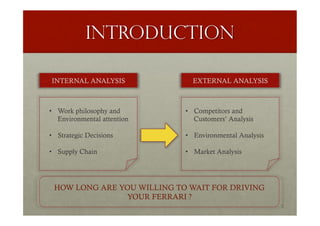
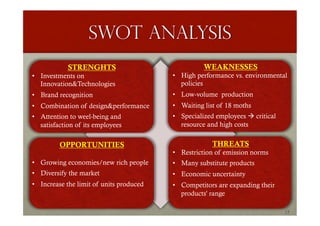
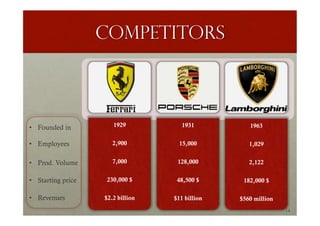
The document provides a comprehensive overview of Ferrari's organization, management, history, and strategic initiatives from 2014 to 2016, highlighting its focus on innovation and sustainability. It details Ferrari's market position, competitive analysis, supply chain strategies, and the impact of environmental policies on operations. Additionally, it identifies strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats through a SWOT analysis, concluding with insights on Ferrari's exclusivity and growth strategies.