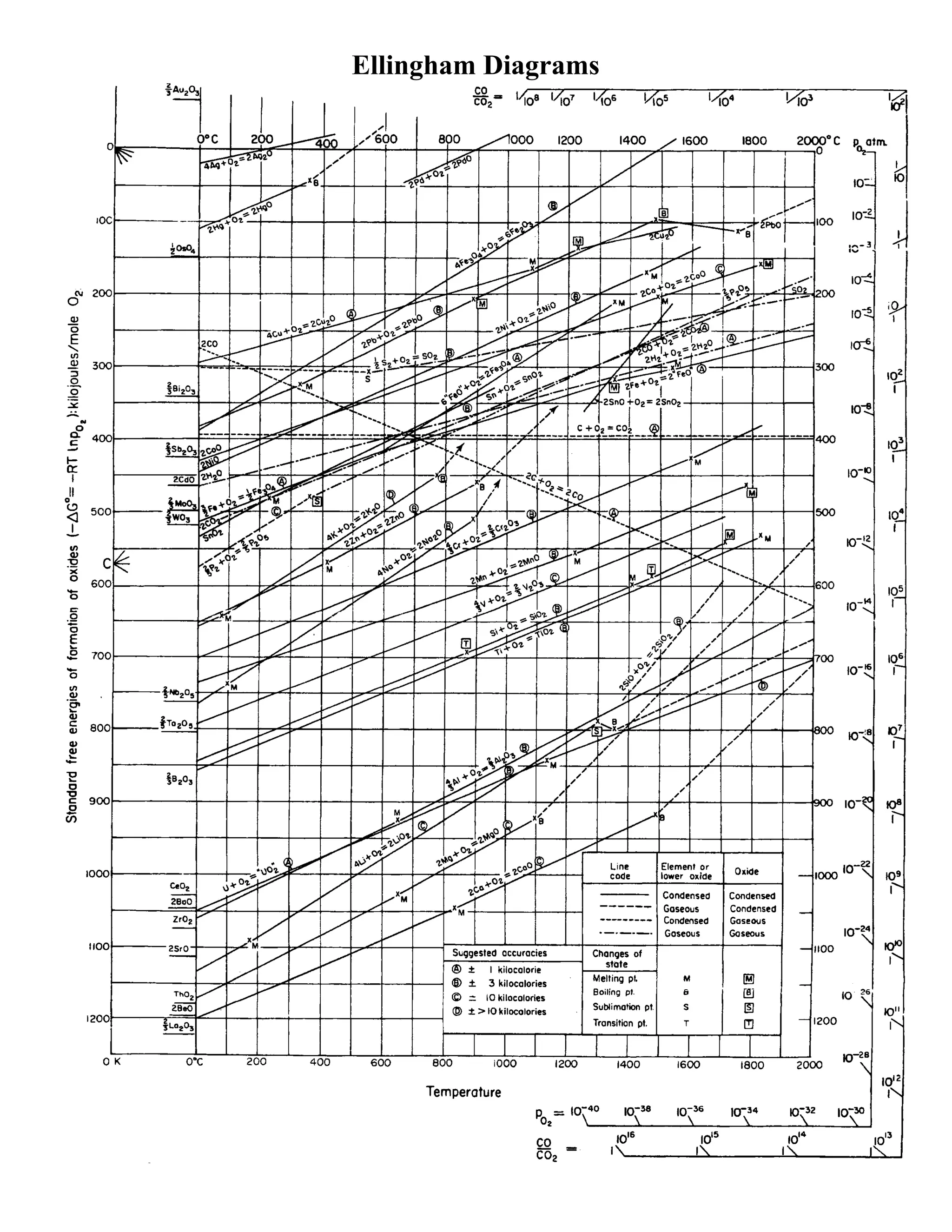
An Ellingham diagram plots the change in Gibbs free energy (ΔG) versus temperature for reactions where metals form oxides. It shows the relative stability of metal oxides through their position - oxides higher on the diagram are more easily reduced. The diagram is used to determine:
1. The ease of reducing a metal oxide to the metal based on its position relative to other metal oxides.
2. The equilibrium partial pressure of oxygen that can exist with a metal oxide at a given temperature.
3. The minimum ratio of carbon monoxide to carbon dioxide needed to reduce an oxide at a temperature.