liceseminar-151230105450 (1).pptx
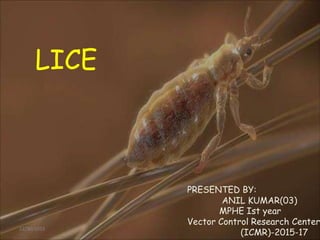
- 1. LICE PRESENTED BY: ANIL KUMAR(03) MPHE Ist year Vector Control Research Center 12/30/2015 (ICMR)-2015-17
- 2. MALLOPHAGA INTRODUCTION : • Worldwide more than 550 species of louse have been reported. These are obligatory ectoparasites of humans, cattles and animals. Lice are small, dorsoventrally flattened, exopterygot wingless insects. Two different forms of lice have evolved : - The Mallophaga - The Anoplura The Mallophaga – they retains the • • • • primitive insect mandibulate mouthparts and feed on epidermal structures of birds and mammals(chewing lice). The Anoplura – they evolve specialized • mouthparts for blood feeding and they are only found on humans (host specific) 12/30/2015 Fig. 1. ANOPLURA
- 3. Contd. Introduction… • Three types of lice are there to be considered under medical importance for humans based on the part they feed on: - Pediculus humanus capitis (head louse), - Pediculus humanus corporis (body louse), and - Pthirus pubis ("crab" louse/pubic louse). Human lice survive by feeding on human blood. Lice infestation are most commonly caused by close person-to-person contact. Body louse is only reported to spread diseases. Treatment is available, so identification can help in taking accurate control measures. • • • • 12/30/2015
- 4. Classification : Phylum • Arthopoda Class • Insecta Order • Anoplura • Pediculidae Family • • Pediculidae humanus Phthirus Genus 12/30/2015
- 5. .,.....,_ ~- ""_"* ,... -..... !)""""'.... ---- _ ,___ ..... .. -...·- II._- _...................- Mq .. , ..... ..,,~ - de-- -- - Generalised Morphology DORSA L • VENTilA L I [ i)[ t ~ . I j • • i - .. .. . [ [ " y " .. .. 12/30/2015 ,
- 6. (Head louse) The adult lice are obligate blood sucking ectoparasites that require warmth and a source of human blood to survive. Reservoir : Human (susceptible- children) Transmission : person to person contact Oviposition site : Base of head hairs They will die if separated from human host for 24hrs Hemimetabolous (no pupa) No. of blood meals : 4 - 10/day Longevity of adults : Up to 35 days Reduced compound eyes no ocelli Crawling speed : 30 cm/min 12/30/2015 Pediculus humanus capitis
- 7. Figure 1. Head lice feeding on a human scalp. Lice engorge and enlarge on blood and will become a reddish color when recently fed. Figure 2. A close up high• resolution image of an adult male head louse in its natural environment. Figure 3. Head lice eggs (nits) on a person's hair. Dandruff, hair casts, globules of hair spray, and scalp conditions such as psoriasis or eczema Figure 2
- 8. fllRD MOULT EN DAYS AFTER IATCHINO 1. FEMALE LAYS FtgT EOO I OR Z OAY9 AFTER MATING I.FEMALE LAYS APPROXIMATELY• TO I EGGS FOR 'fflENEXT II DAYS II. 'f •. SECOND MOULT FlVEOAYS AFTE R HATCijlNG t 3. FIRST MOULT TWO DAYS Al"Tl!R HATCHIN G AFTER 1,7 DAYS I.HAVING UVl!D 32 TO 35 DAYS SINCE BEING LAID AS A NIT 'fflE LOUSE 2. LOUSE EMERGES 1. EOO 18 I.AIO ON HAIR SHAFT. EGG IS CAL L ED "II
- 9. Eggs or Nits : Eggs are laid in their shells (the nits) Shape: oval or flask shaped and have a lid (operculum) that covers the free end Colour: documented as grayish-white, transparent but turns to dark brown after tanning Size: 0.3 mm – 0.8 mm After hatching, empty white to dull yellow and almost clear colored nit casing or shells are left behind. They remain tightly adhered to hair shaft. Viable nits are always found close to the scalp (1 – 4 mm). Human hair grows slowly at an average rate of approximately 0.37 mm/ day. Nits found several millimeters from the scalp are now empty egg cases. Egg is tightly glued to the base of the hair shaft, nearest the scalp with chitin. Eggs are usually deposited 1 – 4 mm from the scalp. Eggs hatch within 6 – 10 days. Only eggs deposited by inseminated female lice will hatch. • • • • • • • • • • • • 12/M 30/a 20 y15persist for months, even after treatment, if not
- 10. Nymph : • • • • Looks like adult louse, but smaller and immature. Size: 1 mm in length, size of pinhead. Matures in 3 stages. They grow by molting or shedding their skin 3 times before reaching adulthood. Duration of nymph stage is 7-14 days. Nymphs tend to remain on the head where they hatch. The newly hatched nymph will crawl and seek a place to feed immediately. The three nymphal stages last about 8-12 days. • • • • 12/30/2015
- 11. ck. Adult : Wingless, elongated body with 3 segments (head, thorax and abdomen). Short antennae with 4 segments. Small head with anterior piercing mouthparts that are used to pierce the scalp and feed on blood. 6 short and stubby legs with single tarsal segments, with powerful hook-like claws at the end of each leg. These claws are used to grasp the hair shaft. Dorsoventrally flattened. • • • • • • • • • • • 3rd abdominal segment : As long as wide Female body length : 2.4 - 3.3 mm Male body length : 2.1 - 2.6 mm Mating only occurs once fully grown. Colour: have been documented as grey, tan, brown, red or bla Colour changes to rust coloured after a blood meal. 12/30/2015 Hy : hypopharynx Pm : prementum
- 12. Body louse differ from head louse with only few characters, namely Head louse Body louse 1B 2/l 3 0 o/d 20 m 15 eal 4 - 10 per day 1-5 per day Characteristics Head louse Body louse Color Dark Light Female body length 2.4 - 3.3 mm 2.4 - 3.6 mm Male body length 2.1 – 2.6 mm 2.3 – 3.0 mm Antennae shape Short and wide Long and narrow 3rd antennal segment As long as wide Slightly longer than wide Abdominal indentations Prominent Not prominent Apices of paratergal plates Extending into intersegmental Didn’t extend to membranes intersegmental plates Eggs laid 4 - 8 per day 8 - 12 per day Oviposition site Base of head hairs Clothing fibers Longivity 35 days 60 days Pediculus humanus humanus (Body louse)
- 13. • They can survive up to 1 week after getting separated from human host without feeding Mouthparts same as head louse, piercing and sucking type The body louse is the vector of three bacterial diseases - epidemic or louse-borne typhus, caused by Rickettsia -trench fever, caused by Rochalimaea quintana (Rickettsia quintana) -louse-borne relapsing fever, caused by Borrellia recurrentis (Lebert) • • 12/30/2015
- 14. • • It is associated with poor hygiene condition or socioeconomic status Pubic lice are adapted to a sedentary life style on pubic hair, armpits, sometimes on eyelashes/moustaches/beard and body hair. They are usually transmitted during sexual contact, and have been associated with other sexually transmitted diseases. They do not cause any disease They look like crab in shape thus also known as crab lice which makes it easily distinguishable from head and body lice • • • • Life cycle remains same in pubic lice i.e, Egg, Nymph and Adult seen is in duration of different stages during life cycle, only difference 12/30/2015 Stages Duration Egg 6 - 8 days Nymph (I) 5-6 days Nymph (II) 9 – 10 days Nymph (III) 13 – 17 days Adult 15 – 25 days Pthirus pubis (Pubic louse)
- 15. The crab louse may be distinguished readily from the body louse or head louse by the following: • • • • forelegs delicate, with long, slender claws; other legs very stout, with short, stout claws: thumb like process of tibia short and stout; abdomen very short and broad; segments 1-5 closely crowded, thus the stigmata of segments 3-5 apparently lying in one lateral process. adult size 1.1 – 1.7 mm they can feed continuously for hours without retracting their mouthparts. • • All legs of the body louse or head louse are stout; thumb like process of tibia very long and slender, bearing strong spines, forelegs stouter than the others; abdomen elongate, segments without lateral processes. 12/30/2015
- 16. Collection technique : Mechanical method - • Hand picking : Using a fine watch-repairer's forceps (BB or NN) one can conveniently pick up the lice. Plucking the barbs of the feathers, or hairs, holding a little below the louse will avoid crushing of the specimen in the process. Brushing technique : The host should be separated and fumigants (ether/chloroform/carbon disulphide) should be sprinkled over the infested area in such a way that the fumigant should not come in direct contact/affect the host. After 30 min comb the hair with fine comb in such a way that all sample should fall on a white paper. The specimens can be preserved in vials containing 70-95% alcohol. • Chemical method 12/30/2015
- 17. Preservation technique : The specimen collected can be conveniently preserved in a liquid medium or mounted on slides. • Storing in liquid media : The material can be preserved in small glass vials containing 70% - 95% alcohol, plugged with cotton or air tight plastic stoppers (cork stoppers should not be used), while in case of specimens which are placed in a large jar should contain 95% alcohol. • Whole mounts Resin mount : Elhel (1967) quoted Emerson's procedure of mounting. In this process, after treating in KOH or NaOH solution, the specimens were washed well with water (about 20 min.) and then placed in 40% alcohol (15 min.). They were then transferred to a solution of Ziehl Nielson's Carbol-Fuchsin for about 30 minutes. The material then passed through 70% alcohol (30 min.), 95% alcohol (15 min.) washed in absolute alcohol, and then placed in Beechwood creosote (1 hr to overnight), and finally mounted in Damar gum or Canada balsam. 12/30/2015
- 18. REFRENCES : BOOKS: • Proceeding of the workshop on techniques in parasitology, Zoological Survey of India, Calcutta., 1980 Michigan head lice manual, Michigan department of education., August 2013 • JOURNALS : Amina Boutellis, Laurent Abi Rached, Didier Raoult., The origin and distribution of human lice in the world., Infection, Genetics and Evolution 23(2014); page 209-217 Denise L. Bonilla and et al., The Biology and Taxonomy of Head and Body Lice – Implication for Louse-Borne Disease Prevention., PLOS Pathogen 9; November 2013 Elston DM., What’s Eating You? Pediculus humanus (Head Louse and Body Louse). CUTIS. Vol. 63, May 1999; p. 259 H. V. Weems, Jr. and T. R. Fasulo., Crab Louse, Pthirus pubis (Linnaeus) (Insecta: Phthiraptera (Anoplura): Pediculidae)., University of Florida, EENY-103 12/30/2015