The Anatomy and Physiology of Vision and Olfaction
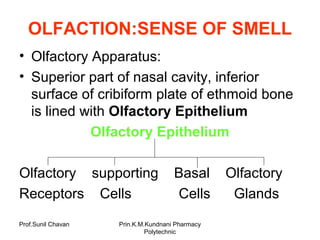
- 1. Prof.Sunil Chavan Prin.K.M.Kundnani Pharmacy Polytechnic OLFACTION:SENSE OF SMELL • Olfactory Apparatus: • Superior part of nasal cavity, inferior surface of cribiform plate of ethmoid bone is lined with Olfactory Epithelium Olfactory Epithelium Olfactory supporting Basal Olfactory Receptors Cells Cells Glands
- 2. Prof.Sunil Chavan Prin.K.M.Kundnani Pharmacy Polytechnic
- 3. Prof.Sunil Chavan Prin.K.M.Kundnani Pharmacy Polytechnic Olfactory Receptors: • These are first order neurons of Olfactory Pathway • Each Olfactory receptor is a bipolar neuron • Knob shaped dendrites have olfactory hairs, cilia, these causes transduction. • Axons project through cribiform plate & end in Olfactory bulb • Olfactory receptors respond to chemical stimulation of an odorant molecule by producing nerve impulse.
- 4. Prof.Sunil Chavan Prin.K.M.Kundnani Pharmacy Polytechnic
- 5. Prof.Sunil Chavan Prin.K.M.Kundnani Pharmacy Polytechnic Supporting Cells: • These are columnar epithelium cells of mucus lining of nose. • Provide physical support, nourishment & electrical insulation for olfactory receptors. Basal Cells: • These are stem cells, located between bases of supporting cells. • These continually undergo cell division to produce new olfactory receptors.
- 6. Prof.Sunil Chavan Prin.K.M.Kundnani Pharmacy Polytechnic Olfactory Gland (Bowman’s): • These are present within connective tissue that support olfactory epithelium. • These produce mucus that is carried to surface to epithelium. • Secretion moisten surface & dissolves odorants, so that transduction can occur.
- 7. Prof.Sunil Chavan Prin.K.M.Kundnani Pharmacy Polytechnic Physiology of Olfaction Odorant molecule binds to olfactory hair It causes transduction Propagation of impulse along axon of olfactory receptor In some cases odorant binds to G-Protein in Plasma membrane of olfactory receptor activates enzyme adenylate cyclase Production of cAMP Influx of Na+ Generation of impulse & propagation of impulse
- 8. Prof.Sunil Chavan Prin.K.M.Kundnani Pharmacy Polytechnic Olfactory Pathway • On each side of nose, bundles of axons of olfactory receptors extend through 20 olfactory foramina in cribiform plate • These bundles collectively form Right & Left Olfactory Nerve (I). • These nerve terminate in olfactory bulb. Here axons of receptors form synapses with dendrites of second order neurons in olfactory pathway. • Axons of olfactory bulb extend posteriorly & form olfactory Tract
- 9. Prof.Sunil Chavan Prin.K.M.Kundnani Pharmacy Polytechnic Olfactory Tract Some axons project to primary olfactory area conscious awareness of smell begins Other axons projected to Limbic system & Hypothalamus Responsible for emotional & memory evoked responses to odors
- 10. Prof.Sunil Chavan Prin.K.M.Kundnani Pharmacy Polytechnic GUSTATION:SENSE OF TASTE • Taste-Chemical sense • Five primary tastes: Sour, Bitter, Sweet, Salty, & U…. • Anatomy of Taste Buds & Papillae • Vallate: Circular, large, 8-12, form inverted V shape. Each papilla has 100-300 taste buds. • Fungiform: Mushroom shapr, entire surface, each papilla has about 5 taste buds. • Foliate: Located in small trenches on lateral margins. These degenerate in early childhood
- 11. Prof.Sunil Chavan Prin.K.M.Kundnani Pharmacy Polytechnic
- 12. Prof.Sunil Chavan Prin.K.M.Kundnani Pharmacy Polytechnic Taste Buds: Receptors for sensation of taste • About 10,000 TB in young adult • Most of them on tongue, some of them on soft palate, pharynx & epiglottis. • No. of TB declines with age. • Oval body-consist of 3 kinds of epithelial cells: Supporting cell, Gustatory receptor cell Basal cell • Supporting cell: Surround about 50 gustatory receptor cells in each taste bud.
- 13. Prof.Sunil Chavan Prin.K.M.Kundnani Pharmacy Polytechnic • Gustatory Receptor Cell: Each cell projects single long microvillus-Gustatory hair. • Basal Cell; Present at periphery, produce supporting cells Gustatory receptor cell. Each has 10 days life span. • At the base gustatory receptor cell synapses with dendrites of first-order neuron. This neuron forms the first part of gustatory pathway.
- 14. Prof.Sunil Chavan Prin.K.M.Kundnani Pharmacy Polytechnic Physiology of Gustation Testant Dissolved in Saliva Gustatory hair Transduction Receptor Potential Exocytosis of Synaptic vesicles Liberation of Neurotransmitter Trigger nerve impulse
- 15. Prof.Sunil Chavan Prin.K.M.Kundnani Pharmacy Polytechnic SWEET, BITTER, UMAMI TESTANTS • Binds to receptors on plasma membrane linked to G-proteins Activates several different chemicals (secondary messengers) Release of Neurotransmitter
- 16. Prof.Sunil Chavan Prin.K.M.Kundnani Pharmacy Polytechnic Salty food: Na + from testants Na+ Gustatory receptor Cell Accumulation of Na+ inside Opening of Ca2+ channels Influx of Ca2+ Exocytosis of Synaptic Vesicles Sour Food: H+ from testants
- 17. Prof.Sunil Chavan Prin.K.M.Kundnani Pharmacy Polytechnic Gustatory Pathway Taste Buds Taste Buds Taste buds in In Ant.2/3 in post. 1/3 throat, epiglottis Facial Glossopharyngeal Vagus Nerve(VII) Nerve(IX) Nerve(X) Medulla Oblongata Limbic System Thalamus & Hypothalamus Primary Gustatory Area (Parietal lobe)
- 18. Prof.Sunil Chavan Prin.K.M.Kundnani Pharmacy Polytechnic EYE : SENSE OF VISION (SIGHT) Vision: important to human survival More than half sensory receptors Larger part of cerebral cortex
- 19. Prof.Sunil Chavan Prin.K.M.Kundnani Pharmacy Polytechnic Anatomy of Eye Ball Wall of Eyeball Fibrous Vascular Retina layer layer Neuronal layer -Cornea -Choroid -Sclera -Ciliary body -Iris
- 20. Prof.Sunil Chavan Prin.K.M.Kundnani Pharmacy Polytechnic
- 21. Prof.Sunil Chavan Prin.K.M.Kundnani Pharmacy Polytechnic Interior of Eye ball Aqueous Vitreous Lens Humour body
- 22. Prof.Sunil Chavan Prin.K.M.Kundnani Pharmacy Polytechnic Fibrous Layer: • Outer coat of eyeball • Consist of anterior cornea, posterior sclera CORNEA: -Transparent epithelial coat, covers iris -Curved shape helps focus light into retina SCLERA (white of eye): -Layer of dense connective tissue, mostly collagen fibers & fibroblasts -Covers eyeball except cornea -Gives shape to eyeball, make it more rigid, protects inner parts
- 23. Prof.Sunil Chavan Prin.K.M.Kundnani Pharmacy Polytechnic Canal of Schlemm: • An opening at junction of sclera & cornea • It drains aqueous humour from anterior chamber
- 24. Prof.Sunil Chavan Prin.K.M.Kundnani Pharmacy Polytechnic Vascular Layer: • Middle layer of the eyeball • Three parts: Choroid, Ciliary body, Iris CHOROID: -Posterior portion of meddle layer -Lines most of internal surface of sclera -Rich in blood vessels, provides nutrients to retina -Contains melanocytes, produces melanin -Melanin absorbs stray light rays, prevent reflection & scattering of light within eyeball Sharp & clear image
- 25. Prof.Sunil Chavan Prin.K.M.Kundnani Pharmacy Polytechnic CILIARY BODY: -Anterior portion of choroid -Consists of Ciliary Processes & Ciliary Muscle Ciliary processes are folds on internal side, contain blood capillaries, secrete aqueous humour Suspensory Ligaments (Zonular fibers): -Extends from Processes to lens Ciliary muscle- circular band of smooth muscle. Its contraction/relaxation Tightness of zonular fibers alters shape of lens
- 26. Prof.Sunil Chavan Prin.K.M.Kundnani Pharmacy Polytechnic
- 27. Prof.Sunil Chavan Prin.K.M.Kundnani Pharmacy Polytechnic IRIS: -Coloured portion of eyeball -Suspended between Cornea & Lens -Melanocytes, Circular & Radial smooth muscle fibers Amount of melanin Colour of eye -Regulate amount of light entering through pupil
- 28. Prof.Sunil Chavan Prin.K.M.Kundnani Pharmacy Polytechnic
- 29. Prof.Sunil Chavan Prin.K.M.Kundnani Pharmacy Polytechnic Retina: -Innermost layer of eyeball -Lines about ¾ of eyeball Thickest at the back, thins out interiorly, ends just behind ciliary body -Consists of Pigmented layer & Neural layer Pigmented Layer: -Made up of melanocytes -Melanin helps to absorb stray light
- 30. Prof.Sunil Chavan Prin.K.M.Kundnani Pharmacy Polytechnic
- 31. Prof.Sunil Chavan Prin.K.M.Kundnani Pharmacy Polytechnic NEURAL LAYER: Three distinct layers of retinal neurons: Photoreceptor Layer, Bipolar layer & Ganglion Cell Layer -Separated by two zones: Outer & Inner Synaptic layer PHOTORECEPTORS: Specialized cells, begin process of conversion of light rays to nerve impulse
- 32. Prof.Sunil Chavan Prin.K.M.Kundnani Pharmacy Polytechnic
- 33. Prof.Sunil Chavan Prin.K.M.Kundnani Pharmacy Polytechnic -Cells: two types; ROD- outer segment is cylindrical CONE- outer segment cone shaped -Each retina has about 6 million cones & 120 million rods -Rods allow us to see in dim light -Cones produce colour vision Axons of ganglion cells extend posteriorly exit at a site called OPTIC DISC (Blind Spot) as Optic Nerve.
- 34. Prof.Sunil Chavan Prin.K.M.Kundnani Pharmacy Polytechnic INTERIOR OF EYEBALL LENS: -Highly elastic circular biconvex transparent body -Located behind pupil & iris, enclosed in connective tissue capsule -Held in position by zonular fibers, attached to ciliary processes -Consists of protein Crystallins -Lens help focus image on retina by refraction, facilitates clear vision -Vary its refracting power by changing its thickness
- 35. Prof.Sunil Chavan Prin.K.M.Kundnani Pharmacy Polytechnic LENS DIVIDES interior of eyeball into two cavities: Anterior Cavity & Vitreous Chamber ANTERIOR CAVITY: Consists of two chambers: Anterior Chamber- between cornea & Iris Posterior Chamber-behind Iris & infront of lens & zonular fibers Both chamber are filled with aqueous humour-watery fluid nourishes lens & cornea.
- 36. Prof.Sunil Chavan Prin.K.M.Kundnani Pharmacy Polytechnic Aqueous humour filters out of blood capillaries in ciliary processes & enters posterior chamber -Flows forward between iris & lens, through pupil into anterior chamber -From ant. Chamber it drains into Canal of Schlemm, and then into blood. -it is completely replaced about every 90 minutes
- 37. Prof.Sunil Chavan Prin.K.M.Kundnani Pharmacy Polytechnic VITREOUS CHAMBER: -lies between lens & retina -Contains viscous substance:Vitreous Body -Formed during embryonic development not replaced thereafter. -It contains 99% water, mucoprotein, salts and phagocytic cells -It prevents collapsing of eye walls -It keeps this part clear for unobstructed vision
- 38. Prof.Sunil Chavan Prin.K.M.Kundnani Pharmacy Polytechnic INTRA-OCULAR PRESSURE: -Produced mainly by Aq. Humour & partly by Vitreous body -normal 16 mm Hg (15 – 20 mm Hg) -maintains shape of Eyeball & prevents it from collapsing GLAUCOMA: Condition in which there is increased intraocular pressure due to defective drainage of aqueous humour through canal of Schlemm.
- 39. Prof.Sunil Chavan Prin.K.M.Kundnani Pharmacy Polytechnic Accessory structures of Eye Eyelids, Eyelashes, Eyebrows, Lacrimal Apparatus & Extrinsic eye Muscles Superior rectusrotates eyeball upwards Inferior rectus rotates eyeball downwards Lateral rectusrotates eyeball outwards Medial rectusrotates eyeball inwards Superior obliquerotates eyeball so that cornea turns in downwards & outwards direction Inferior obliquecornea turns upward & outward direction
- 40. Prof.Sunil Chavan Prin.K.M.Kundnani Pharmacy Polytechnic PHYSIOLOGY OF VISION • ISOMERIZATION OF RETINAL: Retinal in photoreceptor cells present in cis- form in darkness. This absorbs light (photon) and converts into trans- form • RELEASE OF NEUROTRANSMITTER: Isomerization activates enzyme that breaks down cyclic Guanosine Monophosphate (cGMP) closure of cGMP gated Na+ channels Na+ influx Membrane potential more negative affects release of Glutamate (Hyperpolarisation)
- 41. Prof.Sunil Chavan Prin.K.M.Kundnani Pharmacy Polytechnic DIM LIGHT-small & brief receptor potential that partially turnoff glutamate release BRIGHT LIGHT-larger & longer receptor potential that completely shut down glutamate release Excites bipolar cell & subsequently stimulates ganglion cells to generate nerve impulse in their axons Axons of all retinal ganglion cells exit eyeball at Optic disc and form Optic Nerve (II)
- 42. Prof.Sunil Chavan Prin.K.M.Kundnani Pharmacy Polytechnic Visual Pathway • At the optic chaism axons from temporal half of each retina do not cross, continue directly to thalamus on same side • Axons from nasal half of each retina cross optic chaism and continue to opposite thalamus • Each optic tract consists of crossed & uncrossed axons • Branches of axon project to midbrain that govern constriction of pupils in response to light & co-ordination of head & Eye movements • Axons of thalamic neurons project to primary visual area in occipital lobe of cortex image is perceived
- 43. Prof.Sunil Chavan Prin.K.M.Kundnani Pharmacy Polytechnic
- 44. Prof.Sunil Chavan Prin.K.M.Kundnani Pharmacy Polytechnic EAR:SENSE OF SOUND (HEARING) Ear- an engineering marvel, contains receptors for Hearing & Equilibrium Transmits 1000 times faster than photoreceptors
- 45. Prof.Sunil Chavan Prin.K.M.Kundnani Pharmacy Polytechnic ANATOMY OF EAR External Ear Middle Ear Internal ear -Auricle (tympanic cavity) (Labyrinth) -Auditory canal -Auditory Ossicles -Bony (acoustic 1.Malleus -Membranous meatus) 2.Incus 3.Stapes -Eustachian Tube
- 46. Prof.Sunil Chavan Prin.K.M.Kundnani Pharmacy Polytechnic
- 47. Prof.Sunil Chavan Prin.K.M.Kundnani Pharmacy Polytechnic External Ear AURICLE (Pinna): • Expanded portion from side of head • Composed of fibroelastic cartilage • Deeply grooved & ridged • Prominent outer ridge-Helix • Soft inferior portion-Lobule, composed of fibrous & adipose tissue, richly supplied with blood capillaries
- 48. Prof.Sunil Chavan Prin.K.M.Kundnani Pharmacy Polytechnic EXTERNAL AUDITORY CANAL (ACOUSTIC MEATUS): • Slightly curved tube, about 2.5cm long, lies in temporal bone, extended from auricle to tympanic membrane • Lined with hairy skin, continues with auricle • Contains numerous specialized sweat glands- Ceruminus glands, secret earwax, sticky material containing lysozome & immunoglobins • Prevent foreign material like dust, insects, microbes reaching eardrum. Function:Collection of sound waves & channel them inward eardrum
- 49. Prof.Sunil Chavan Prin.K.M.Kundnani Pharmacy Polytechnic TYMPANIC MEMBRANE/EARDRUM • Thin partition between auditory canal & tympanic cavity • Oval shaped, slightly broader edge upwards • Composed of three layers of tissues- -outer covering of hairless skin -middle layer of fibrous tissue -inner lining of mucus membrane FUNCTION: production of vibrations, as sound waves strike it.
- 50. Prof.Sunil Chavan Prin.K.M.Kundnani Pharmacy Polytechnic
- 51. Prof.Sunil Chavan Prin.K.M.Kundnani Pharmacy Polytechnic Middle Ear/Tympanic Cavity • Small, irregular, air-filled cavity in temporal bone • Cavity & its contents are lined with either simple squamous or cuboidal epithelium • Extend till oval window & round window of internal ear AUDITORY OSSICLES: • Three very small bones extend across cavity- Malleus, Incus, Stapes • Attached to cavity by ligaments • Connected by synovial joints
- 52. Prof.Sunil Chavan Prin.K.M.Kundnani Pharmacy Polytechnic
- 53. Prof.Sunil Chavan Prin.K.M.Kundnani Pharmacy Polytechnic MALLEUS: • Handle is in contact with eardrum • Head forms joint with incus INCUS: • Body articulates with malleus, long process with stapes, stabilized by short process STAPES: • Head articulates with incus, base or footplate fits into oval window
- 54. Prof.Sunil Chavan Prin.K.M.Kundnani Pharmacy Polytechnic EUSTACHIAN TUBE (AUDITORY) • About 4 cm long tube, connects middle ear with nasopharynx, lined with ciliated epithelium • Normally closed, opens during swallowing, yawning, sneezing • Balanced pressure allows eardrum vibrates freely as sound waves strike it FUNCTION: Transmission of vibrations till oval window, work as piston, its action add force
- 55. Prof.Sunil Chavan Prin.K.M.Kundnani Pharmacy Polytechnic
- 56. Prof.Sunil Chavan Prin.K.M.Kundnani Pharmacy Polytechnic Inner Ear (Labyrinth) • Contains the organs of hearing and balance. • Described in two parts, the bony labyrinth and the membranous labyrinth. BONY LABYRINTH: • This is a cavity within the temporal bone lined with periosteum. • The bony labyrinth consists of: 1 vestibule , 1 cochlea , 3 semicircular canals
- 57. Prof.Sunil Chavan Prin.K.M.Kundnani Pharmacy Polytechnic VESTIBULE: • Expanded part nearest the middle ear • Contains the oval and round windows in its lateral wall. COCHLEA: • Has a broad base where it is continuous with the vestibule and a narrow apex, and it spirals round a central bony column. THE SEMICIRCULAR CANALS: • These are three tubes arranged so that one is situated in each of the three planes of space. They are continuous with the vestibule.
- 58. Prof.Sunil Chavan Prin.K.M.Kundnani Pharmacy Polytechnic MEMBARNOUS LABYRINTH • Contains endolymph • It comprises of: vestibule, cochlea & 3 semicircular canals COCHLEA: contains three compartments: -the scala vestibuli -the scala media, or cochlear duct -the scala tympani.
- 59. Prof.Sunil Chavan Prin.K.M.Kundnani Pharmacy Polytechnic
- 60. Prof.Sunil Chavan Prin.K.M.Kundnani Pharmacy Polytechnic Cochlear duct: • It is triangular in shape • On the base of triangle there are supporting cells and specialised cochlear hair cells containing auditory receptors. • These cells for Spiral organ (of Corti) that responds to vibrations • Auditory receptors are dendrites of efferent nerves that form cohlear nevre, part of 8th cranial nerve
- 61. Prof.Sunil Chavan Prin.K.M.Kundnani Pharmacy Polytechnic
- 62. Prof.Sunil Chavan Prin.K.M.Kundnani Pharmacy Polytechnic PHYSIOLOGY OF HEARING 1. The auricle because of it shape concentrates sound waves and direct them along auditory canal 2. Soundwaves stike eardrumproduces vibrations 3. Transmission of vibrations across middle ear via auditory ossicles 4. As stapes moves back & froth it pushes membrane of oval window in & out
- 63. Prof.Sunil Chavan Prin.K.M.Kundnani Pharmacy Polytechnic 5. Movement of oval window sets up fluid pressure waves in the perilymph of cochlea. It pushes perilymph of scala vestibuli 6. Transmission of pressure from scala vestibuli to scala tympani to roun window 7. Pressure in scala vestibuli & scala tympani transmits pressure waves in endolymph inside cochlear duct
- 64. Prof.Sunil Chavan Prin.K.M.Kundnani Pharmacy Polytechnic 8. Pressure waves in endolymph causes basilar membrane to vibrate, it moves hair cells of spiral organ against tectorial membrane, bending of hair cells of spiral organ against tectorial membrane 9. Bending of hair cell Stereocilia produces receptor potentialgeneration of nerve imp[ulse
- 65. Prof.Sunil Chavan Prin.K.M.Kundnani Pharmacy Polytechnic
- 66. Prof.Sunil Chavan Prin.K.M.Kundnani Pharmacy Polytechnic AUDITORY PATHWAY First order sensory neuron (cochlear branch) Cochlear nuvlei in medulla oblongataOlivery nuclei in ponsInferior colicullus of midbrain Geniculate nucleus of Thalamus Primary Auditory Area in superior temporal gyrus of Cerebral cortex
