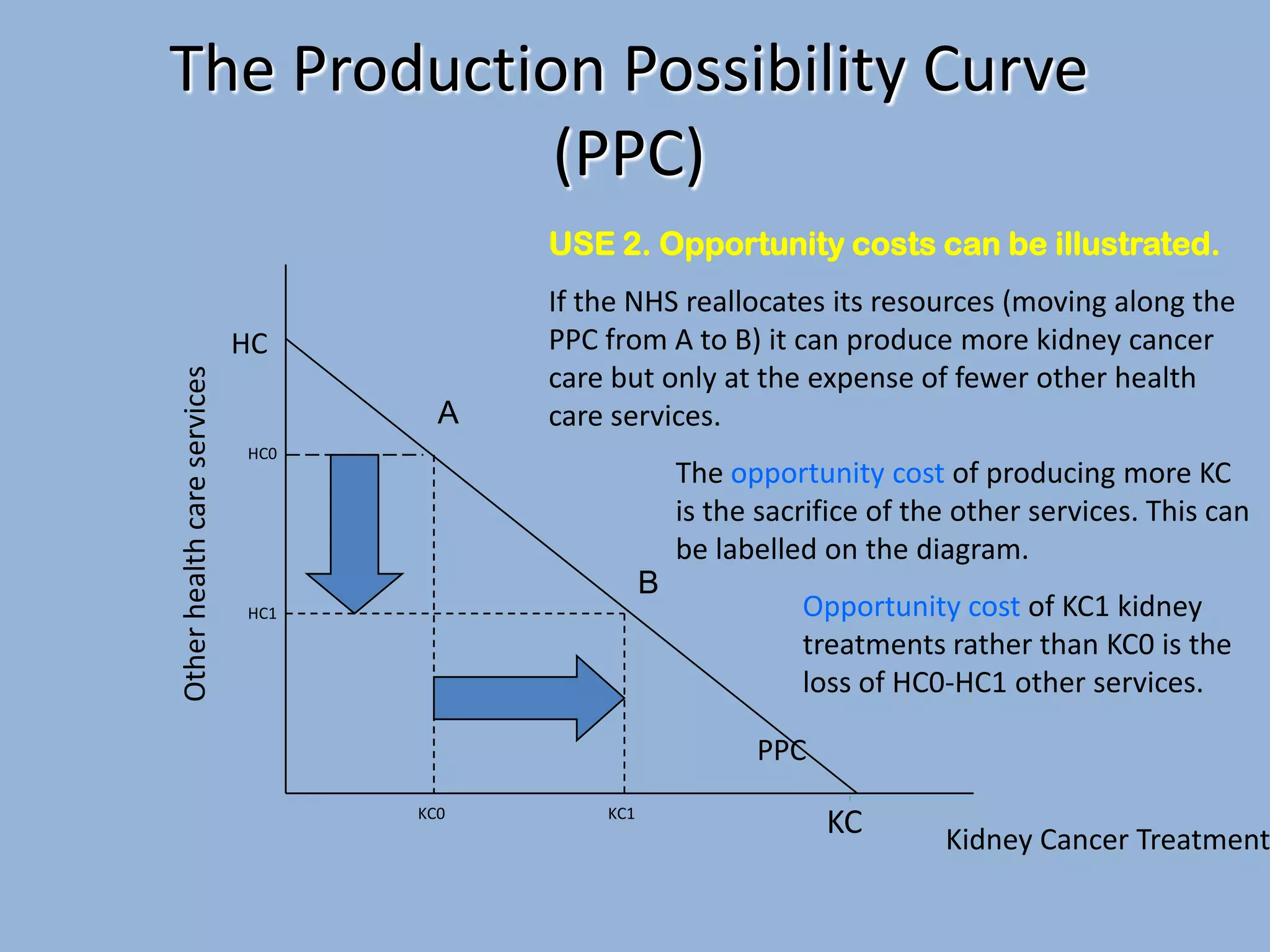
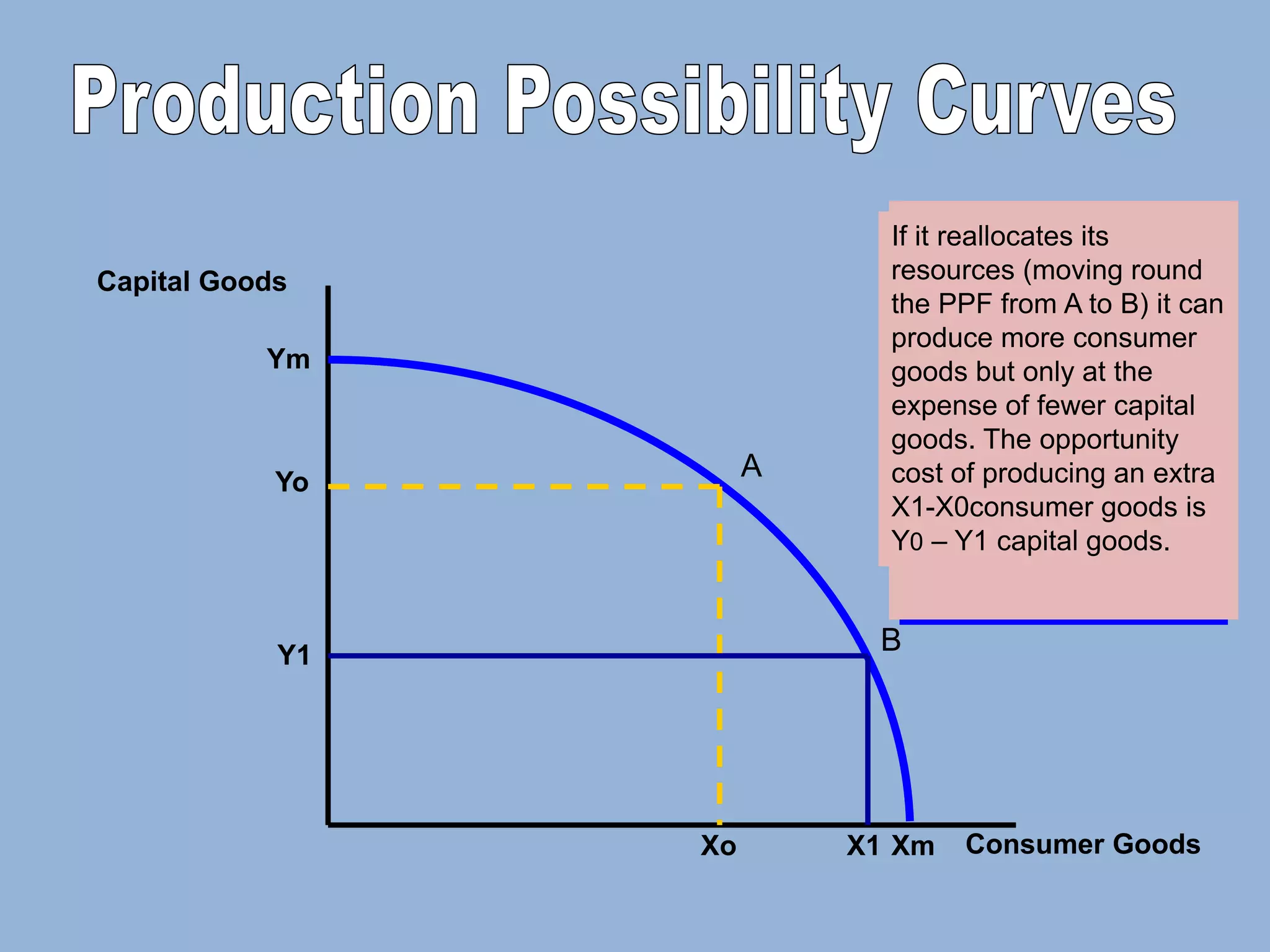
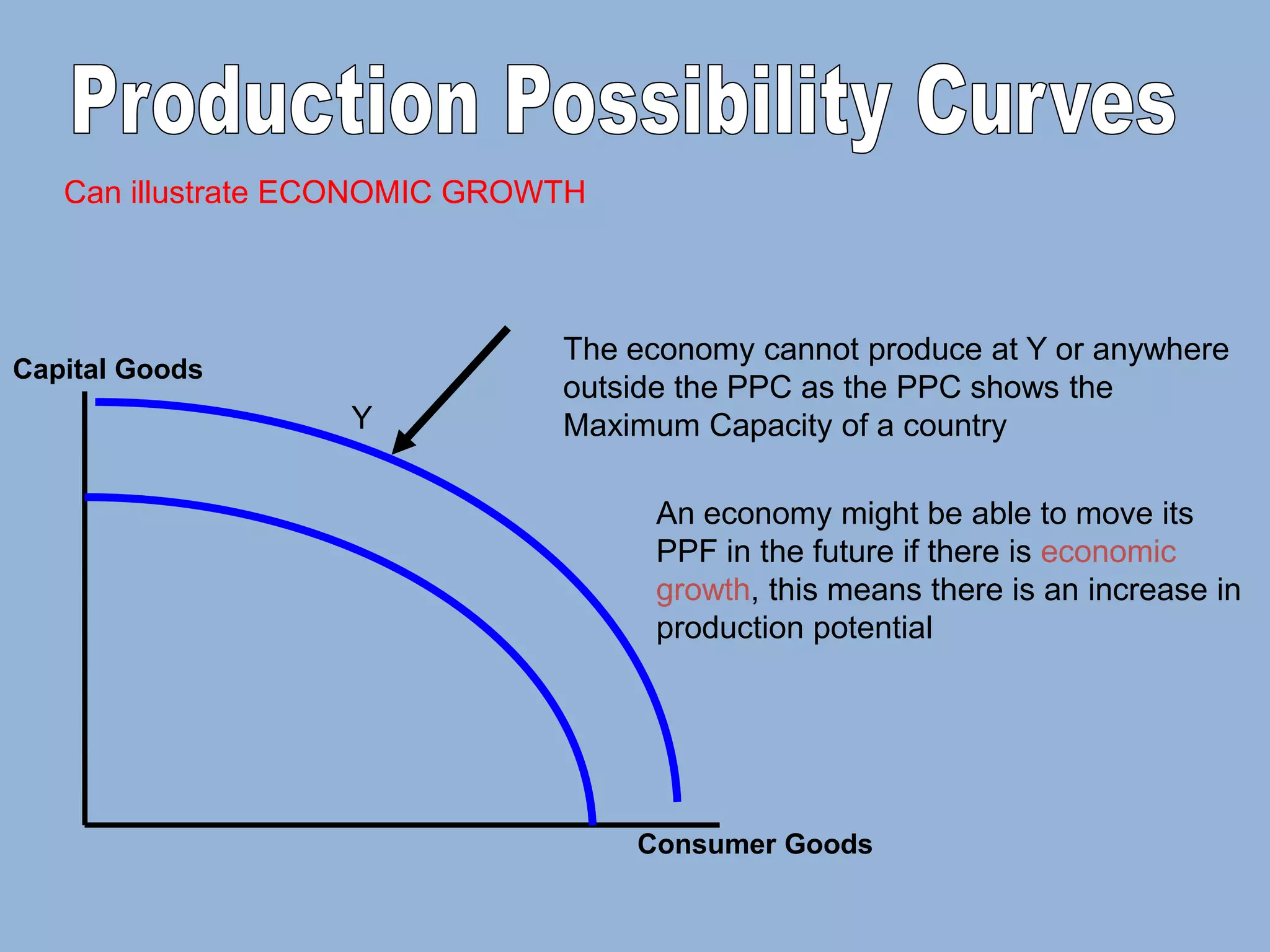
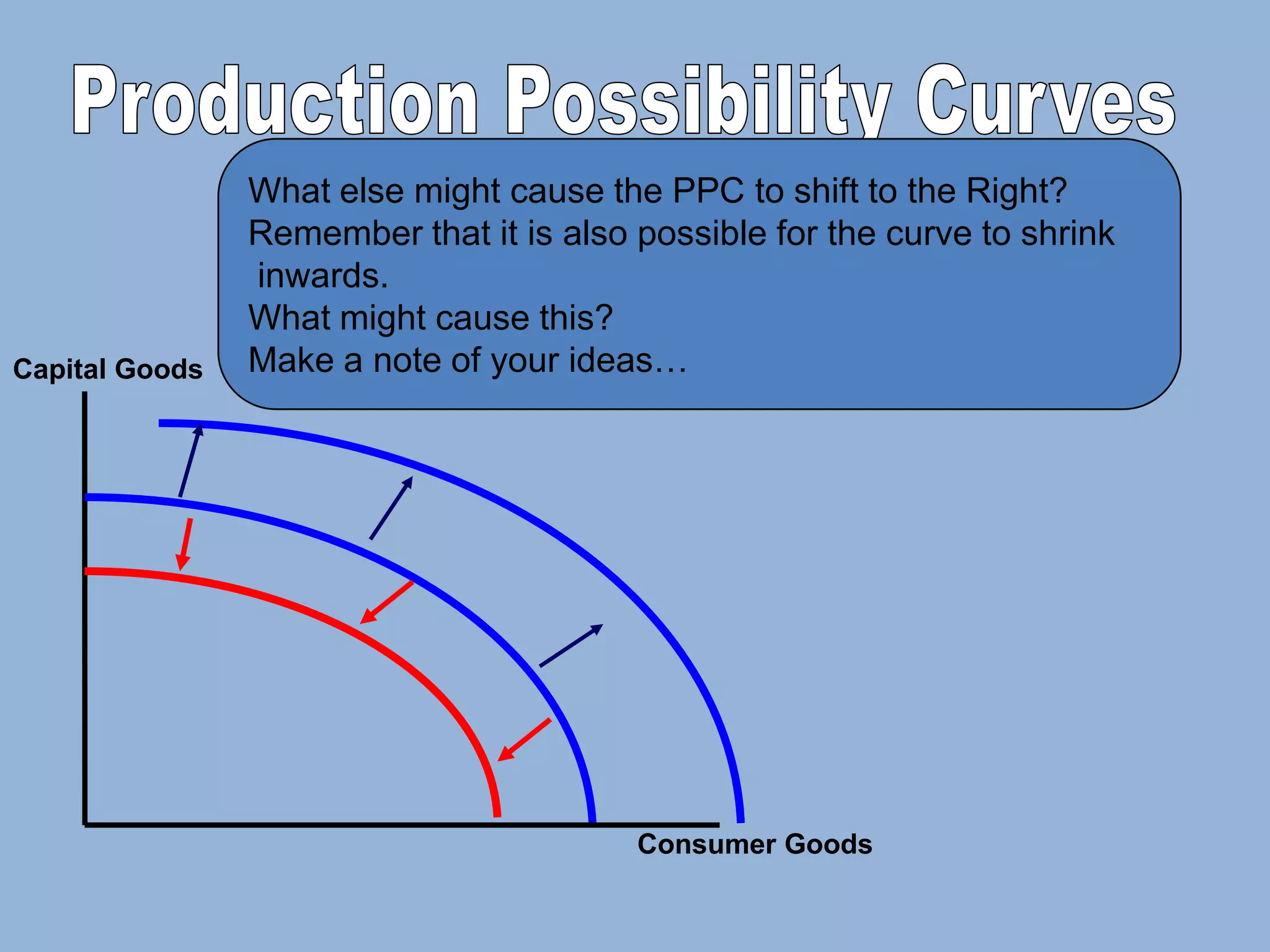
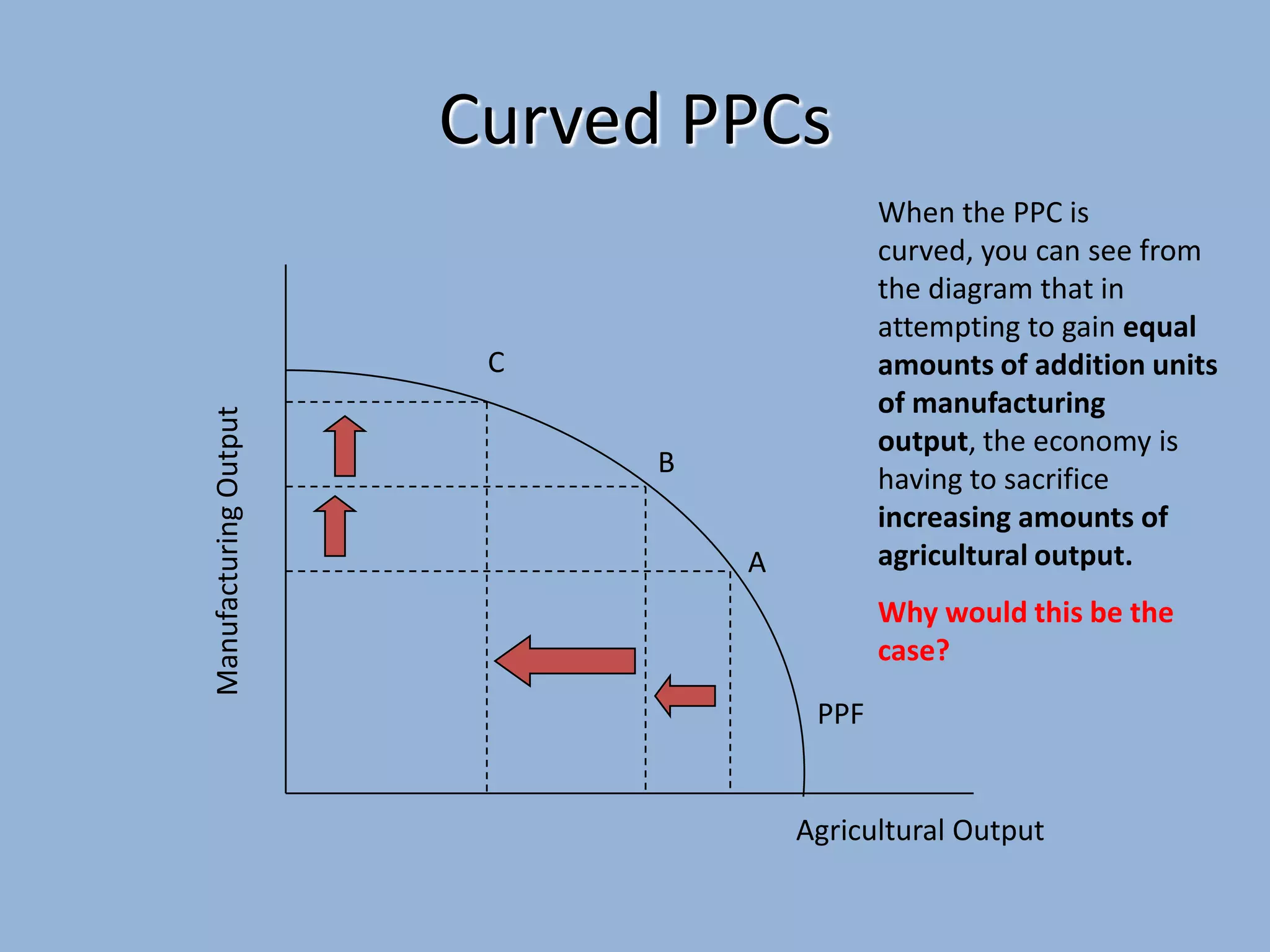
The Production Possibility Curve (PPC) shows the combinations of two goods an economy can produce with its limited resources. It illustrates the core economic problem of scarcity and choice. A PPC demonstrates that an economy must choose between different goods - it can produce more of one good only by reducing production of the other as resources are reallocated between uses. The opportunity cost of choosing one combination over another is the quantity of the forgone good.