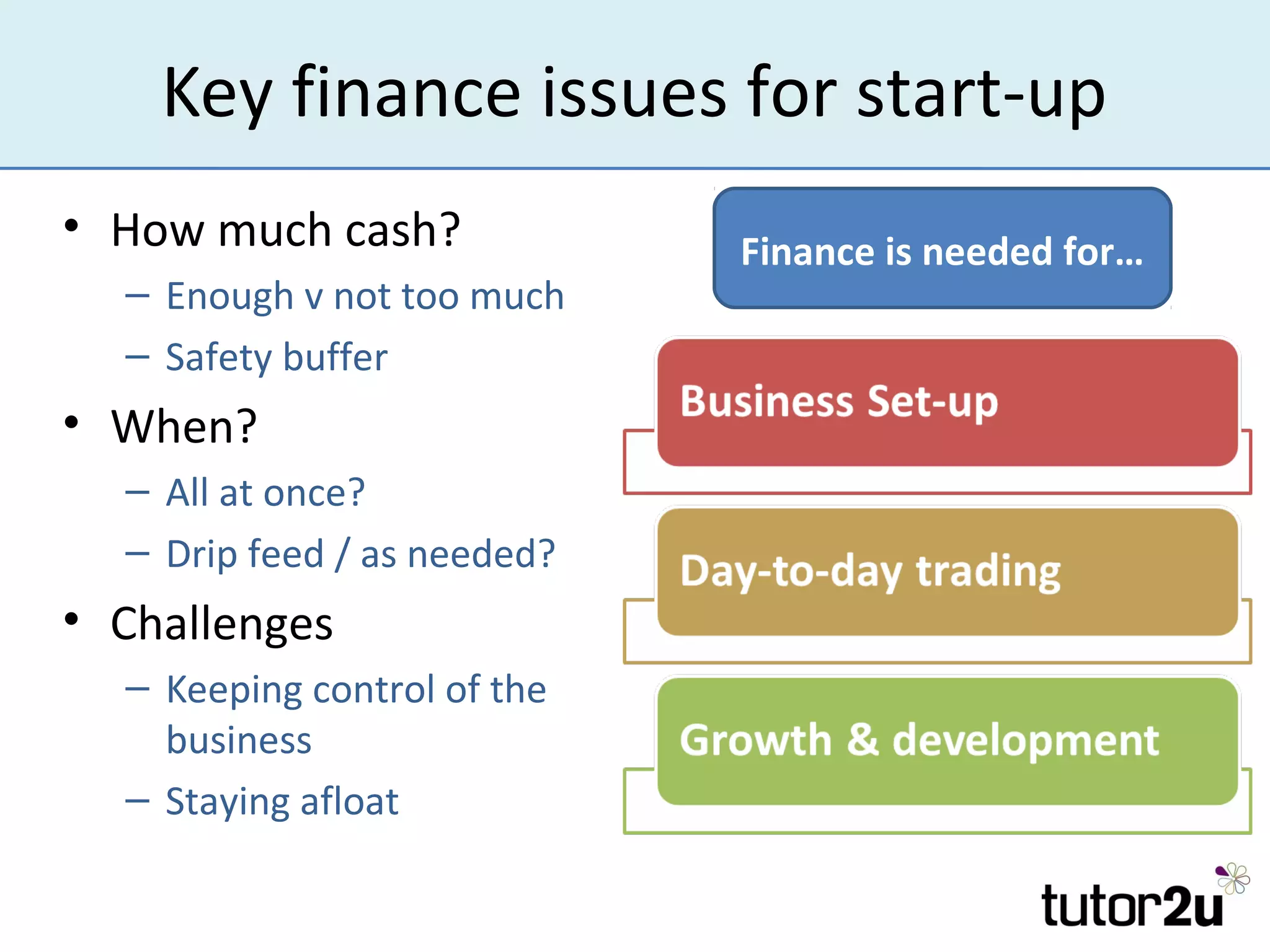
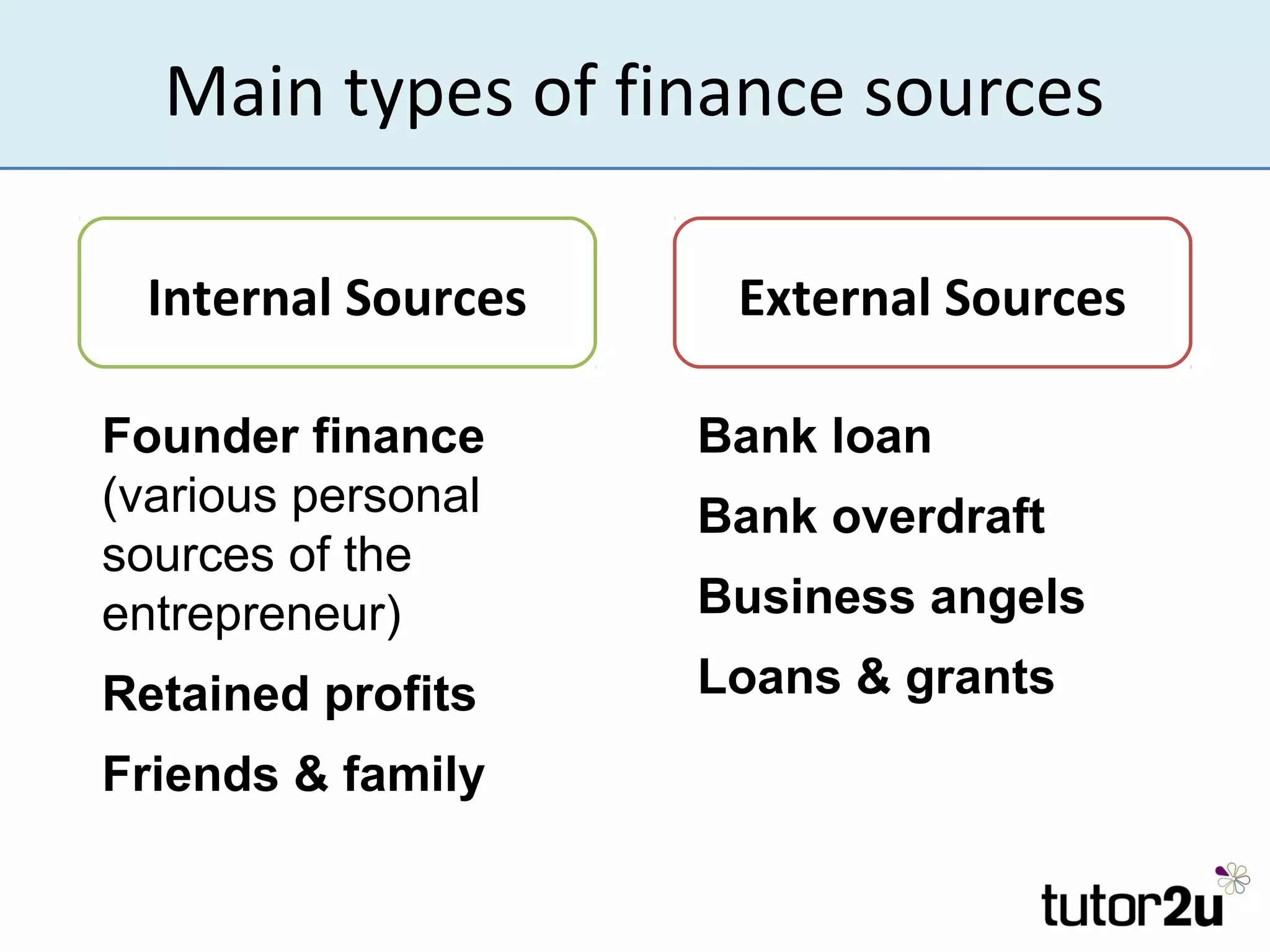
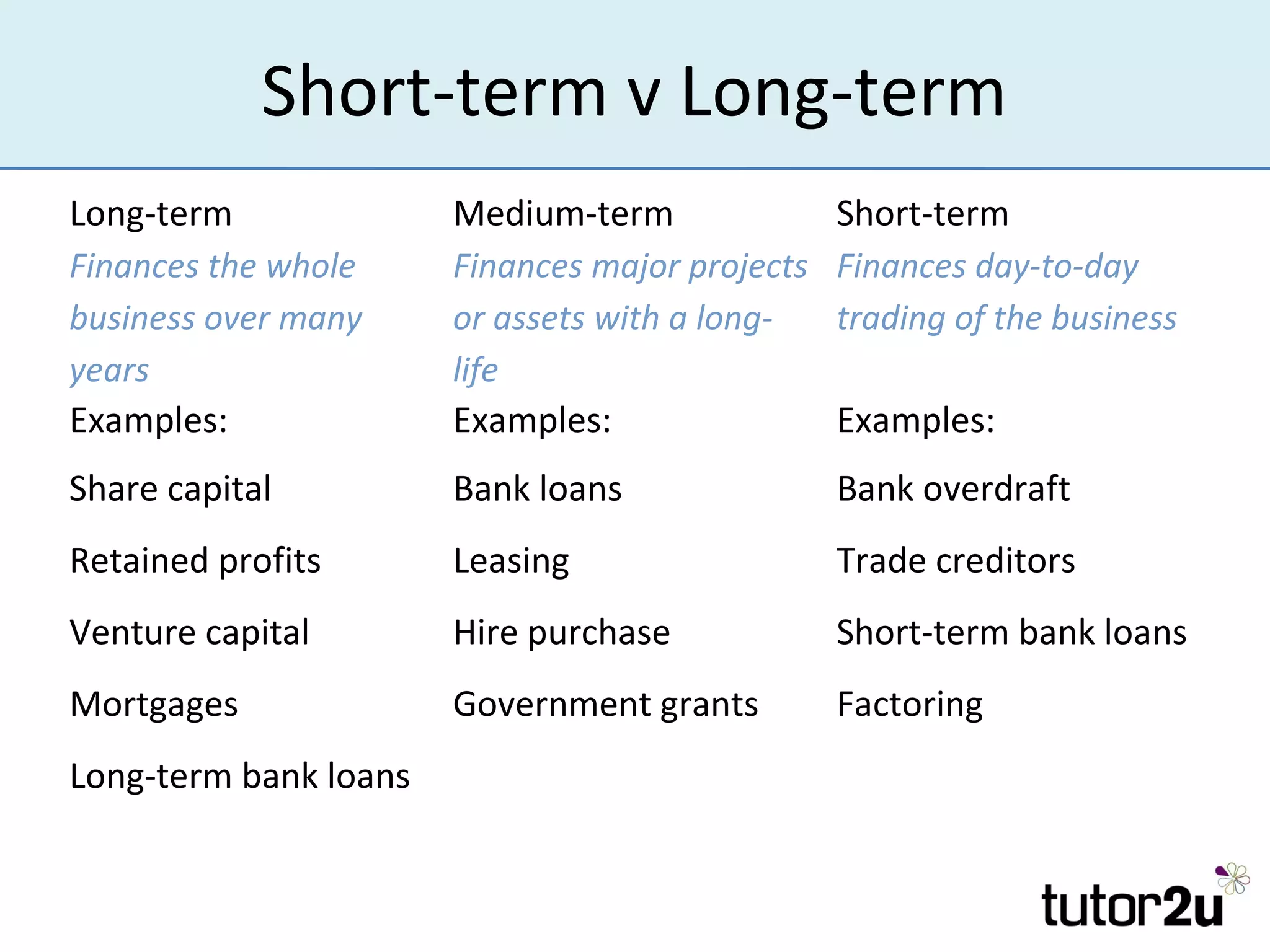
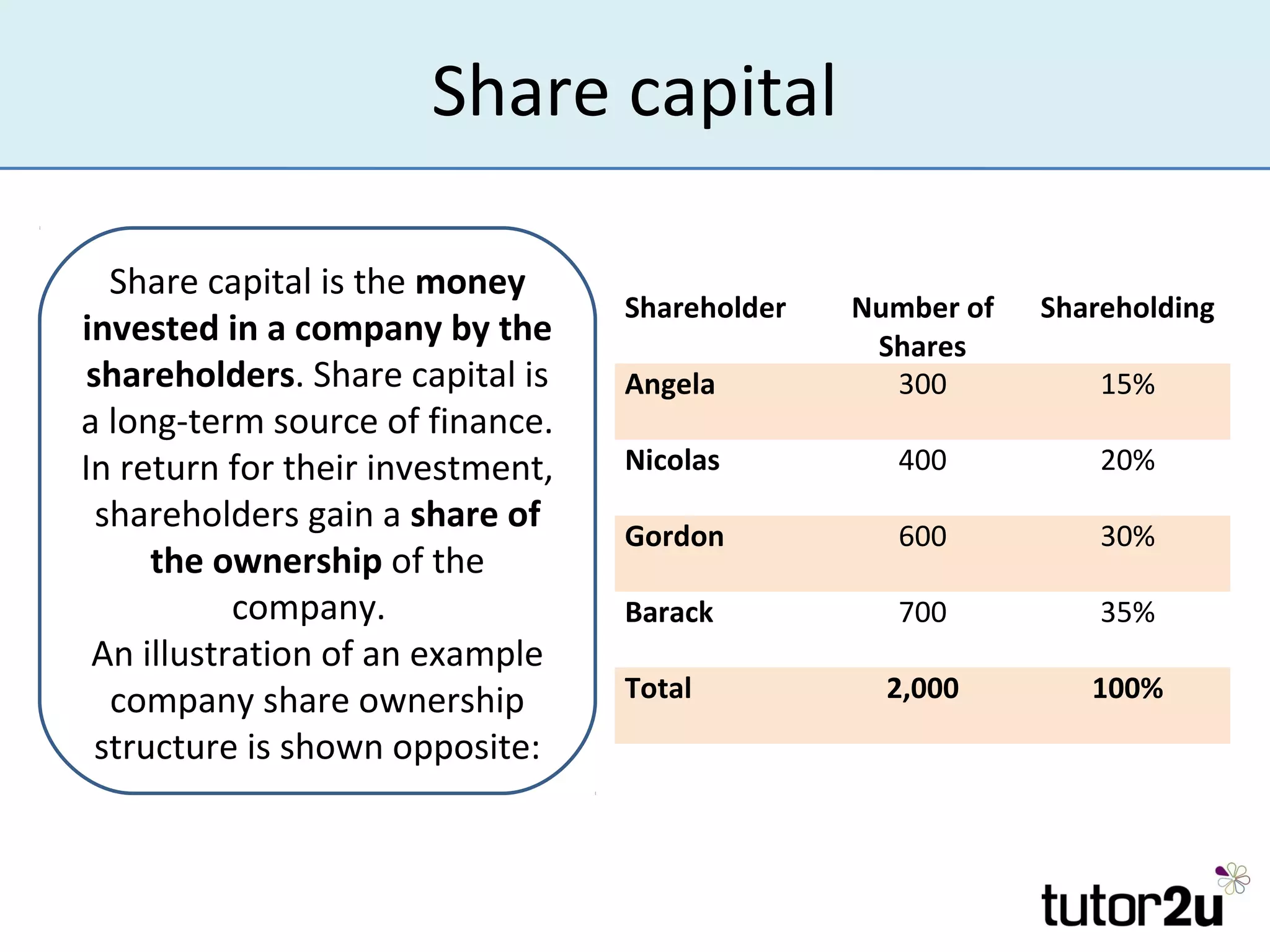
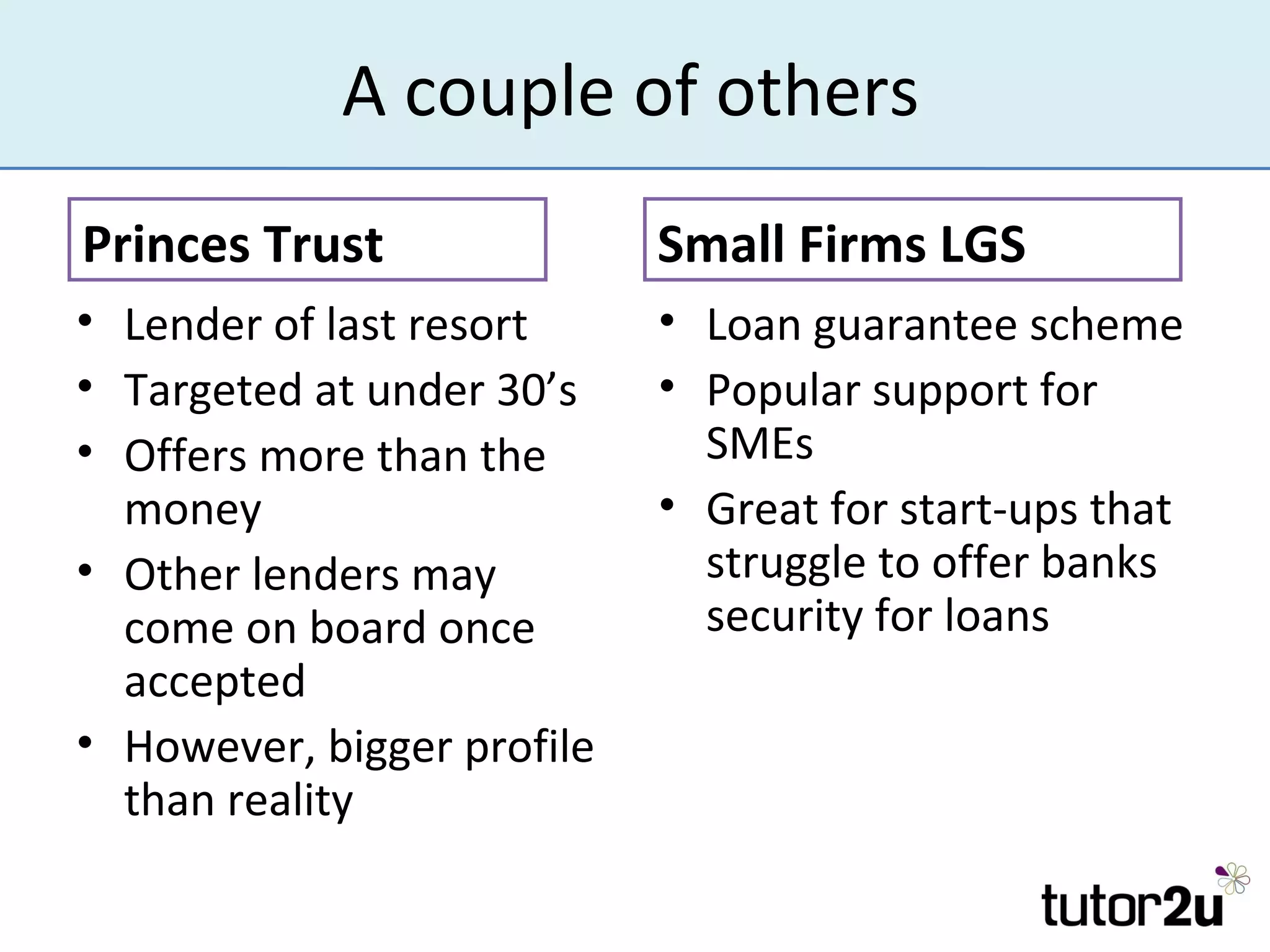
The document outlines the importance of finance for start-ups, emphasizing various internal and external sources, including personal investments, bank loans, and angel investors. It discusses key considerations such as the amount and timing of finance needed, control over the business, and securing investment. Additionally, it highlights challenges faced by entrepreneurs when raising funds and the role of retained profits and trade credit in managing cash flow.