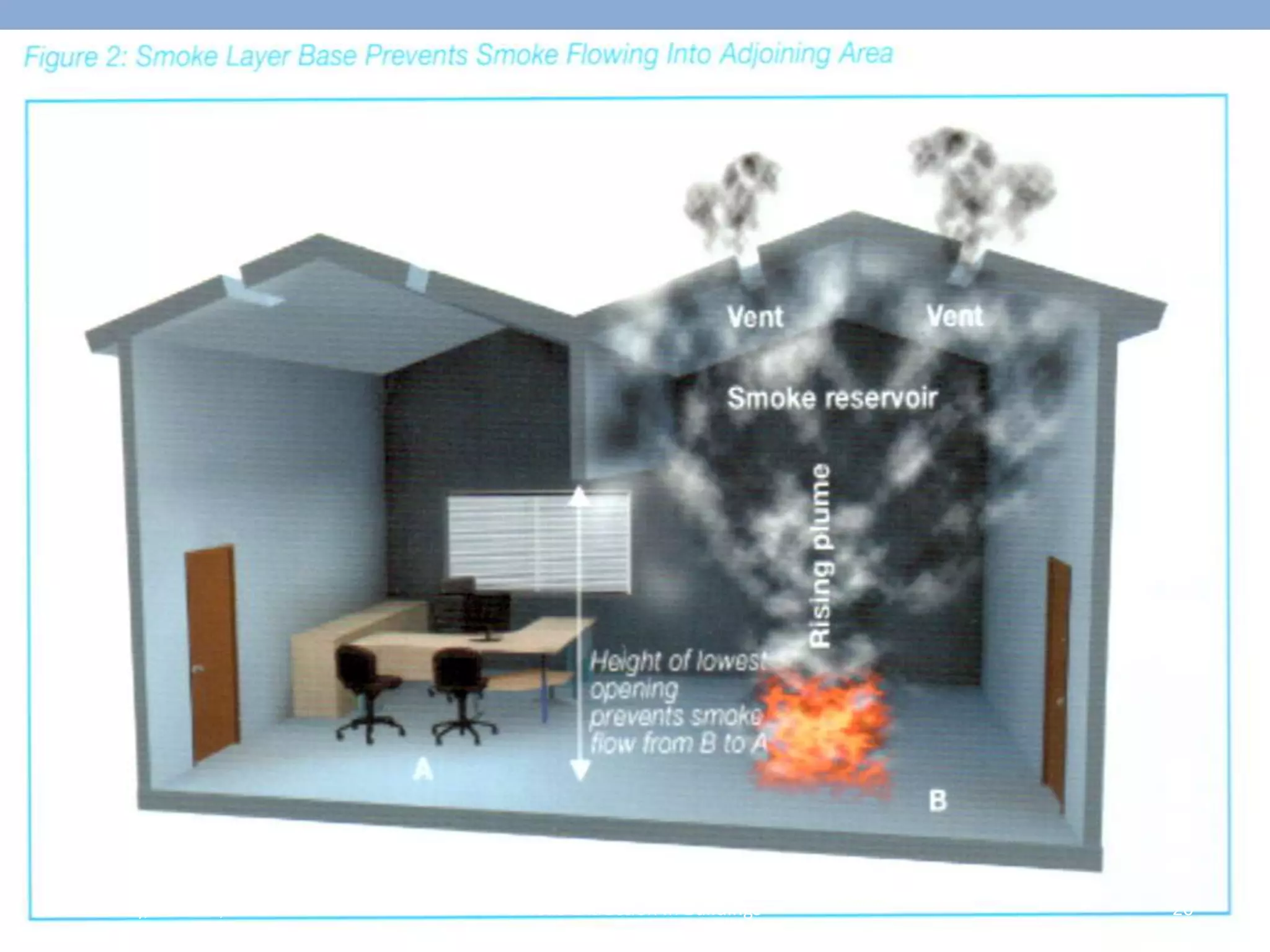
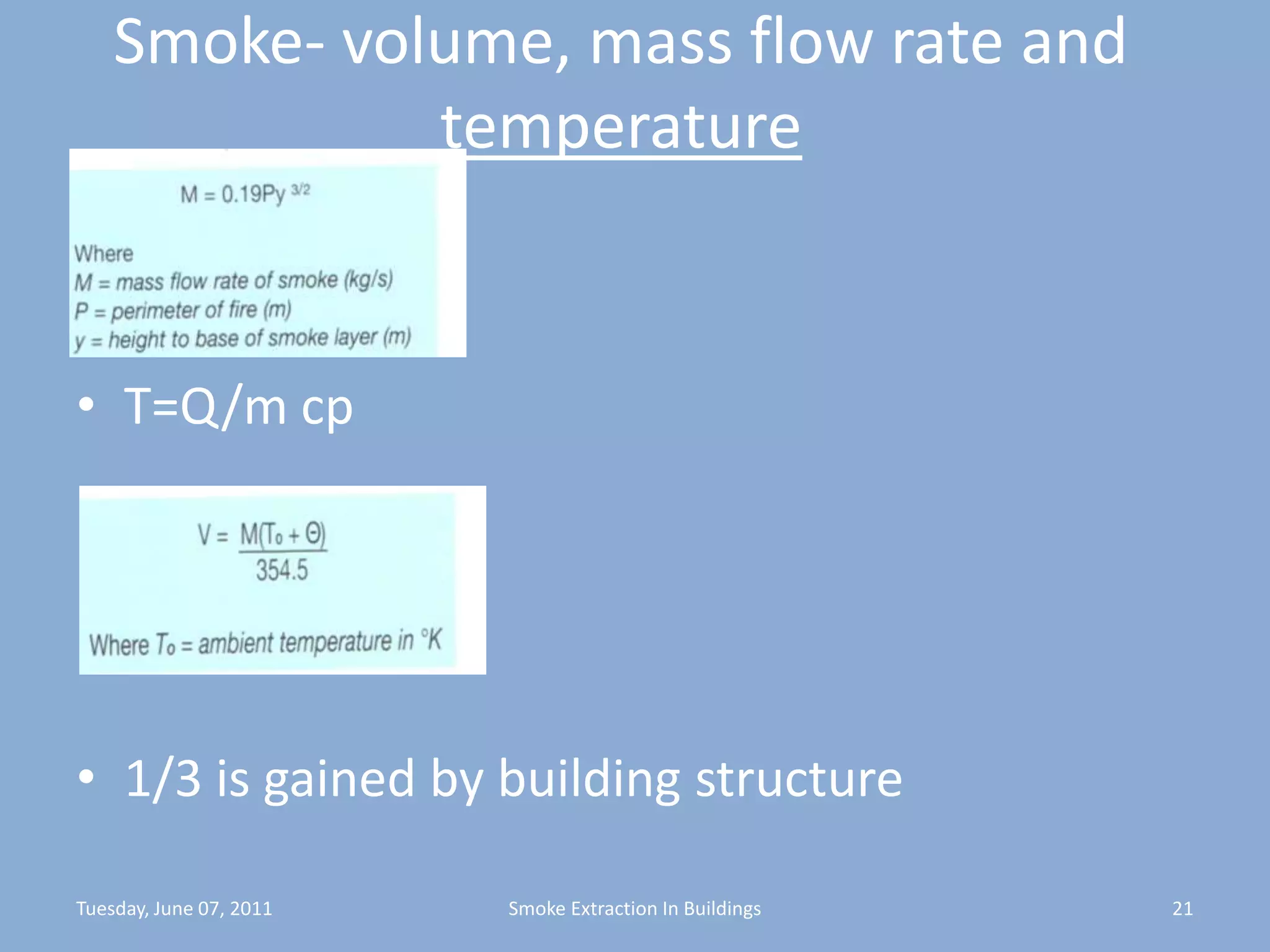
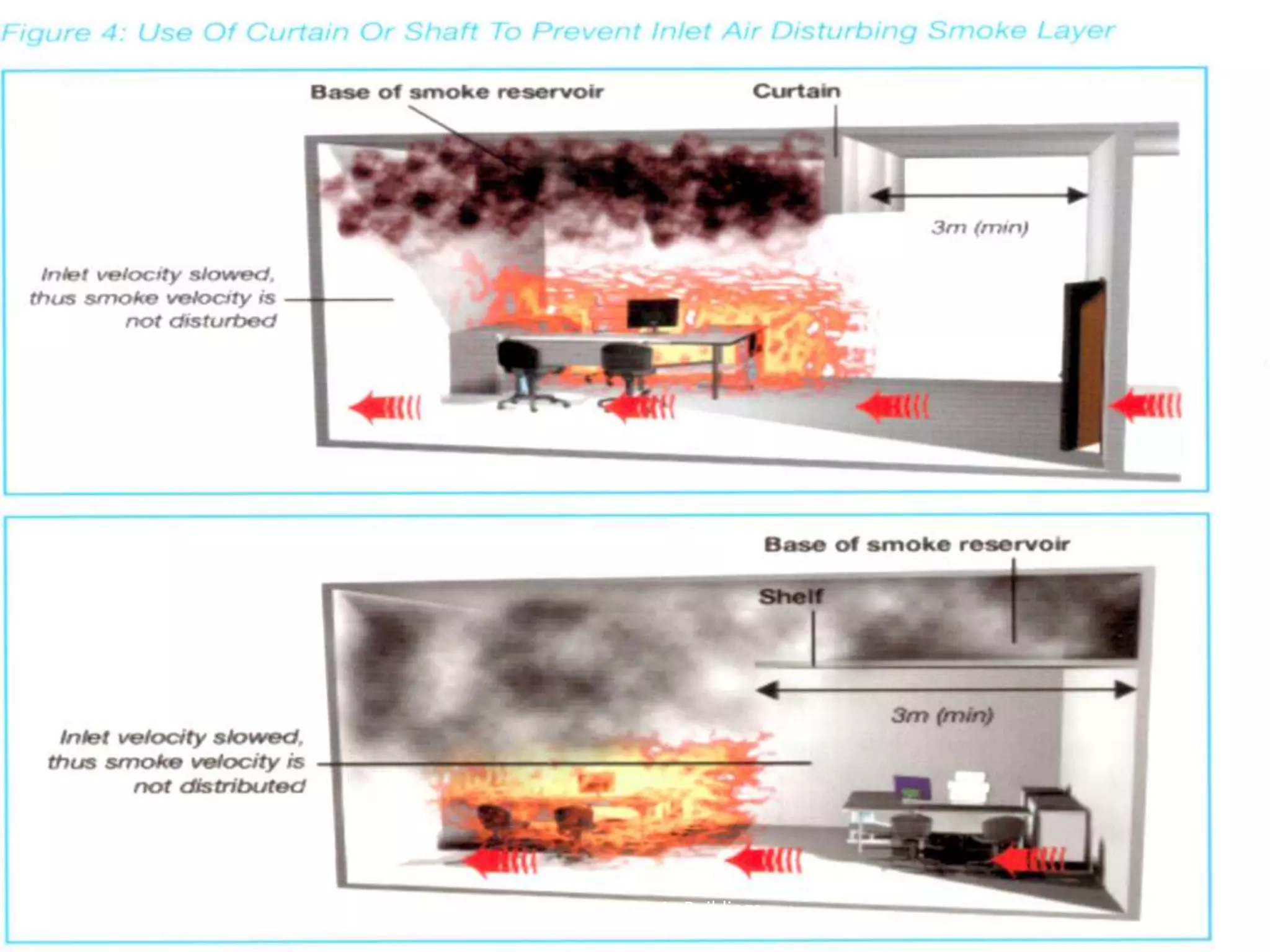
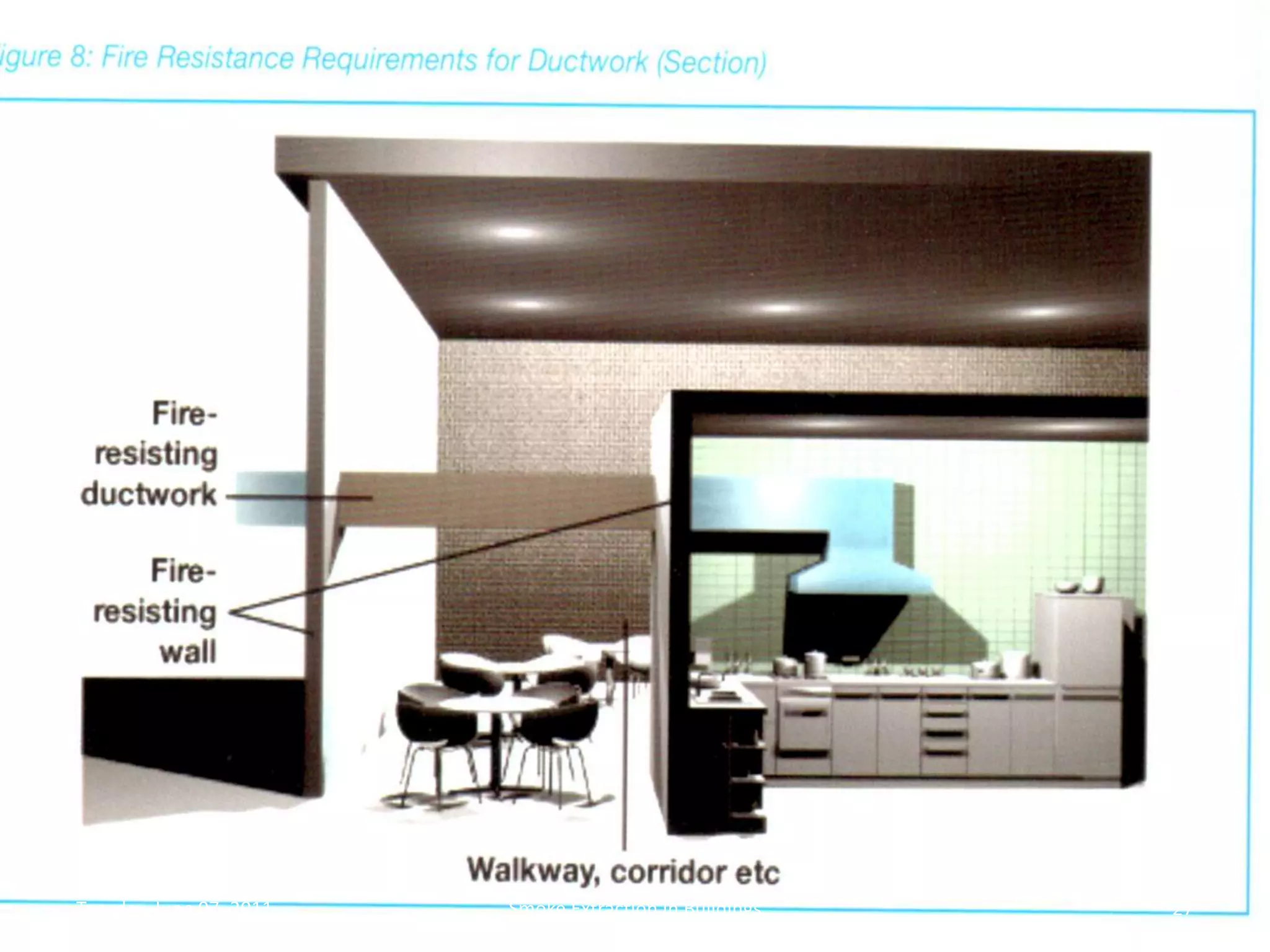
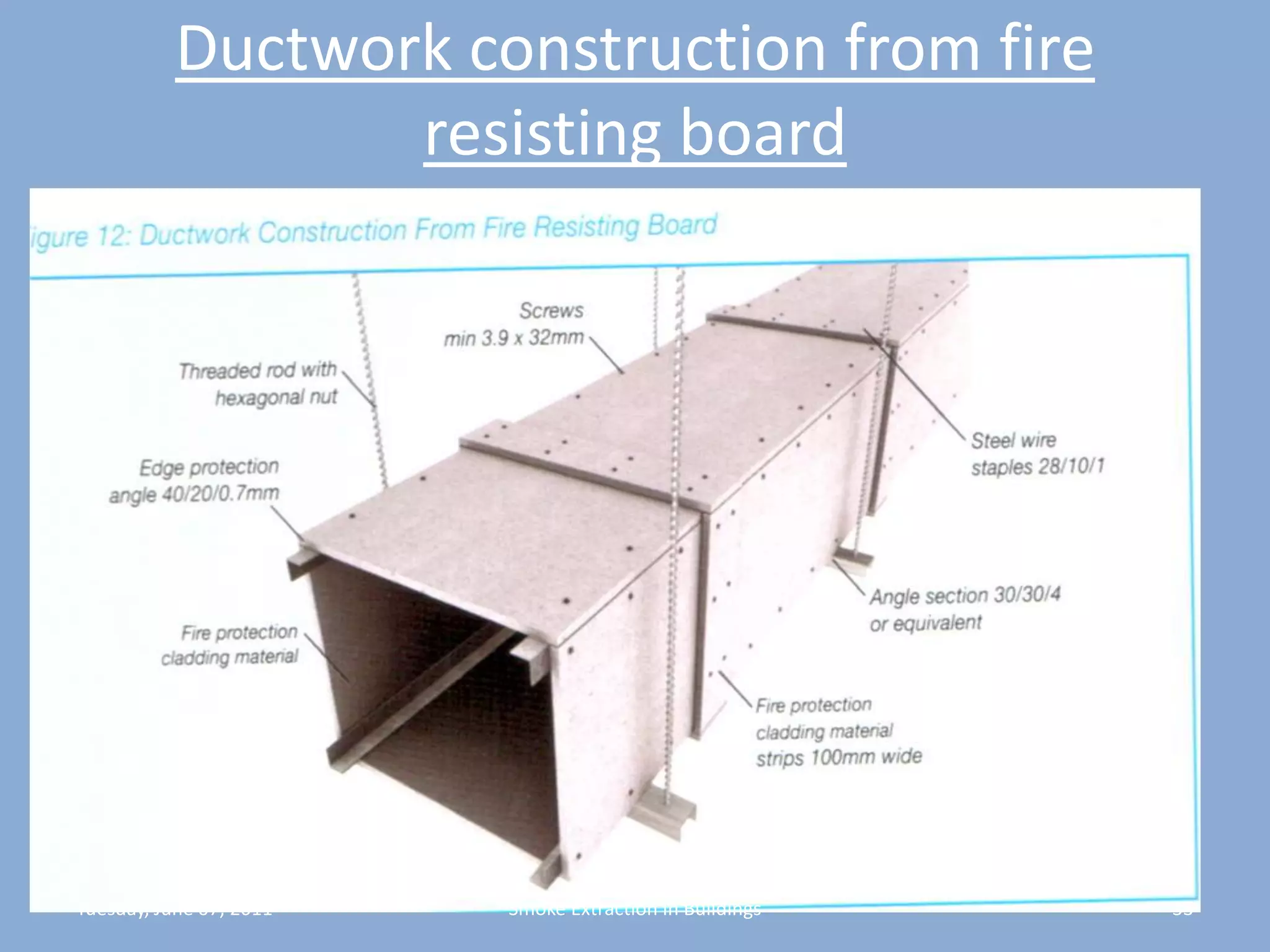
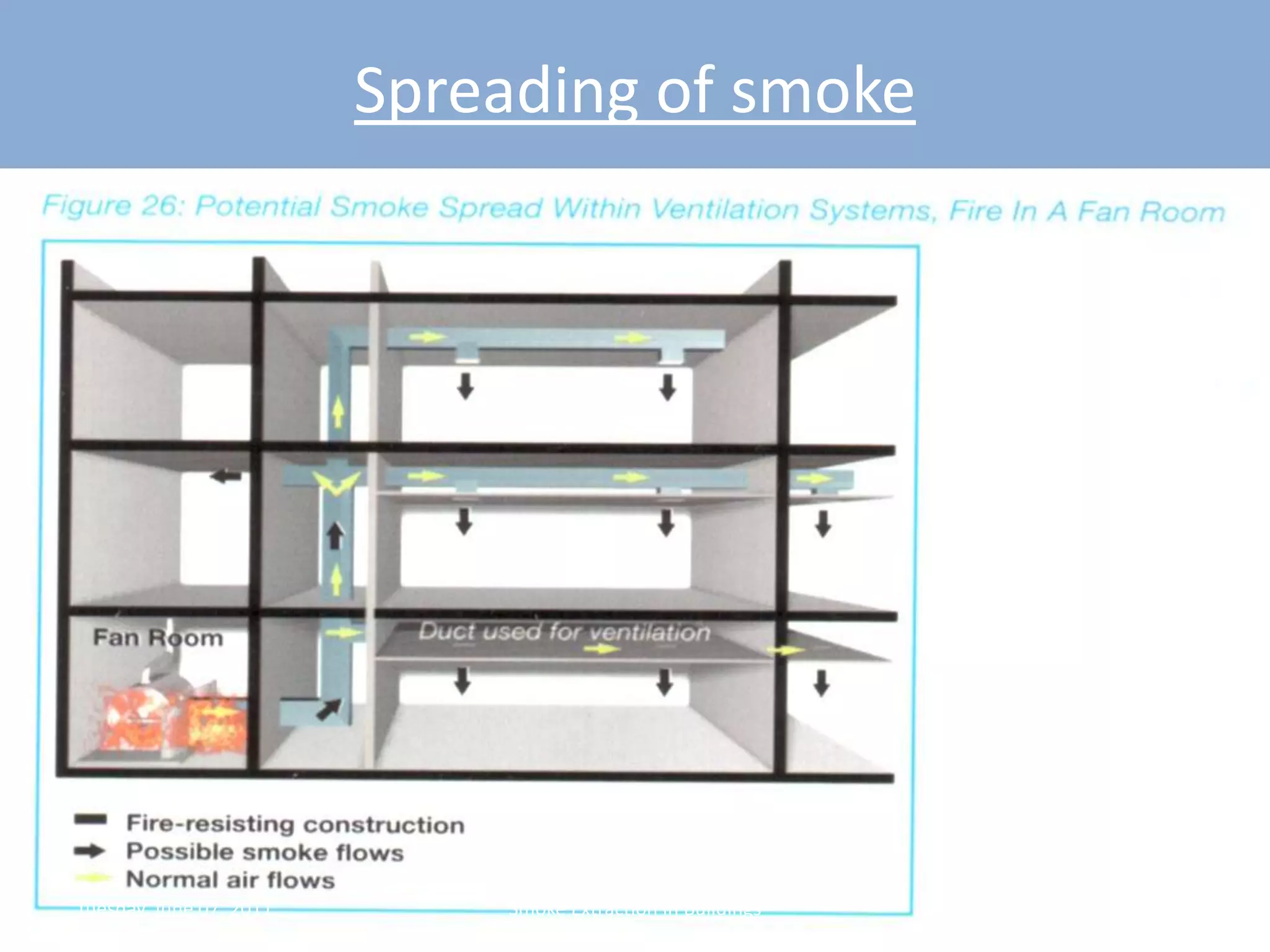
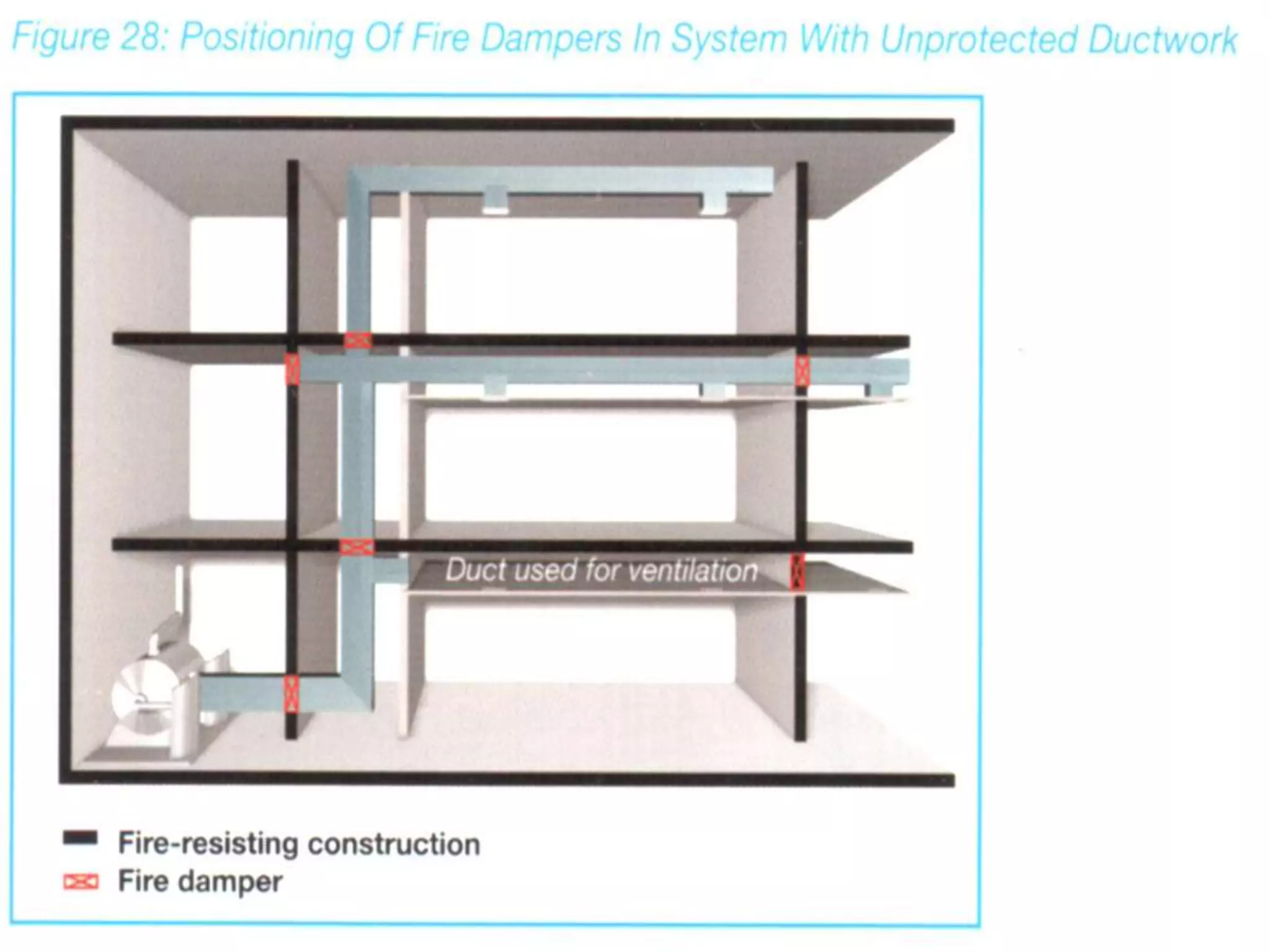
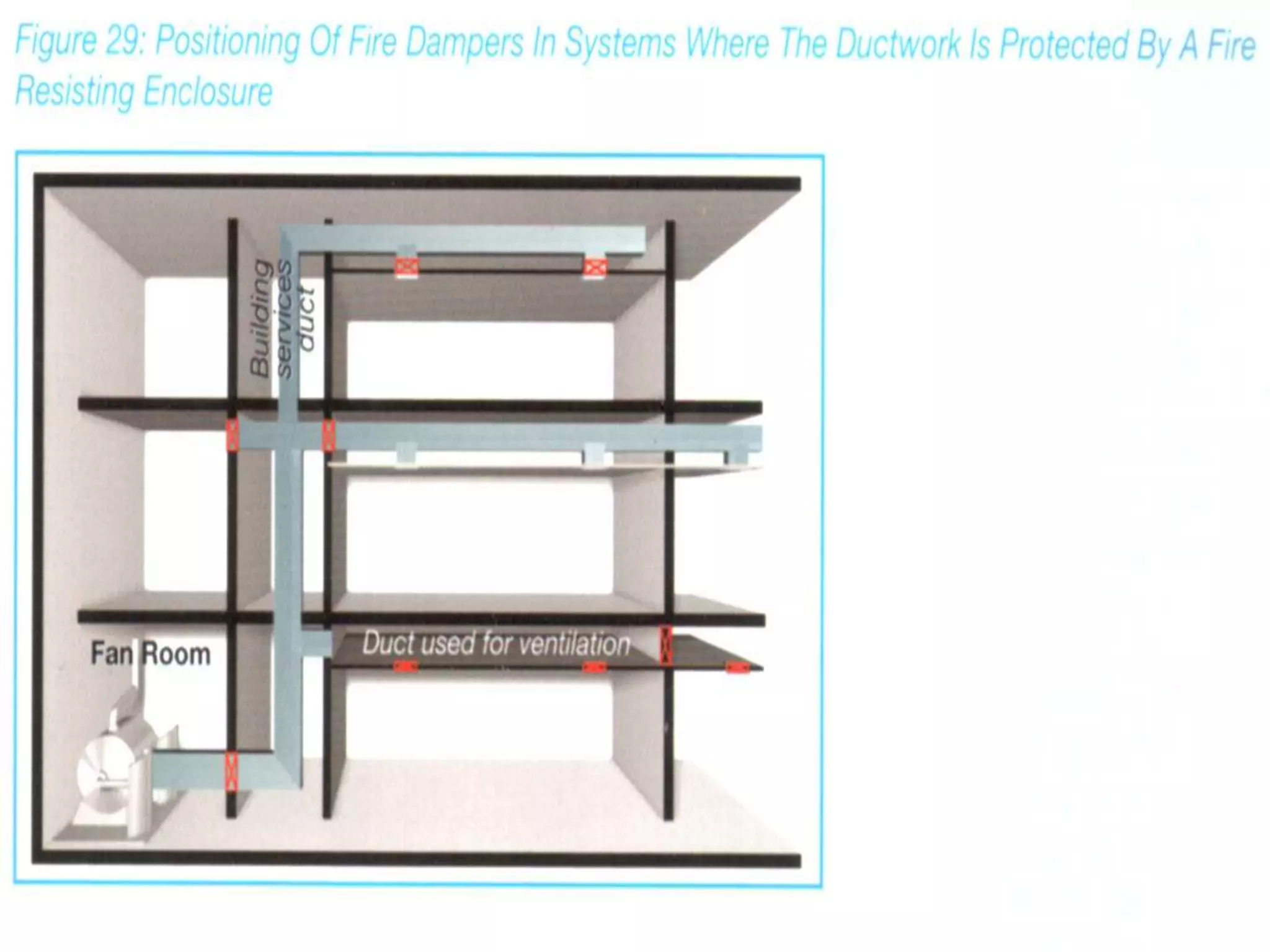
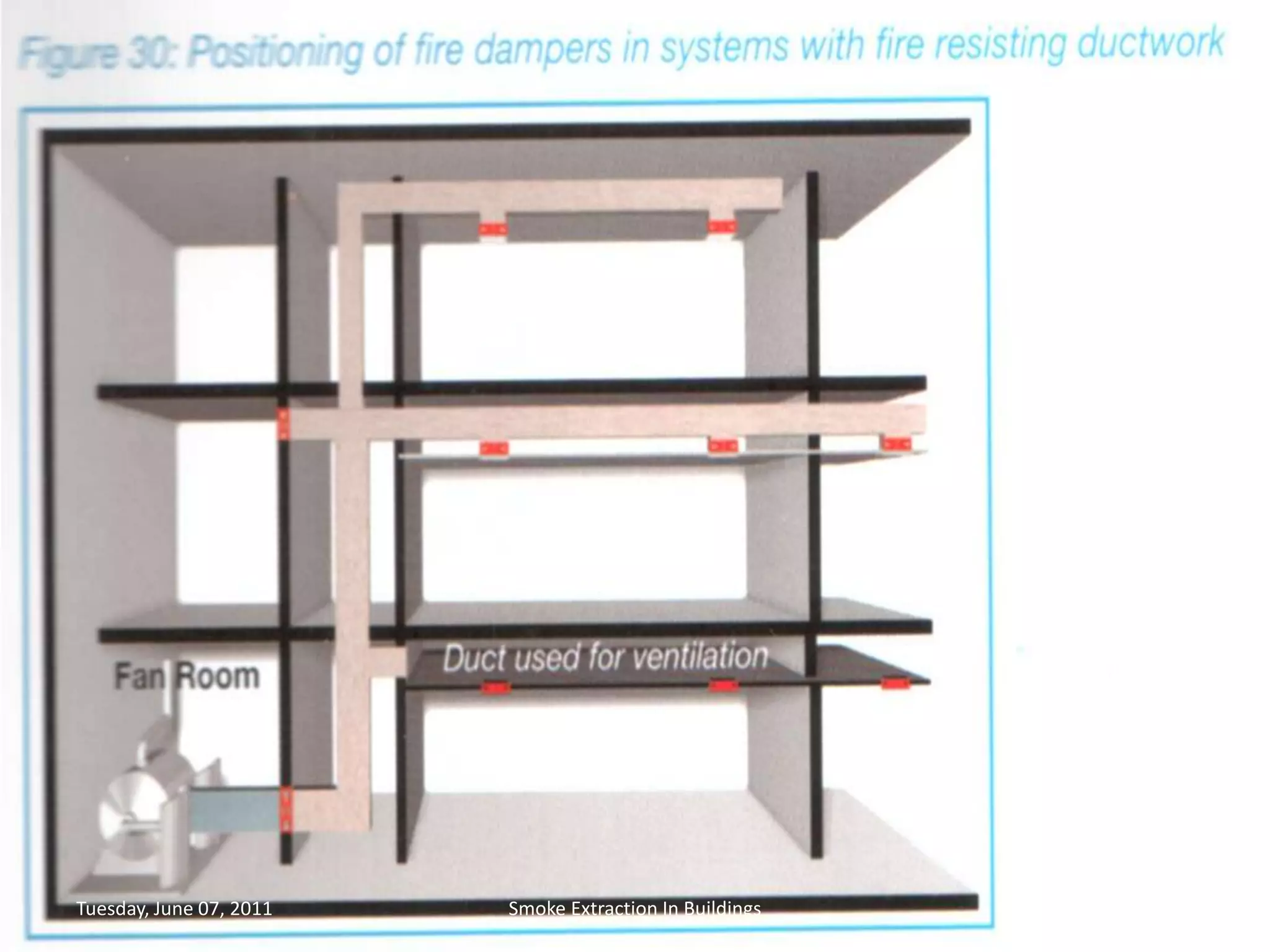
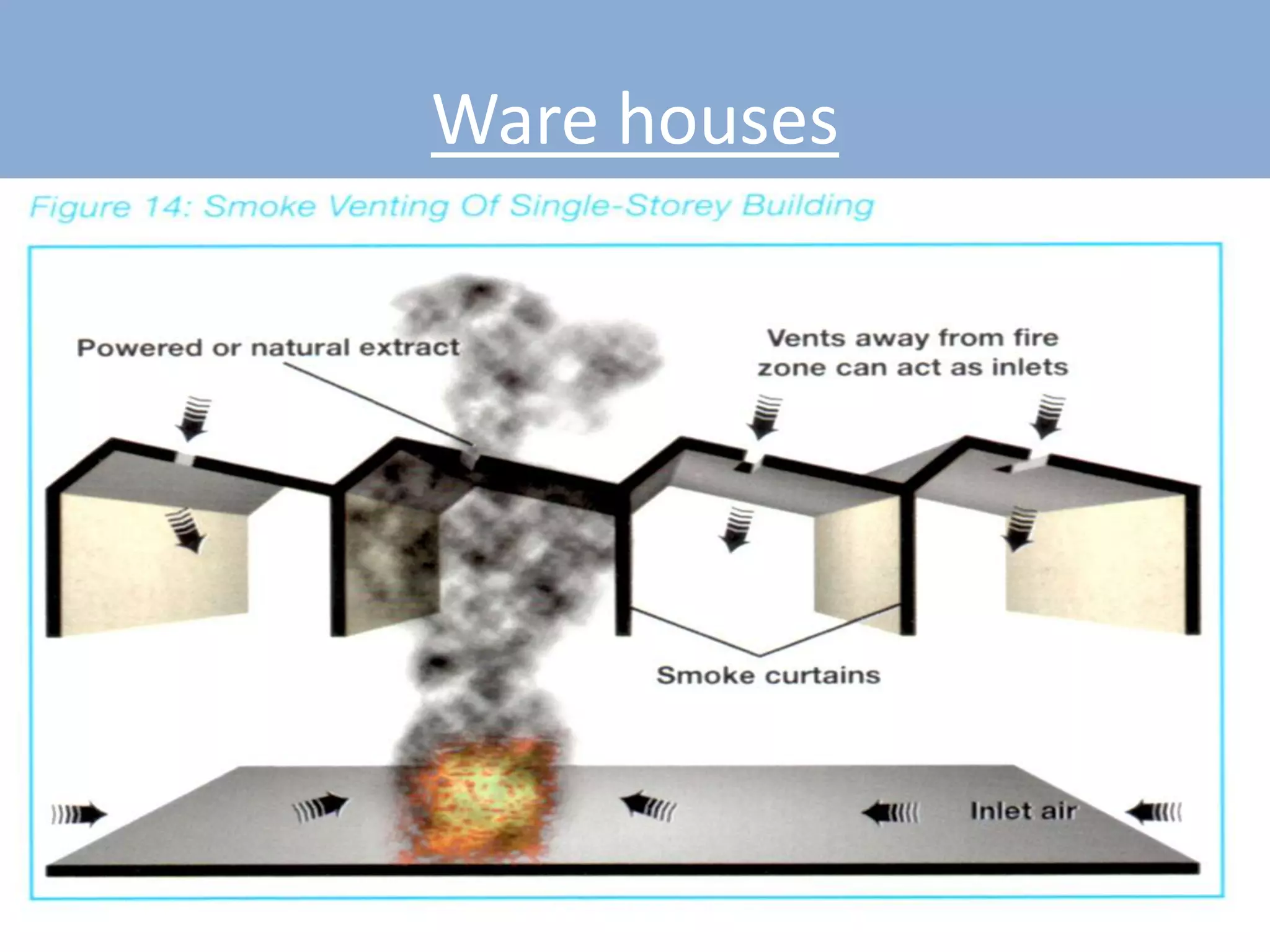
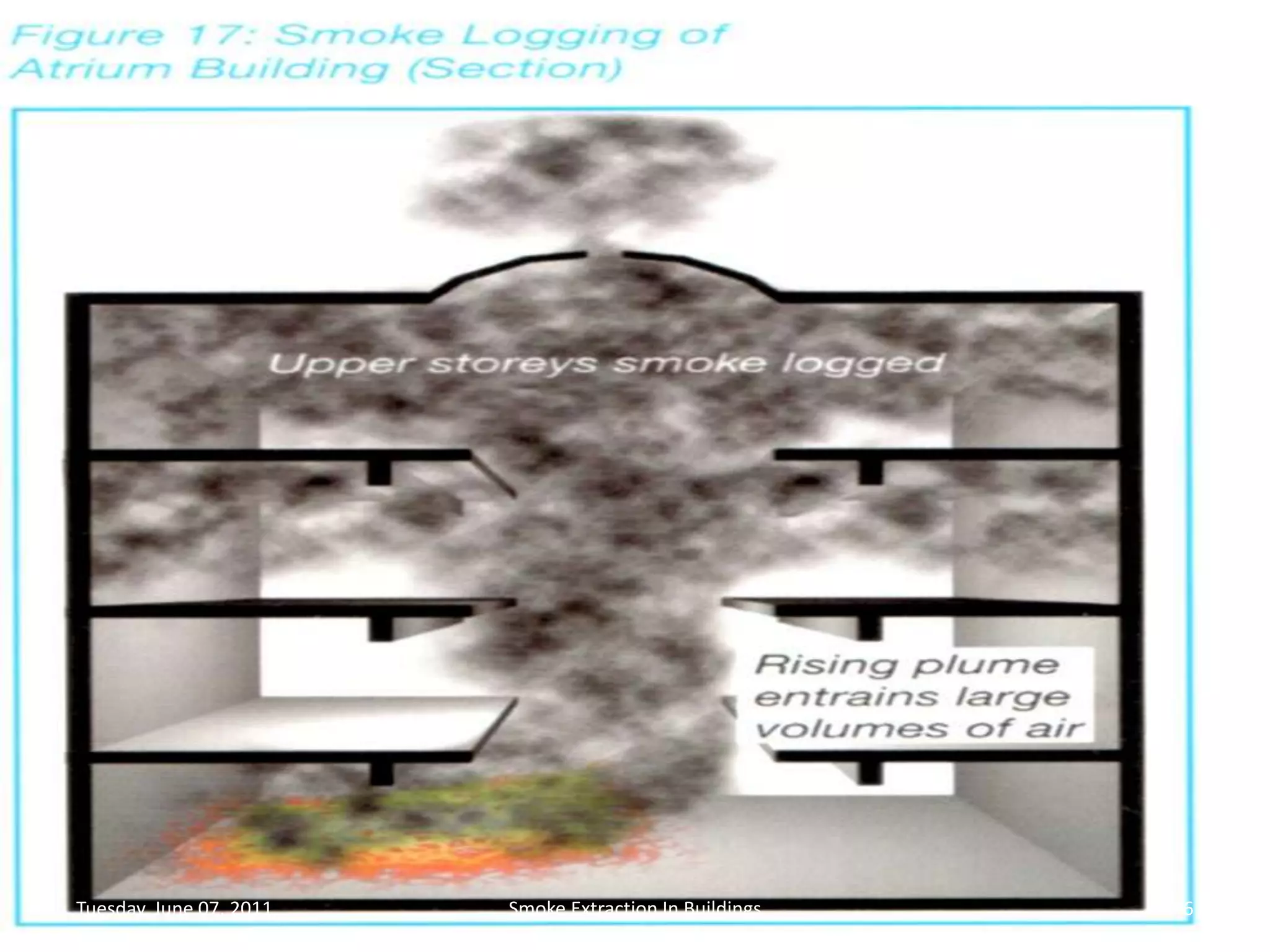
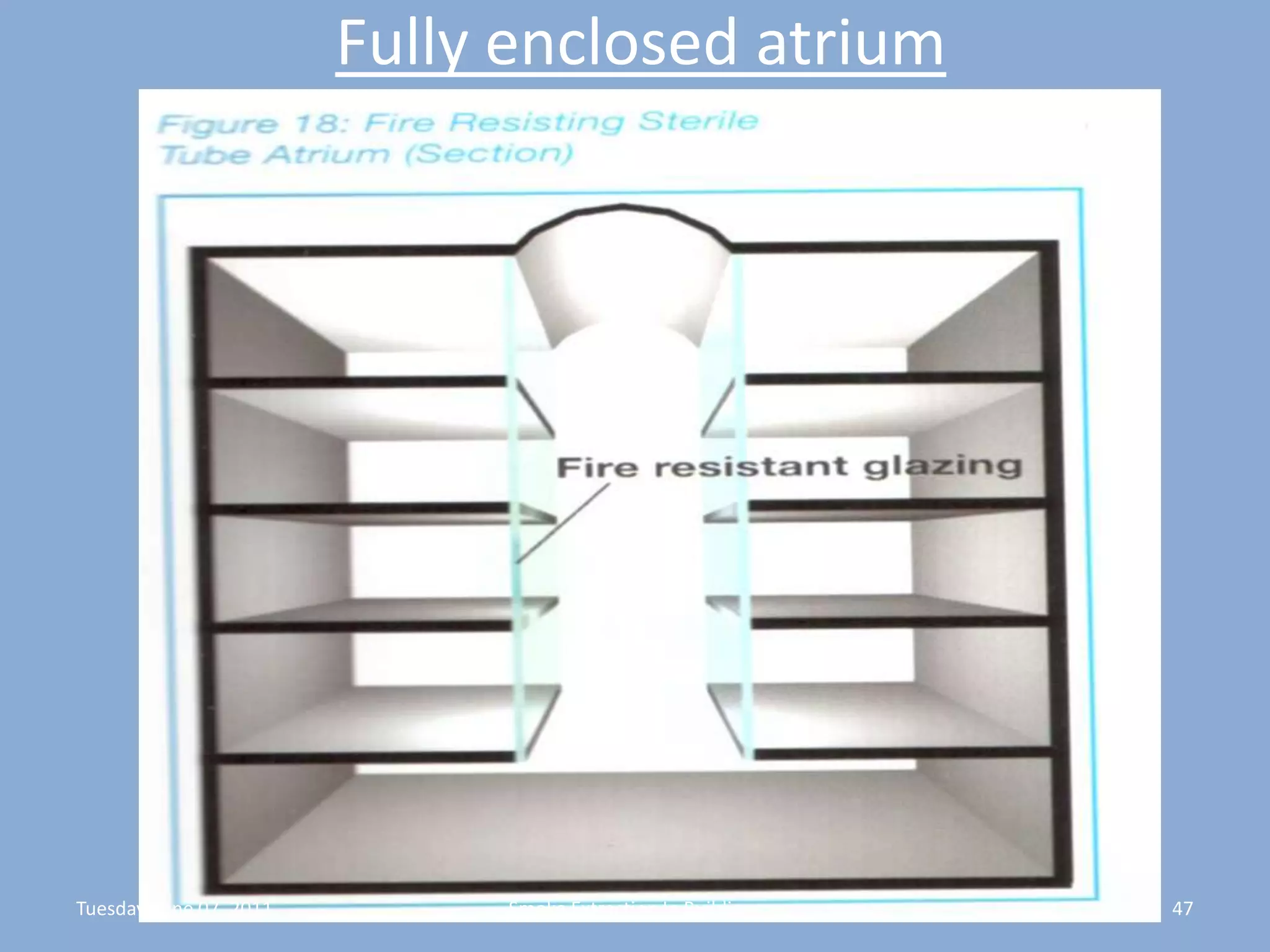
The document discusses smoke extraction in buildings, including key factors in smoke extraction design such as design fire size, smoke layer depth, smoke reservoirs, minimum number of extract points, inlet air, ductwork, and performance criteria for fire resisting ductwork. Effective smoke extraction requires considering smoke pathways, production, and movement, and extraction methods vary depending on building type, such as for multi-story offices, warehouses, underground parking, atriums, and shopping malls. Following approved agency guidance can significantly reduce fire and smoke threats.