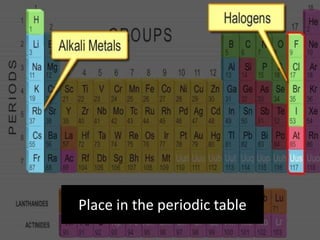
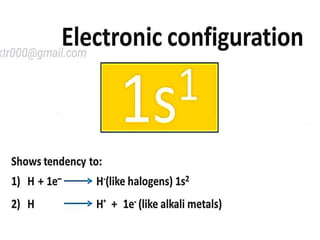
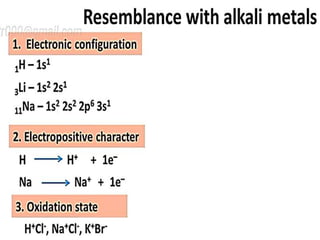
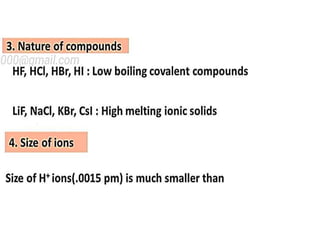
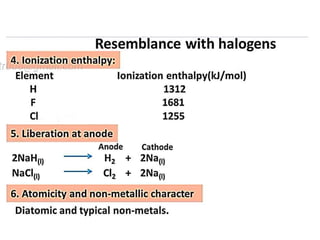
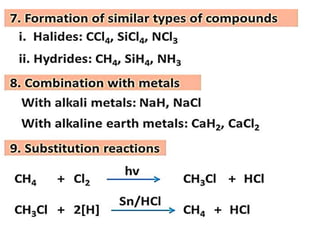
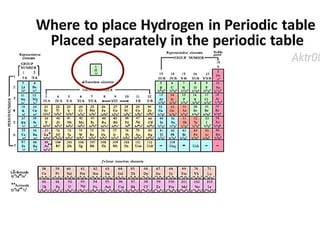
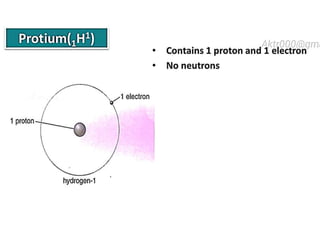
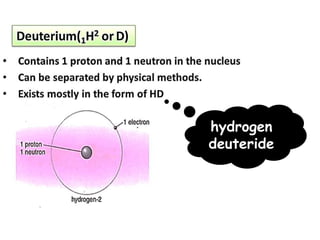
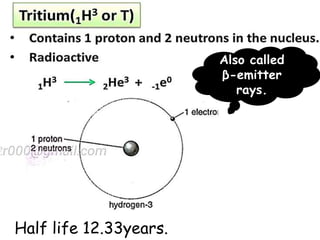
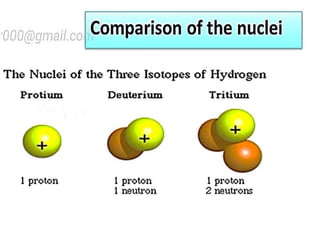
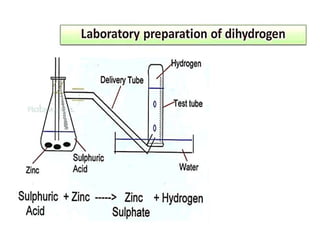
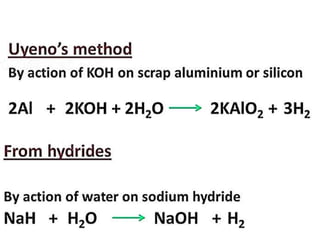
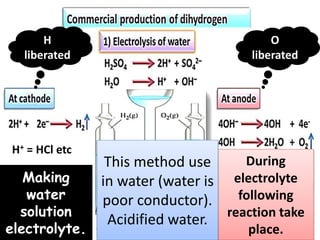
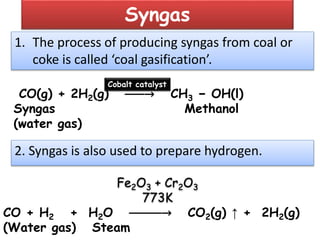
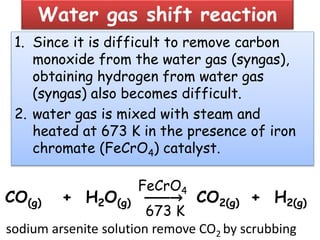
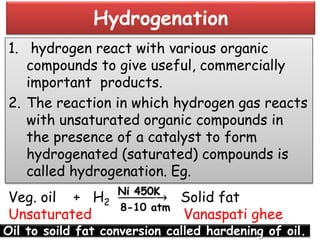
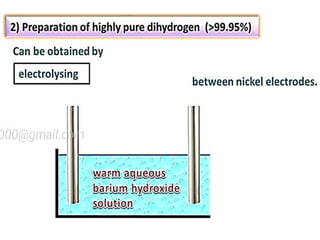
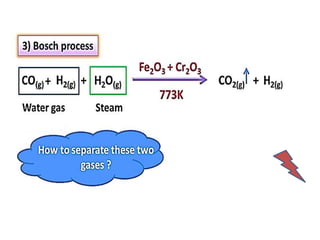
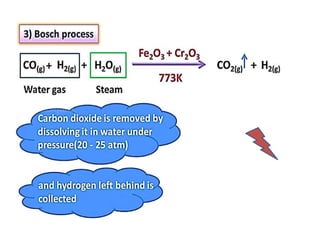
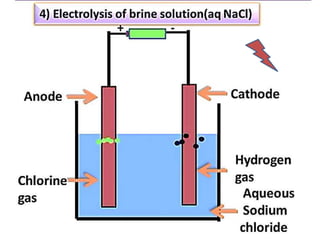
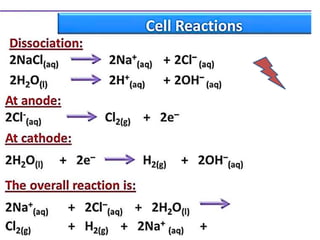
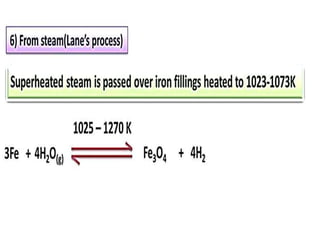
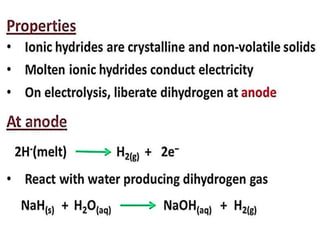
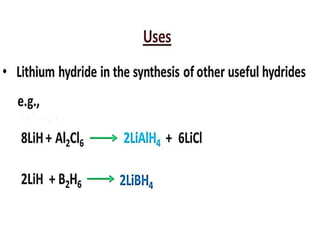
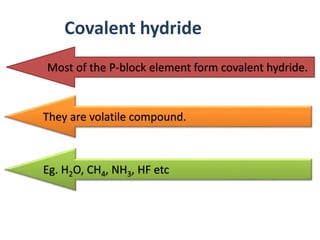
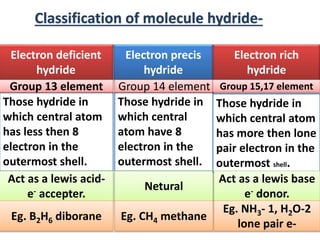
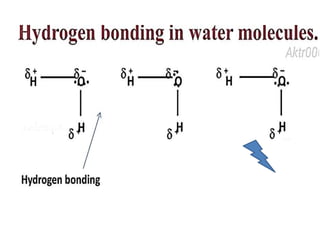
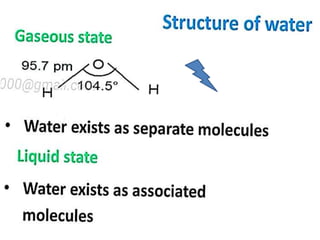
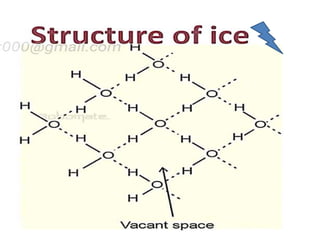
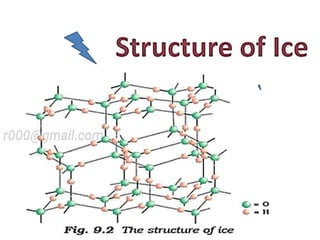
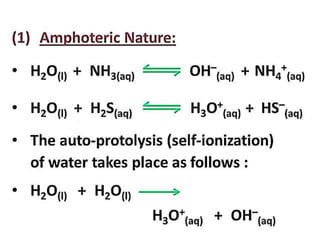
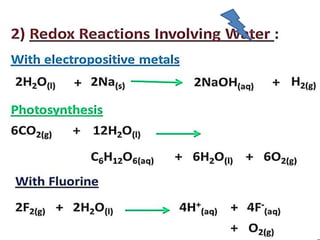
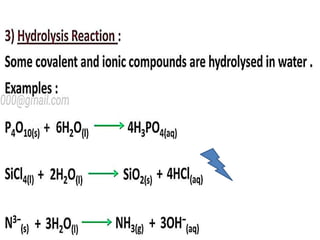
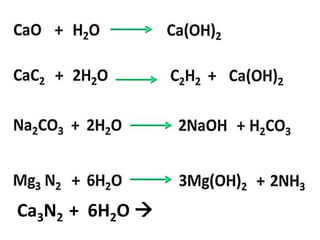
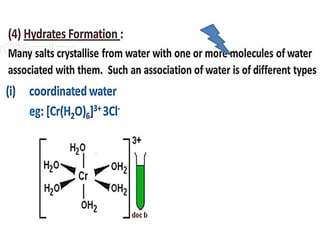
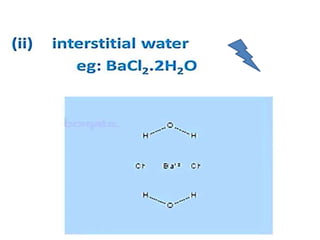
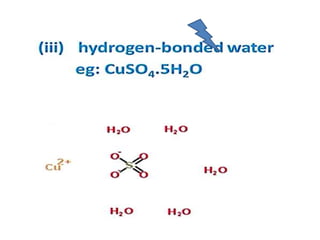
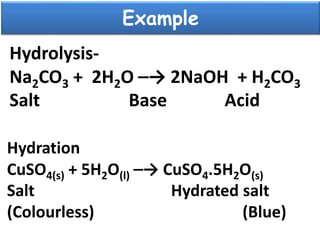
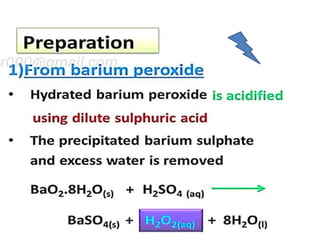
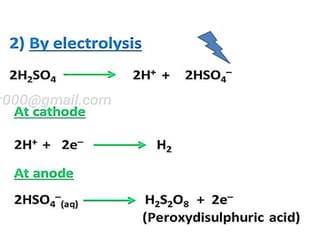
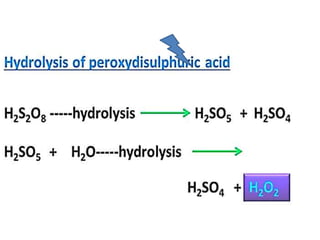
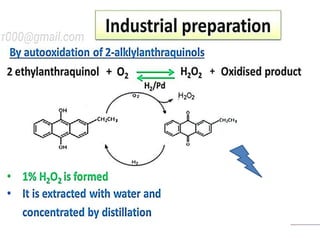
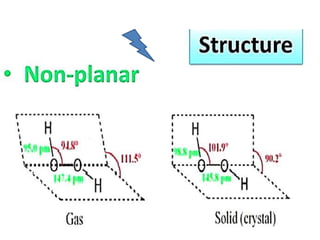
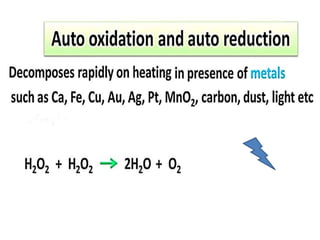
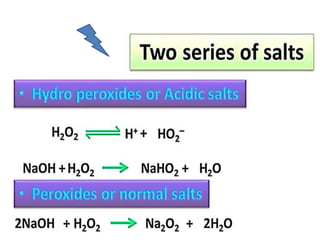
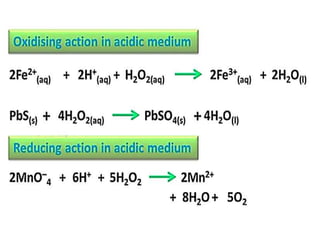
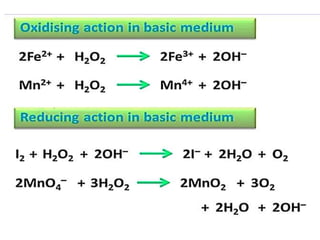
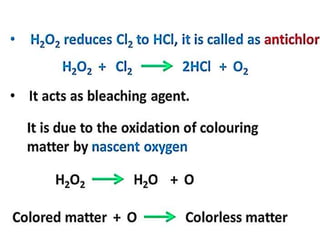
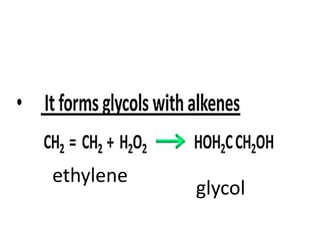
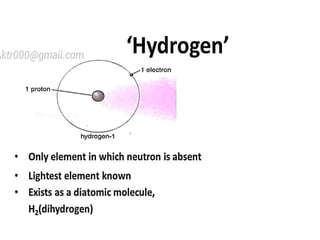
The document discusses the properties and chemical behavior of hydrogen, including its diatomic nature and the process of hydrogenation. It covers the production and uses of syngas, the importance of hydrogen in industrial applications, and various chemical reactions involving hydrogen. Additionally, it details the formation of hydrides and their classifications based on electron configuration.


![Hydrogen is Diatomic [H2] Why?
1. Hydrogen having one electron in its
valence shell (E.C-1s1).
2. to attain stability, hydrogen has to have
two electrons so that it can complete it's
duplet.
3. therefore, it shares its single electron
with other H-atom to achieve stable inert
gas configuration of He.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hydrogen2017-180302120605/85/Hydrogen-2017-4-320.jpg)