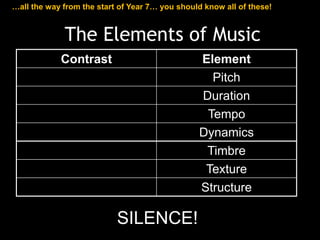
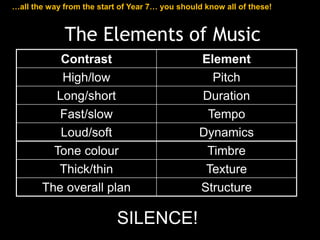
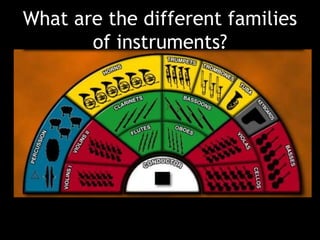
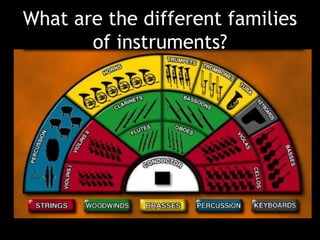
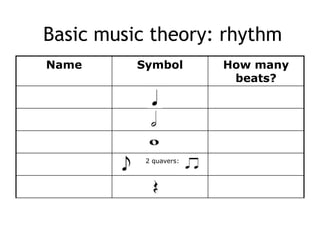
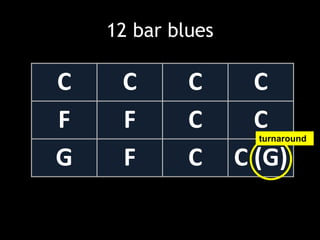
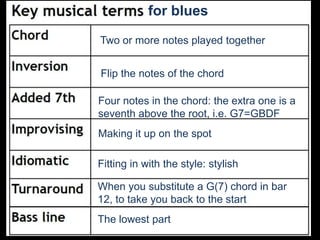
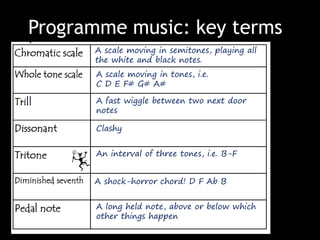
The document provides revision material for an upcoming Year 8 music exam. It will cover all topics studied that year, including the elements of music (pitch, duration, tempo, etc.), instruments families, basic music theory on rhythm and pitch, developing motifs, 12 bar blues form, and key terms for programme music. Students are advised to use the powerpoint and other online resources to prepare for the listening exam.