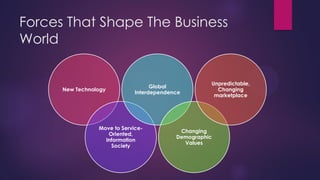
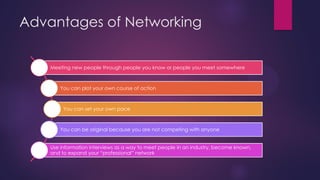
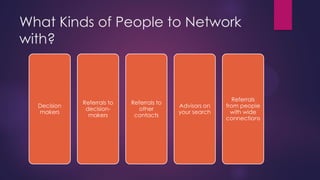
This document discusses trends in the changing labor market including the shift to non-standard employment like part-time work, the need for lifelong learning and skills upgrading, and the transition from a goods-producing to a service-based economy. It also identifies important soft skills for navigating this new environment like adaptability, flexibility, self-promotion and networking. Finally, it outlines the role of career development professionals in providing services like assessment, career counseling, facilitating learning and building community partnerships.