The document summarizes the configuration of UltraESB transports and security features. It describes the key components for configuring transports like HTTP, JMS, and file-based transports. It also provides details on configuring security aspects like HTTP authentication, SSL, WS-Security, and XACML authorization. The root configuration file ultra-root.xml defines core Spring beans and properties.











![UltraESB is a Spring application
● In reality, UltraESB is a Spring application
● The standalone deployment is always
recommended
● The [almost never used] Web container
deployment model too triggers Spring
initialization
– This should ONLY be used where JTA XA is
required over a JEE server such as Jboss](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/configuration-system-160317122345/85/System-Configuration-for-UltraESB-14-320.jpg)
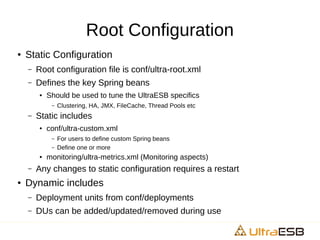


![Setting System Properties
● Sometimes, easier to define/manage within config
– e.g. MQ connectivity over SSL
<bean id="system-properties" class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.MethodInvokingFactoryBean">
<property name="targetObject" value="#{@systemProperties}" />
<property name="targetMethod" value="putAll" />
<property name="arguments">
<util:properties>
<prop key="javax.net.ssl.keyStore">conf/keys/esb.jks</prop>
<prop key="javax.net.ssl.keyStorePassword">password</prop>
<prop key="javax.net.ssl.trustStore">conf/keys/esb.jks</prop>
<prop key="javax.net.ssl.trustStorePassword">password</prop>
</util:properties>
</property>
</bean>
● [Note: System properties can be also set though the conf/wrapper.conf; or via the bin/ultraesb.sh during
development]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/configuration-system-160317122345/85/System-Configuration-for-UltraESB-18-320.jpg)