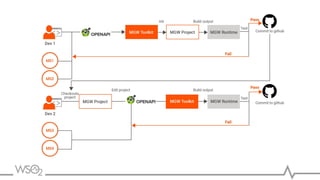
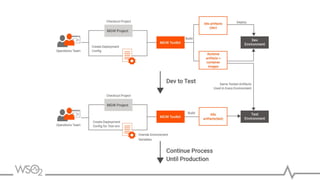
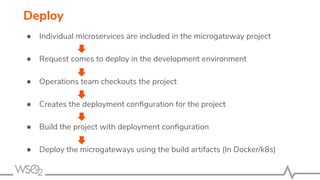
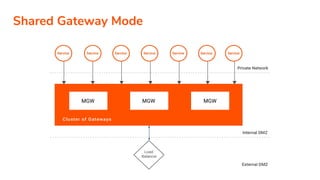
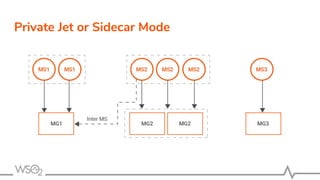
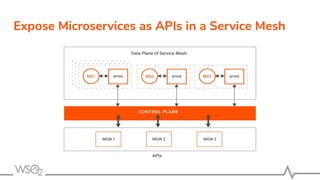
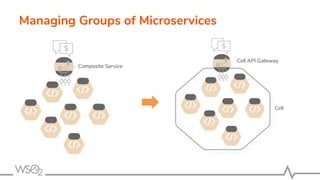
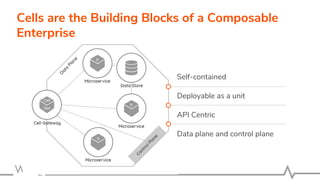
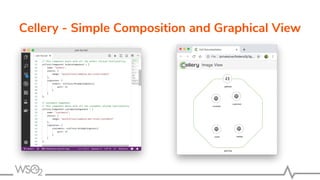
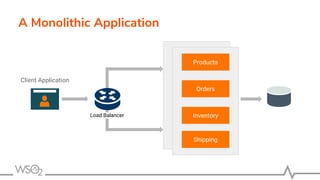
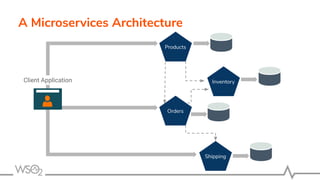
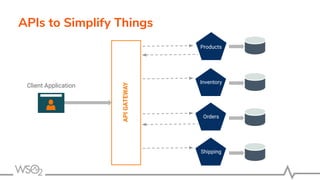
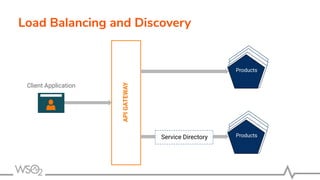
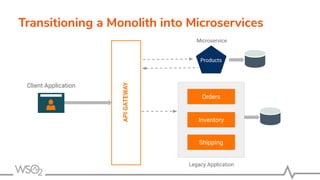
The document discusses WSO2 API Microgateway's role in managing microservices architecture, highlighting its features such as scalability, cloud-native capabilities, and support for CI/CD. It outlines the benefits of microservices, like increased agility and failure isolation, while also addressing the complexities and liabilities associated with deployment. The document also covers operational workflows and integration patterns for microservices within a service mesh environment.










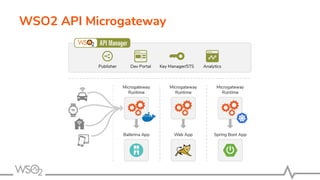

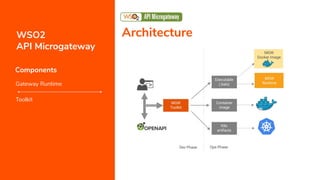


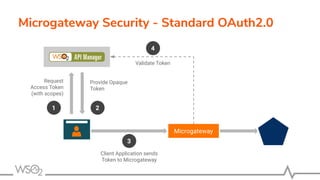
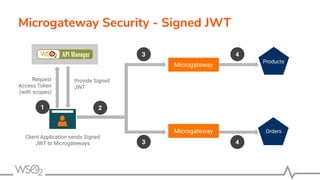
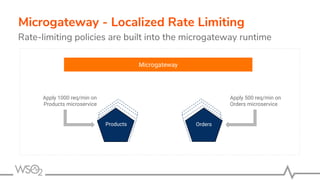
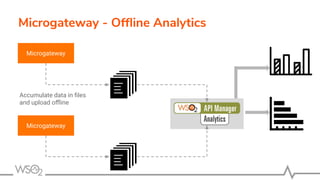
![● Serves the requests applying
○ Security, Rate limiting, Transformations, Analytics, and more
● Available as archived distributions as well as docker images [1]
● Can be built by burning APIs into container images to spawn immutable
containers
● Runs on top of artifacts generated by the toolkit
[1]- https://hub.docker.com/r/wso2/wso2micro-gw
Runtime](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/apimanagementinmicroservicesarchitecture-191029110253/85/Workshop-API-Management-in-Microservices-Architecture-25-320.jpg)