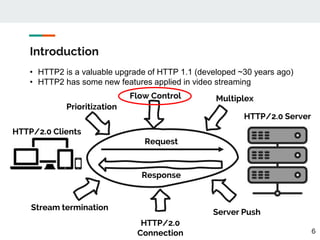
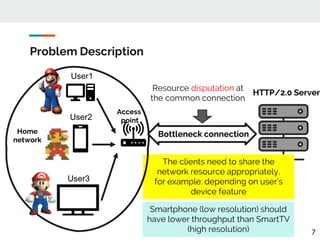
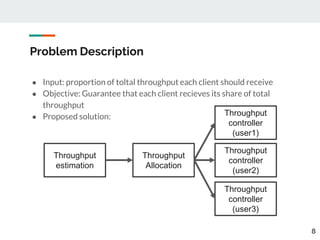
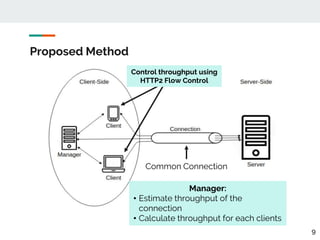
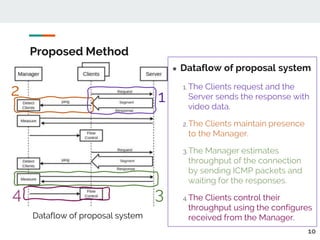
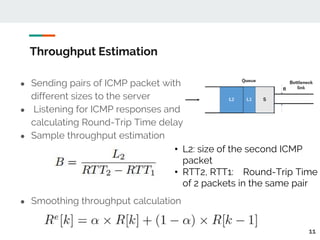
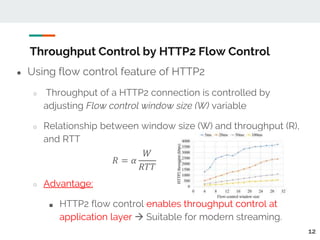
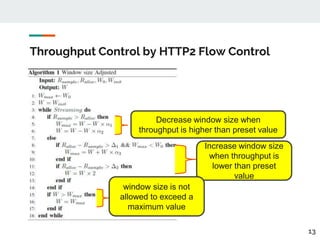
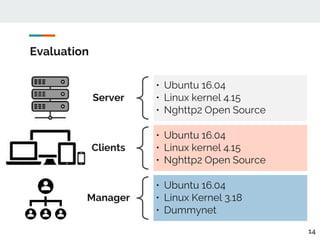
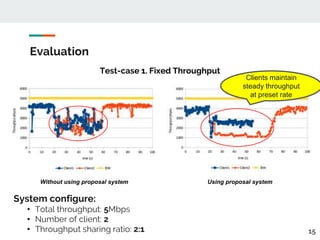
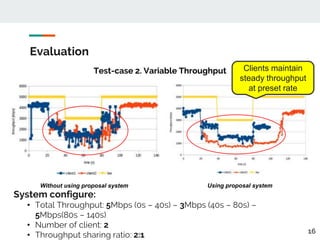
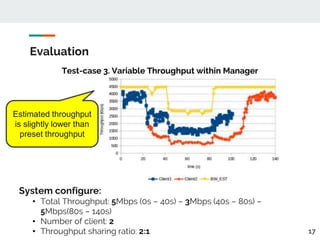
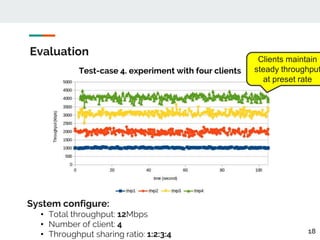
This document proposes a method for controlling throughput for multiple video streaming clients sharing a common network connection using HTTP/2 flow control. It consists of a throughput estimation scheme using ICMP packets and a throughput controller that adjusts the HTTP/2 flow control window size for each client based on their allocated share and the estimated connection throughput. Evaluation results show the method can effectively maintain each client's throughput at their preset ratios. Future work includes improving estimation accuracy and extending the solution without a separate manager component.