1) A hospital provides specialized health care through staff and equipment divided into operational areas.
2) Functional planning norms divide hospitals into categories based on bed count, with guidelines for treatment rooms, wards, and other spaces.
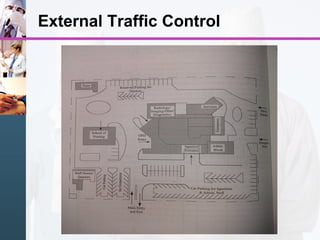
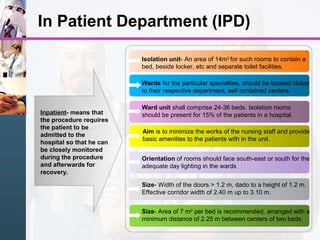
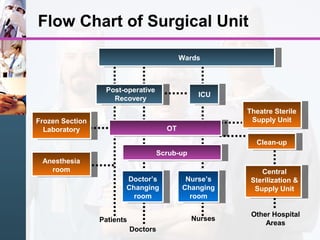
3) Key areas include outpatient departments, inpatient wards, emergency, radiology, operating theaters, and intensive care, each with their own space and connectivity needs to support patient care.