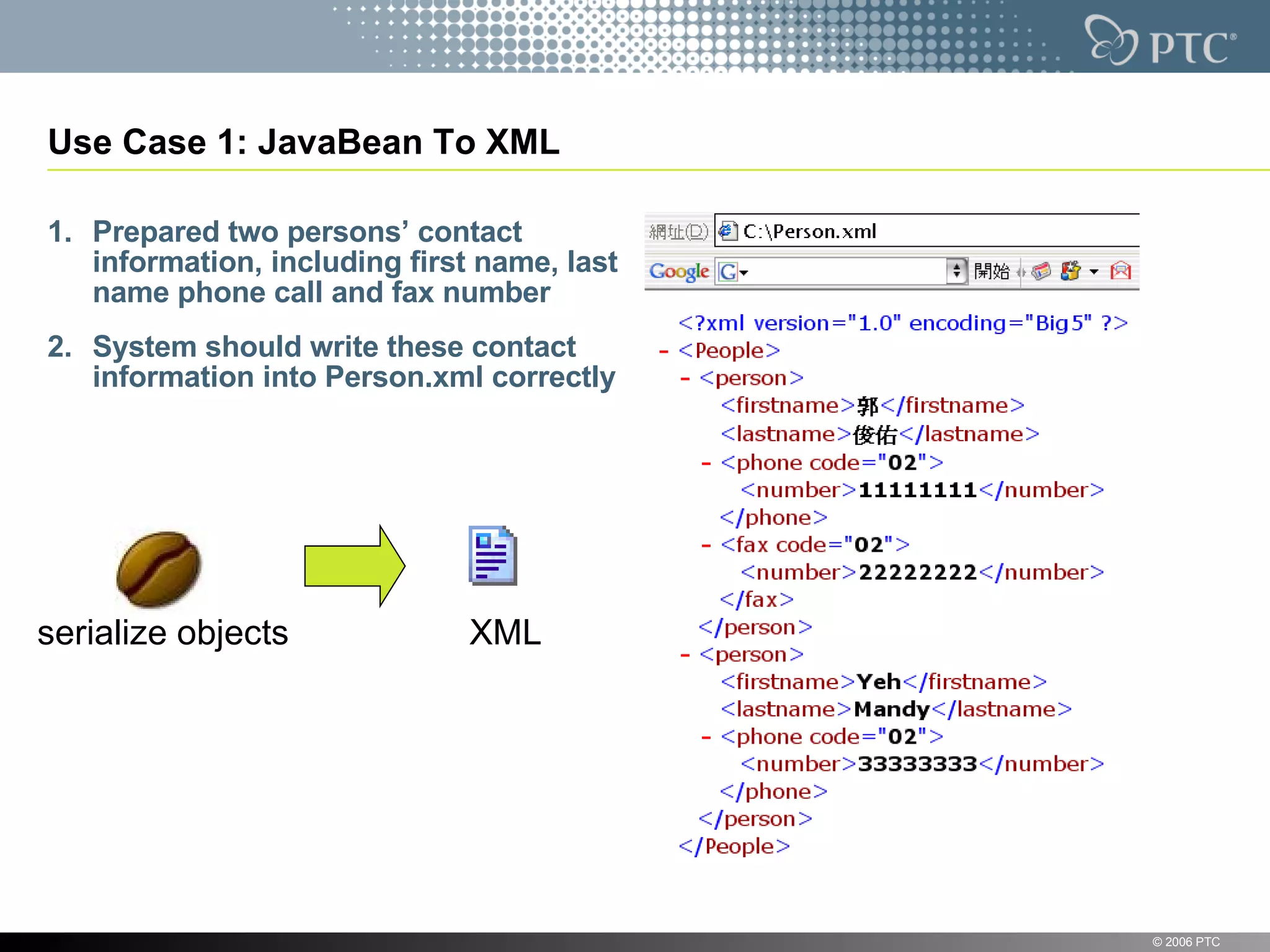
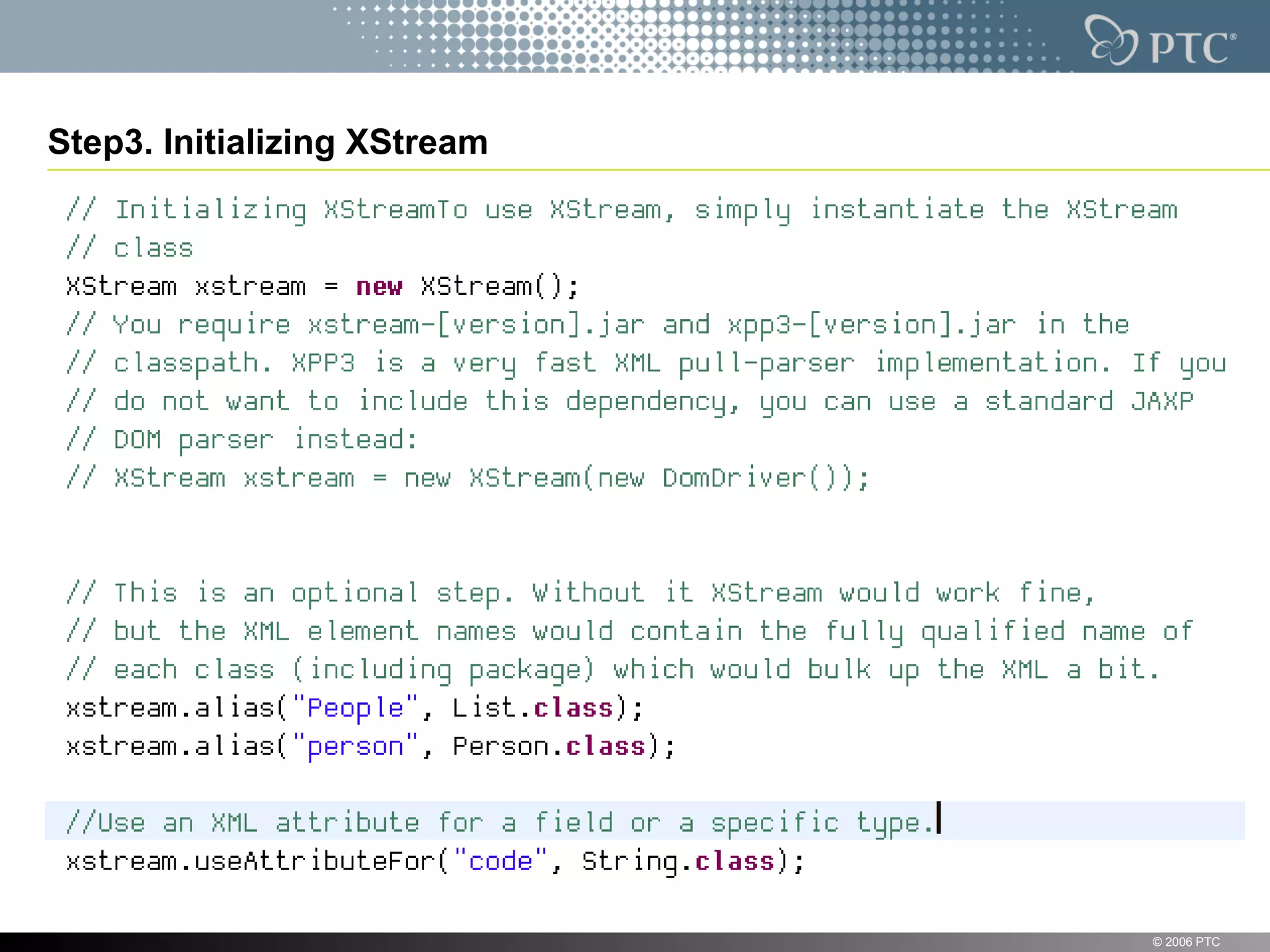
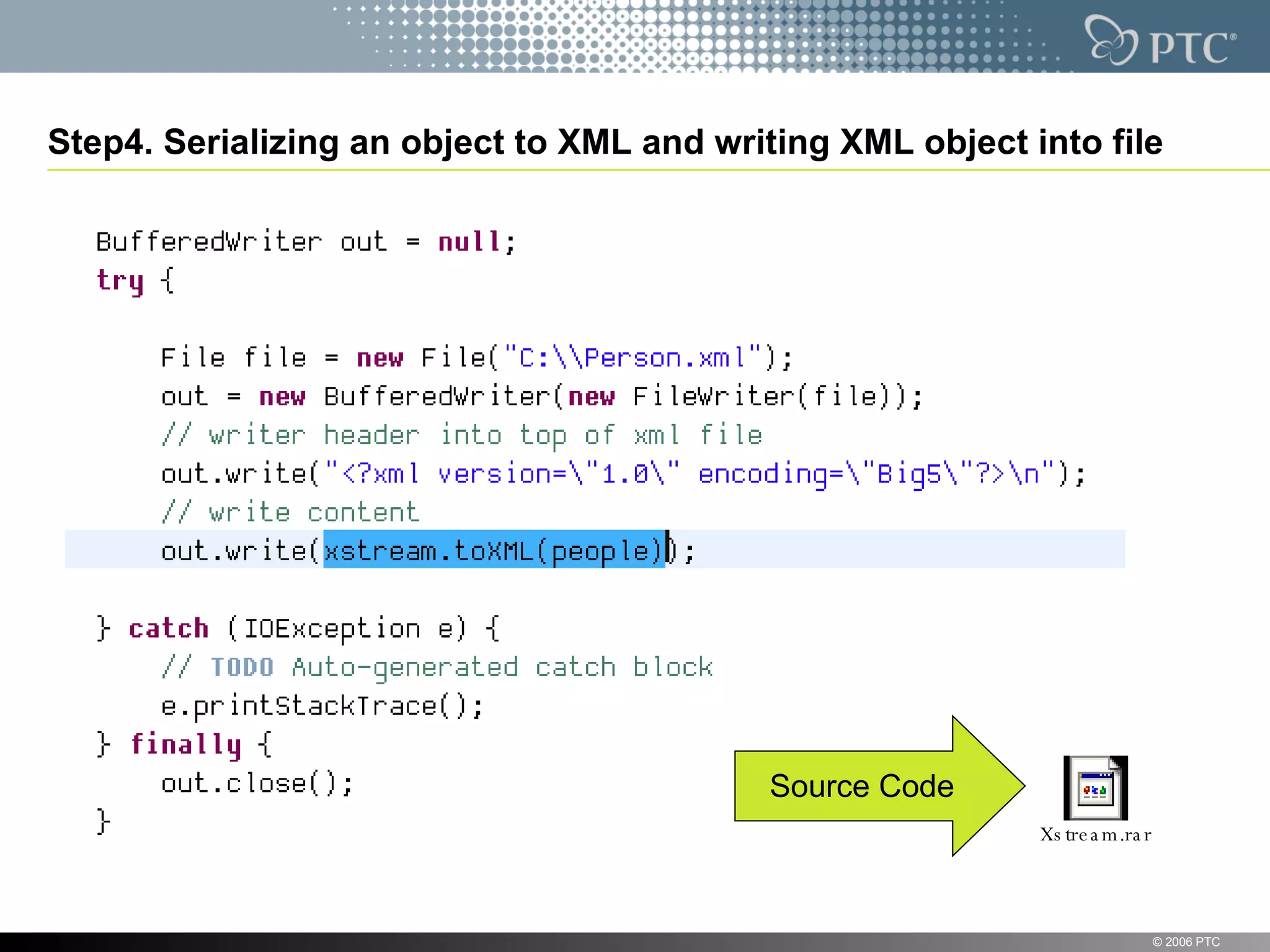
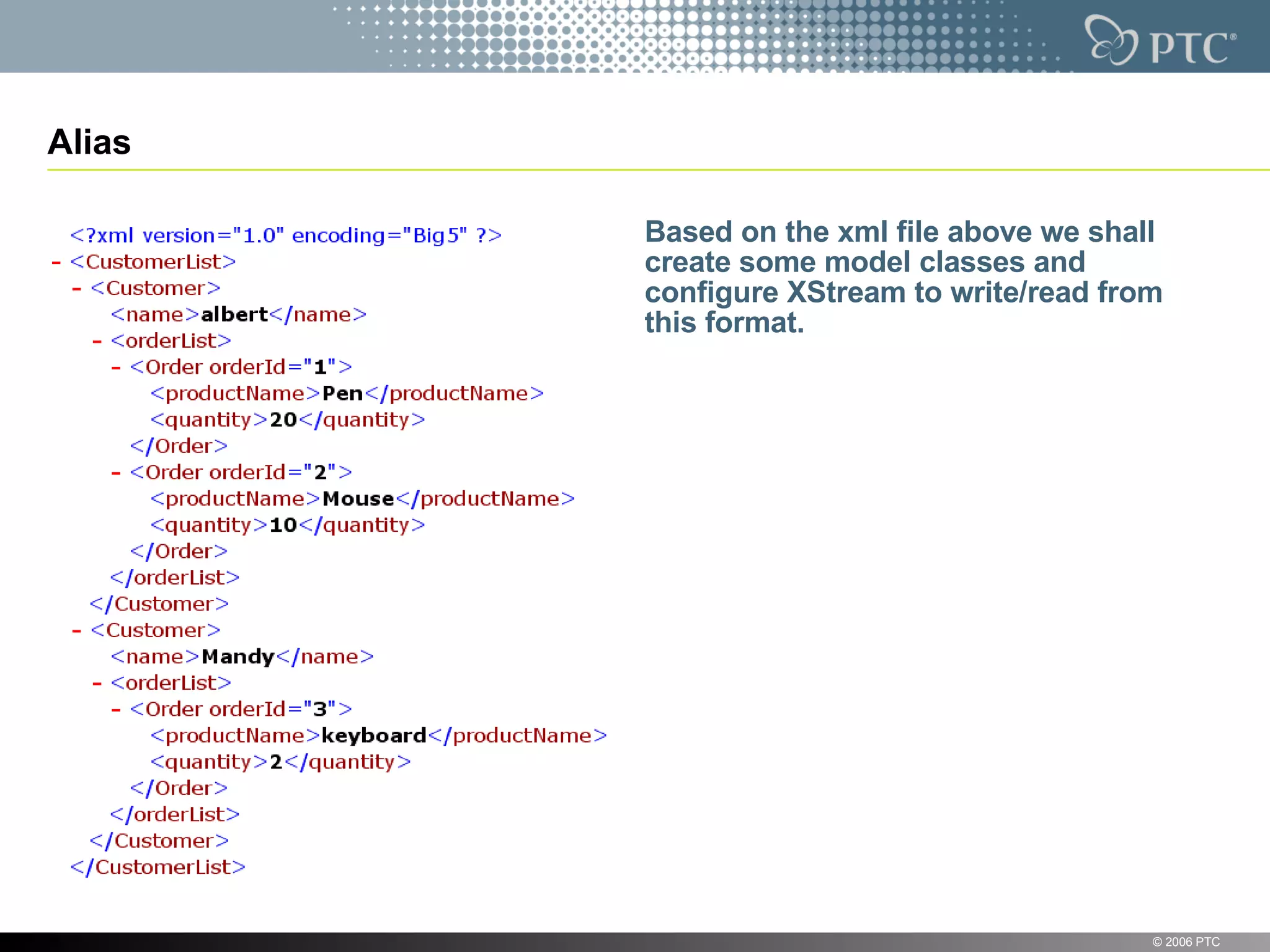
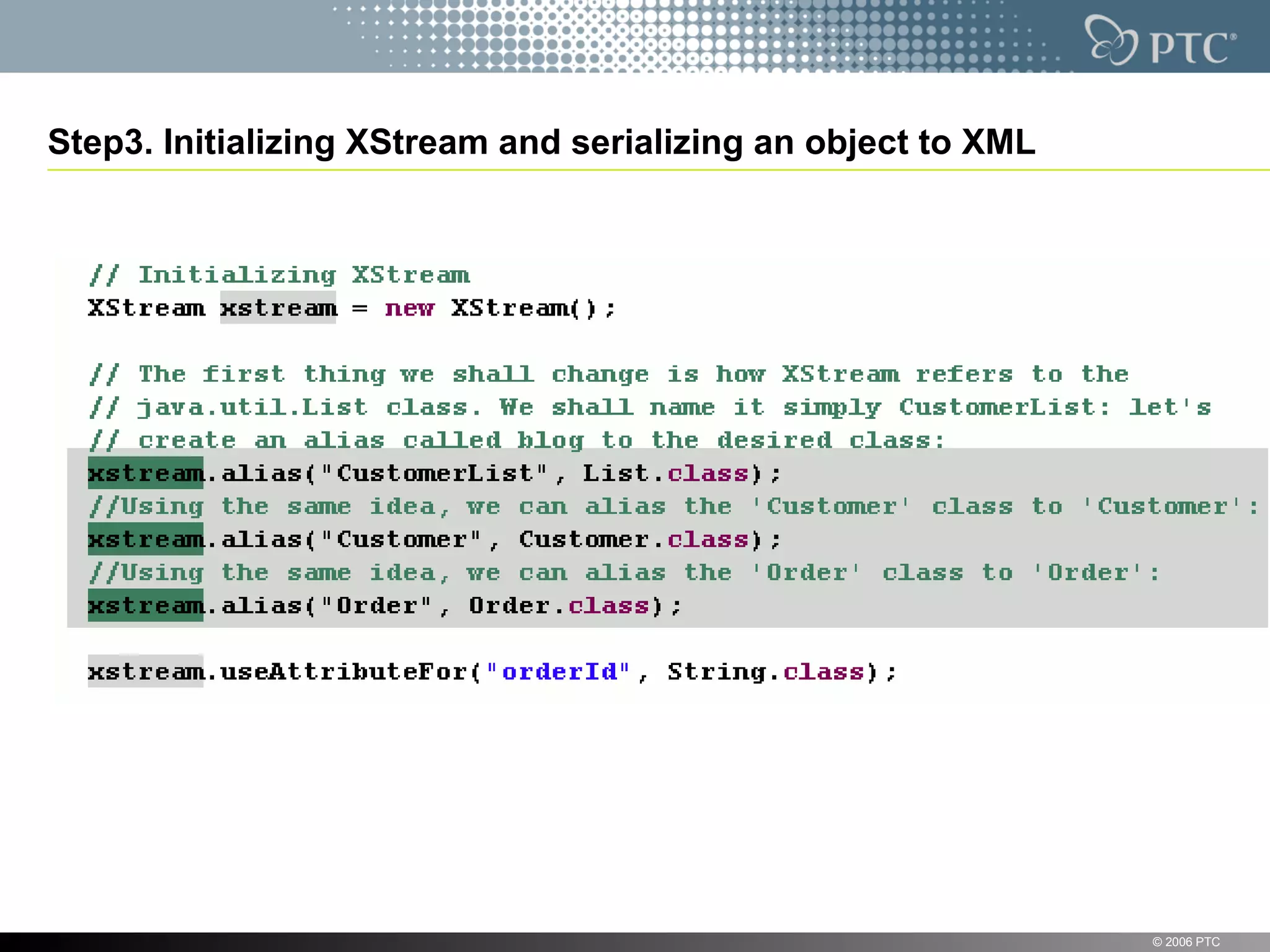
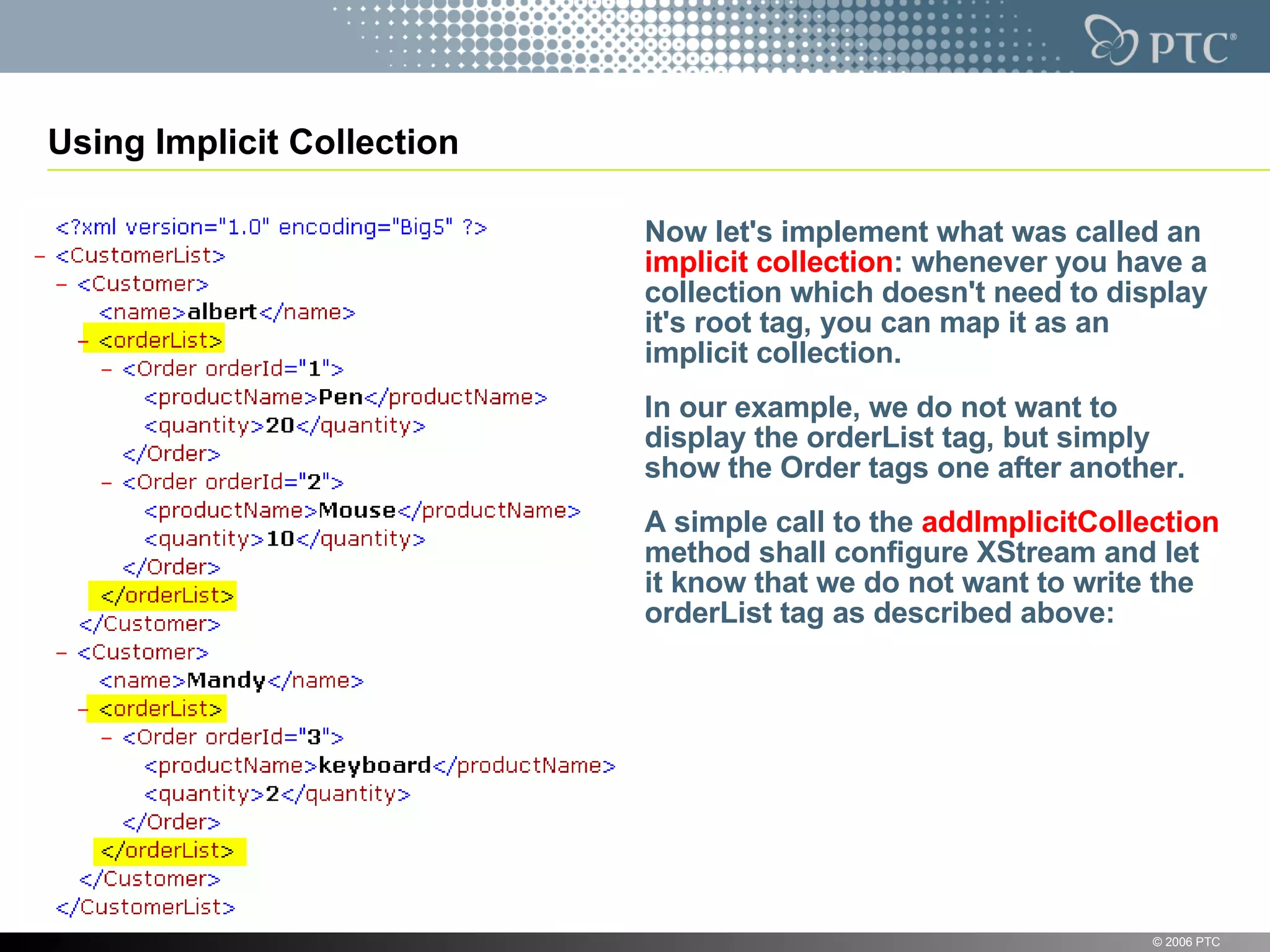
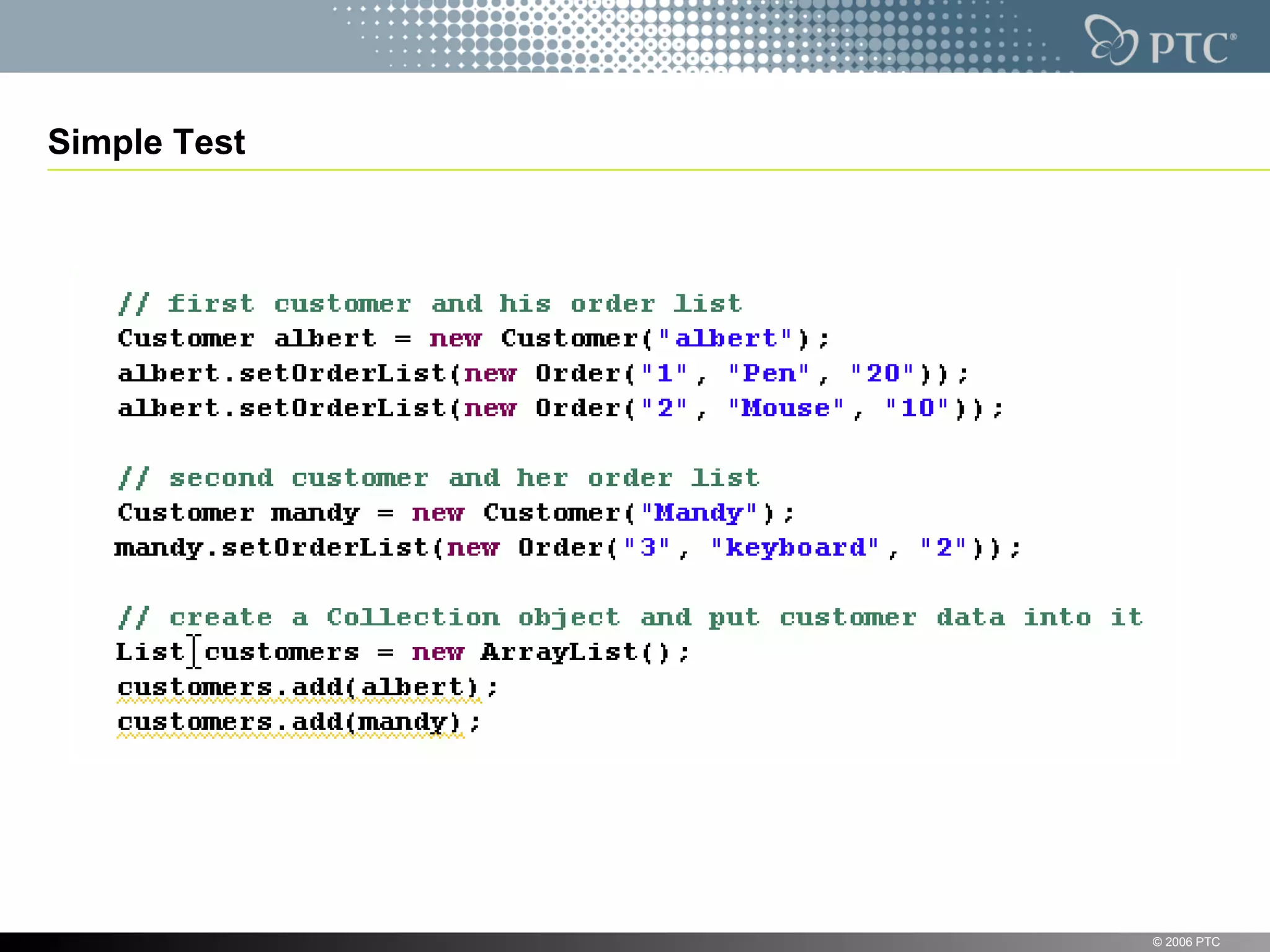
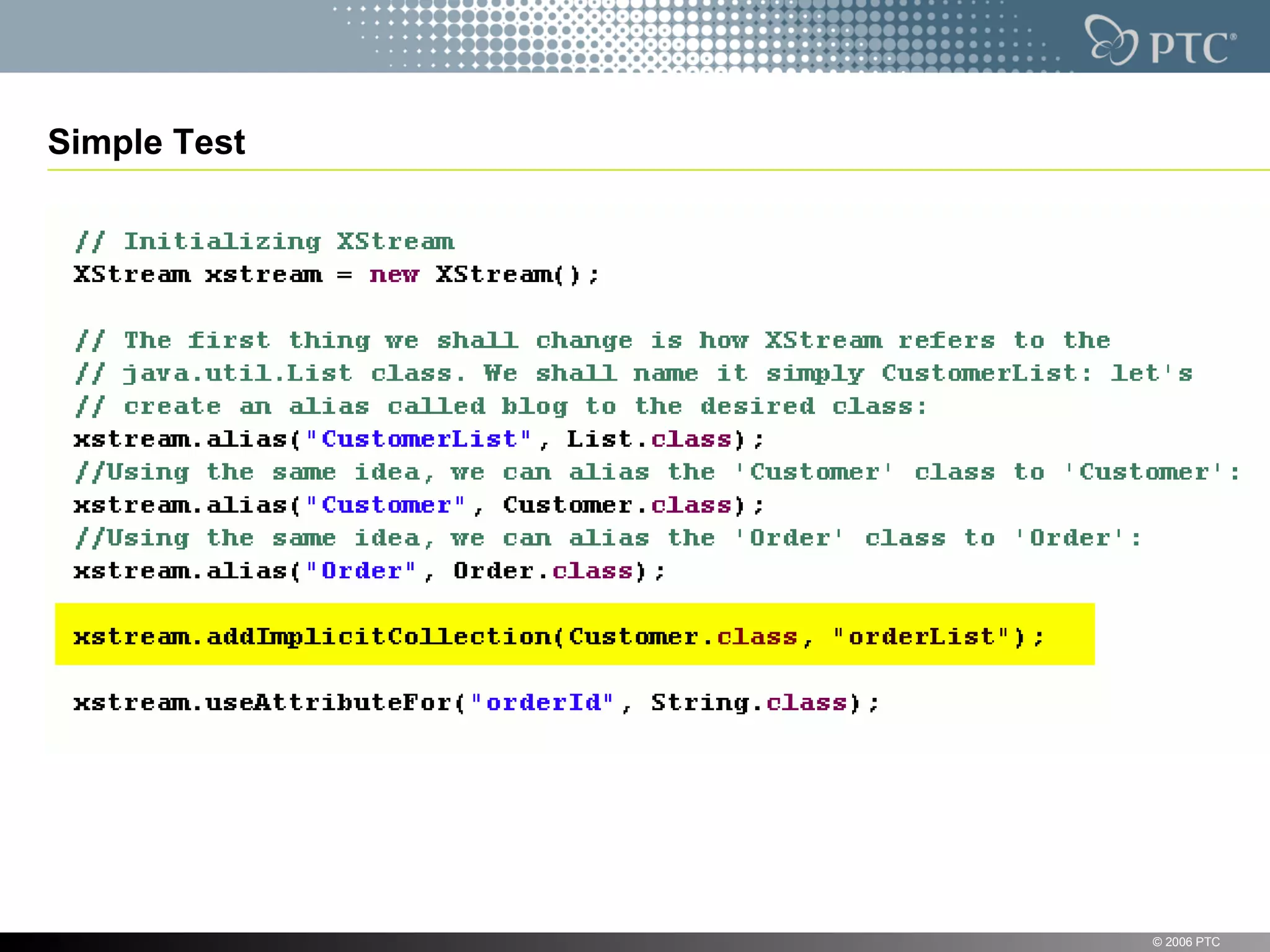
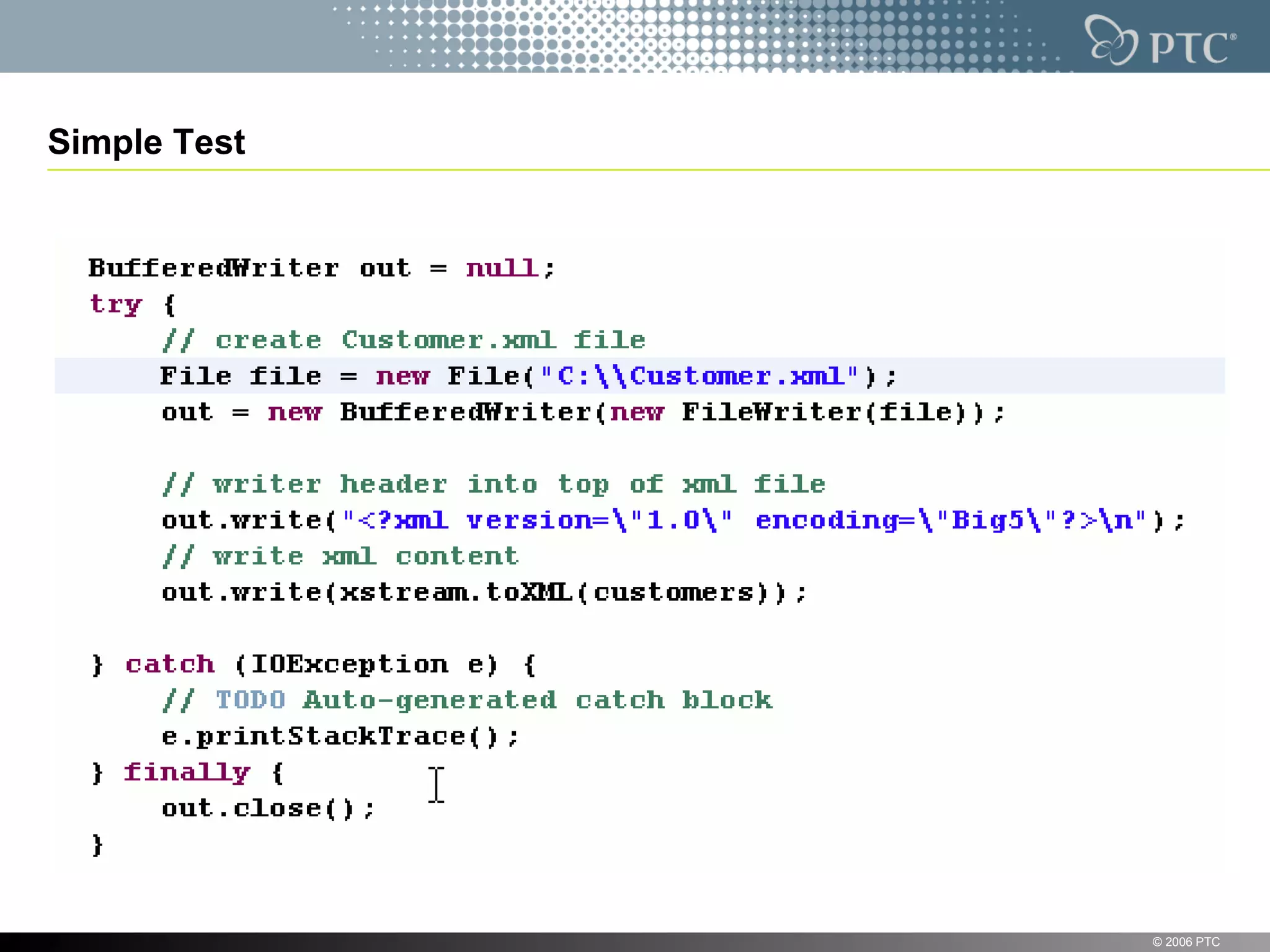
XStream is a library for serializing Java objects to XML and back again. It allows any object to be serialized to XML without requiring the object's classes to be modified. XStream handles serialization of object graphs, duplicate references, and circular references. It provides a simple API and performs serialization without needing mappings or configuration for most common cases. The document provides examples of using XStream to serialize Java objects to XML and deserialize XML back into objects.
![XStream Quick Start Albert Guo [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/xstream-quick-start-1215225952272636-9/75/XStream-Quick-Start-1-2048.jpg)