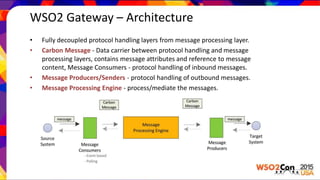
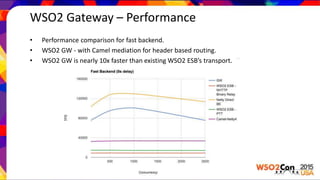
WSO2 Gateway is a high performance message gateway that encapsulates messaging between disparate systems. It uses a fully decoupled architecture with the Carbon Message as the data carrier between protocol handling layers and the message processing engine. The gateway supports thousands of concurrent HTTP/S connections using Netty and Disruptor for high performance. It can route messages using Apache Camel and define REST APIs. Performance tests show it is around 10x faster than the existing WSO2 ESB and can handle more concurrent connections. The gateway is targeted for use in API gateways, load balancers and other integration patterns.


![Motivations
• Paradigm shifts in Non-blocking IO, message/event processing,
concurrent programming - Netty, Disruptor, Java 8, Reactive
Programming.
• Research work - Siddhi CEP based ESB, axis2-Netty transport.
• Overcome the limitations of axis2, synapse etc.
• Reuse the prior knowledge and experience of building high
performance messaging systems to build a better message
Gateway from the ground up.
[1] https://github.com/kasun04/siddhi-esb](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wso2-gw-151105063012-lva1-app6891/85/WSO2-Gateway-4-320.jpg)
![Objectives
• To build a high performance, lightweight and reusable message
Gateway based on Gateway Pattern[1]
• To be used as the foundation component of ESB, API GW, Load
Balancer, Security GW, File GW etc.
[1] http://martinfowler.com/eaaCatalog/gateway.html](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wso2-gw-151105063012-lva1-app6891/85/WSO2-Gateway-5-320.jpg)


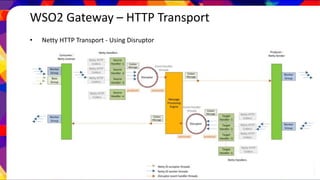
![WSO2 Gateway – HTTP Messaging
• WSO2 Gateway uses Netty based HTTP transport implemented on
message WSO2’s Pass-Thru (PT) architecture [1].
• Overcoming the consumer/producer contention in PT shared
buffer/pipe with a new blocking queue and ring buffer architecture
(Disruptor).
[1] http://wso2.com/library/articles/2013/12/demystifying-wso2-esb-pass-thru-transport-part-ii/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wso2-gw-151105063012-lva1-app6891/85/WSO2-Gateway-9-320.jpg)






![Gateway in Microservices Architecture
• API Gateway is used in most real world microservice
implementations to front microservices.
– Eg Netflix API GW[1]
[1] Source : http://microservices.io/patterns/apigateway.html](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wso2-gw-151105063012-lva1-app6891/85/WSO2-Gateway-18-320.jpg)