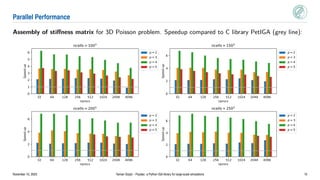
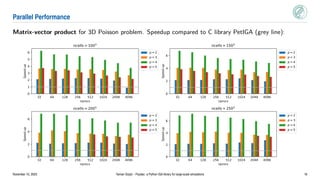
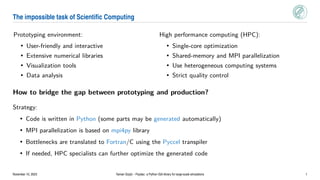
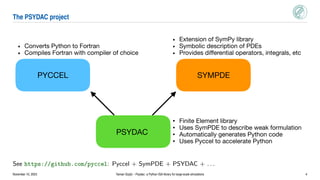
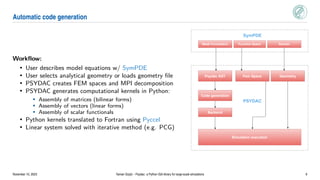
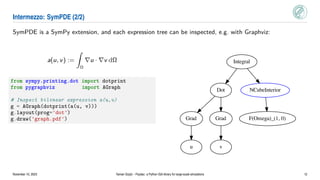
Psydac is an open-source Python library for large-scale isogeometric analysis (IGA) simulations. It allows for rapid prototyping in Python while achieving high performance through code generation and optimization. Psydac uses the SymPDE domain specific language to describe weak formulations of partial differential equations. It then automatically generates optimized C/Fortran code for computationally intensive kernels using the Pyccel transpiler. This bridges the gap between prototyping codes in Python and production simulations, enabling both flexibility and high performance for large-scale scientific computing applications.






![Usage example: 2D Poisson’s equation (2/3)
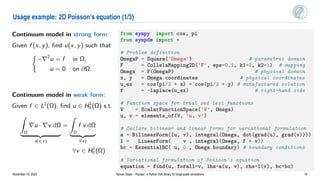
Galerkin method:
• Let uh ≈ u in finite dim. subspace Vh ⊂ H1
0
• Choose basis for Vh = span(ϕ1, ϕ2, . . . ϕN )
• Search for uh(x, y) =
P
k
wk ϕk (x, y)
• Choose test functions v = ϕk
• Linear PDE yields linear system A w = b
Given f ∈ L2
(Ω), find w ∈ RN
s.t.
N
X
j=1
Z
Ωh
∇ϕi · ∇ϕj dΩ
| {z }
Aij
wj =
Z
Ωh
f ϕi dΩ
| {z }
bi
,
for i = 1, . . . , N.
from mpi4py import MPI
from psydac import discretize
# Select MPI communicator (set to None for serial code)
comm = MPI.COMM_WORLD
# Create computational domain
Omega_h = discretize(Omega, ncells=(7, 7), comm=comm)
# Create finite element space (B-splines)
V_h = discretize(V, Omega_h, degree=(3, 3))
# Set up linear system: code generation
equation_h = discretize(equation, Omega_h, [Vh, Vh])
# Compute numerical solution:
# 1. assemble (distributed) sparse matrix A
# 2. assemble (distributed) dense vector b
# 3. solve linear system A w = b
# 4. create callable field u_h(x,y)
u_h = equation_h.solve()
November 10, 2023 Yaman Güçlü – Psydac: a Python IGA library for large-scale simulations 13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/yamangl-psydacapythonigalibraryforlarge-scalesimulations-231204152109-e6a574a9/85/SFSCON23-Yaman-Guclu-Psydac-a-Python-IGA-library-for-large-scale-simulations-14-320.jpg)
![Usage example: 2D Poisson’s equation (3/3)
Domain: 7 × 7 cells
Spline degree: p = 3
- Left: numerical solution
- Right: numerical error
1.0 0.5 0.0 0.5 1.0
x
1.00
0.75
0.50
0.25
0.00
0.25
0.50
0.75
1.00
y
(x,y)
1.0 0.5 0.0 0.5 1.0
x
1.00
0.75
0.50
0.25
0.00
0.25
0.50
0.75
1.00
y
(x,y) ex(x,y)
0.000
0.125
0.250
0.375
0.500
0.625
0.750
0.875
1.000
0.0048
0.0036
0.0024
0.0012
0.0000
0.0012
0.0024
0.0036
0.0048
# Scalar error estimate (L2 norm)
l2norm = Norm(u - u_ex, Omega, kind='l2') # symbolic definition - SymPDE
l2norm_h = discretize(h2_norm, Omega_h, Vh) # code generation - PSYDAC
l2_error = l2norm_h.assemble(u=u_h) # computation
Running the whole thing in IPython:
In [1]: run poisson_2d.py
In [2]: print(l2_error)
Out[2]: 5.17e-03
November 10, 2023 Yaman Güçlü – Psydac: a Python IGA library for large-scale simulations 14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/yamangl-psydacapythonigalibraryforlarge-scalesimulations-231204152109-e6a574a9/85/SFSCON23-Yaman-Guclu-Psydac-a-Python-IGA-library-for-large-scale-simulations-15-320.jpg)