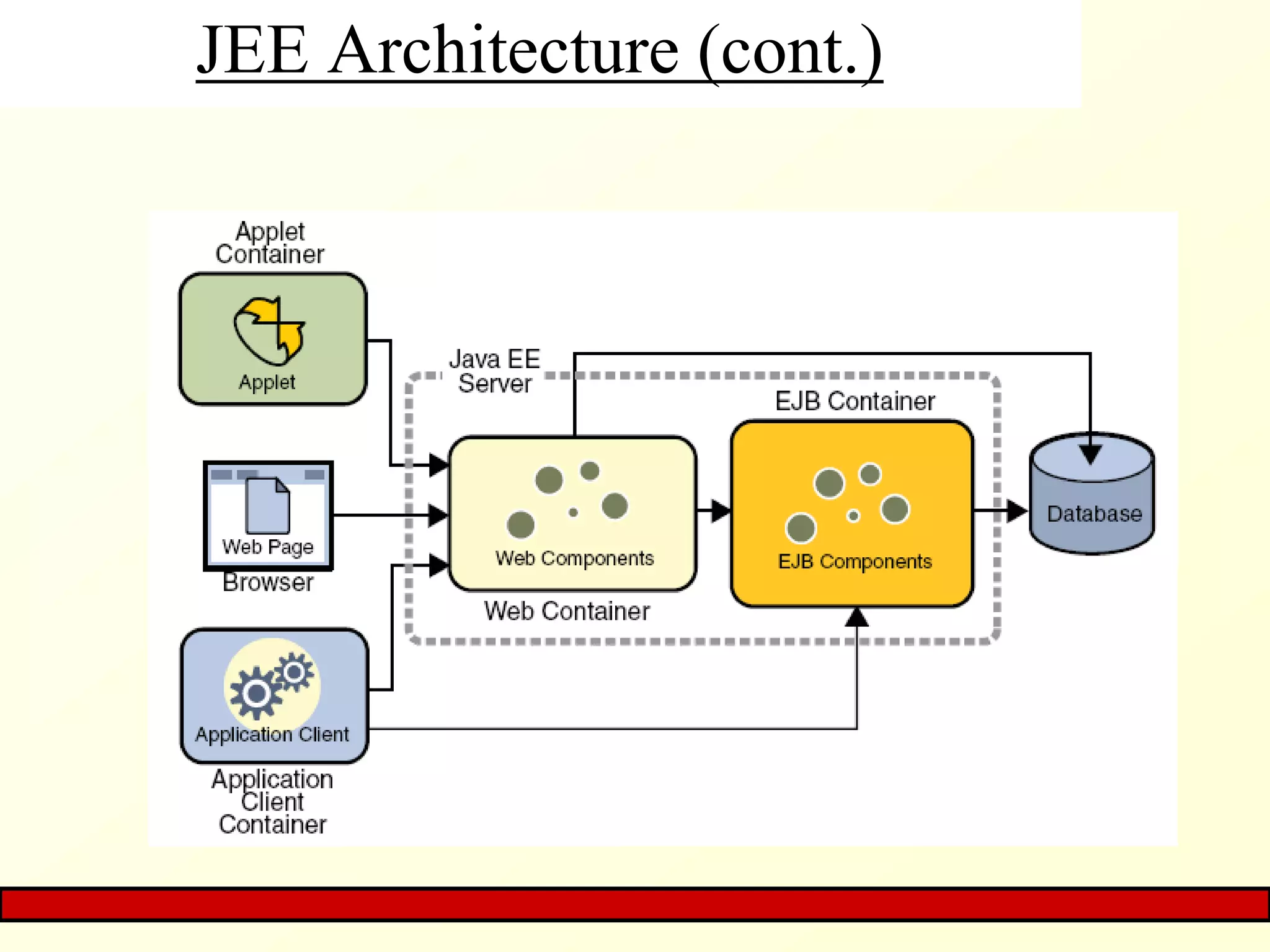
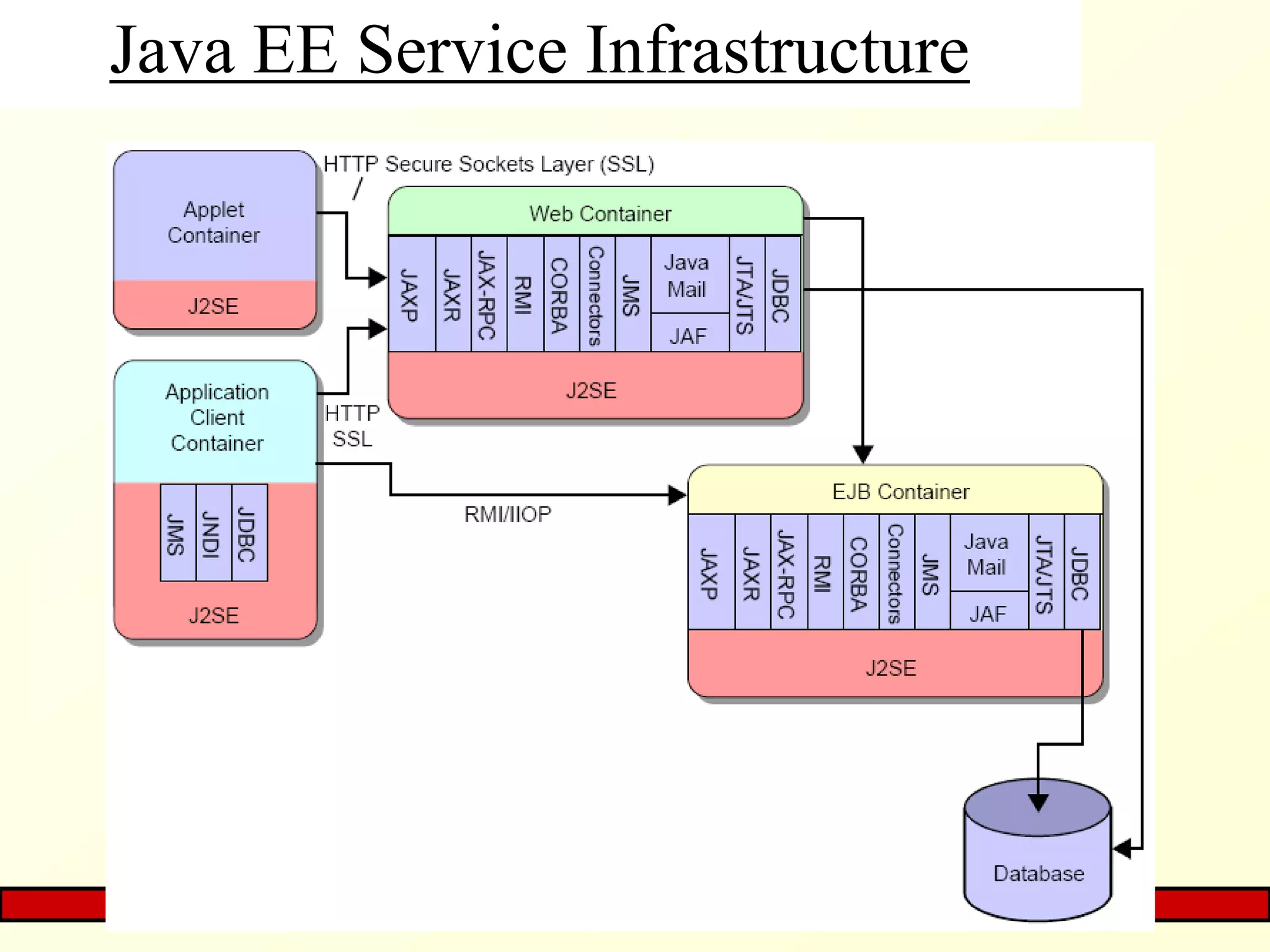
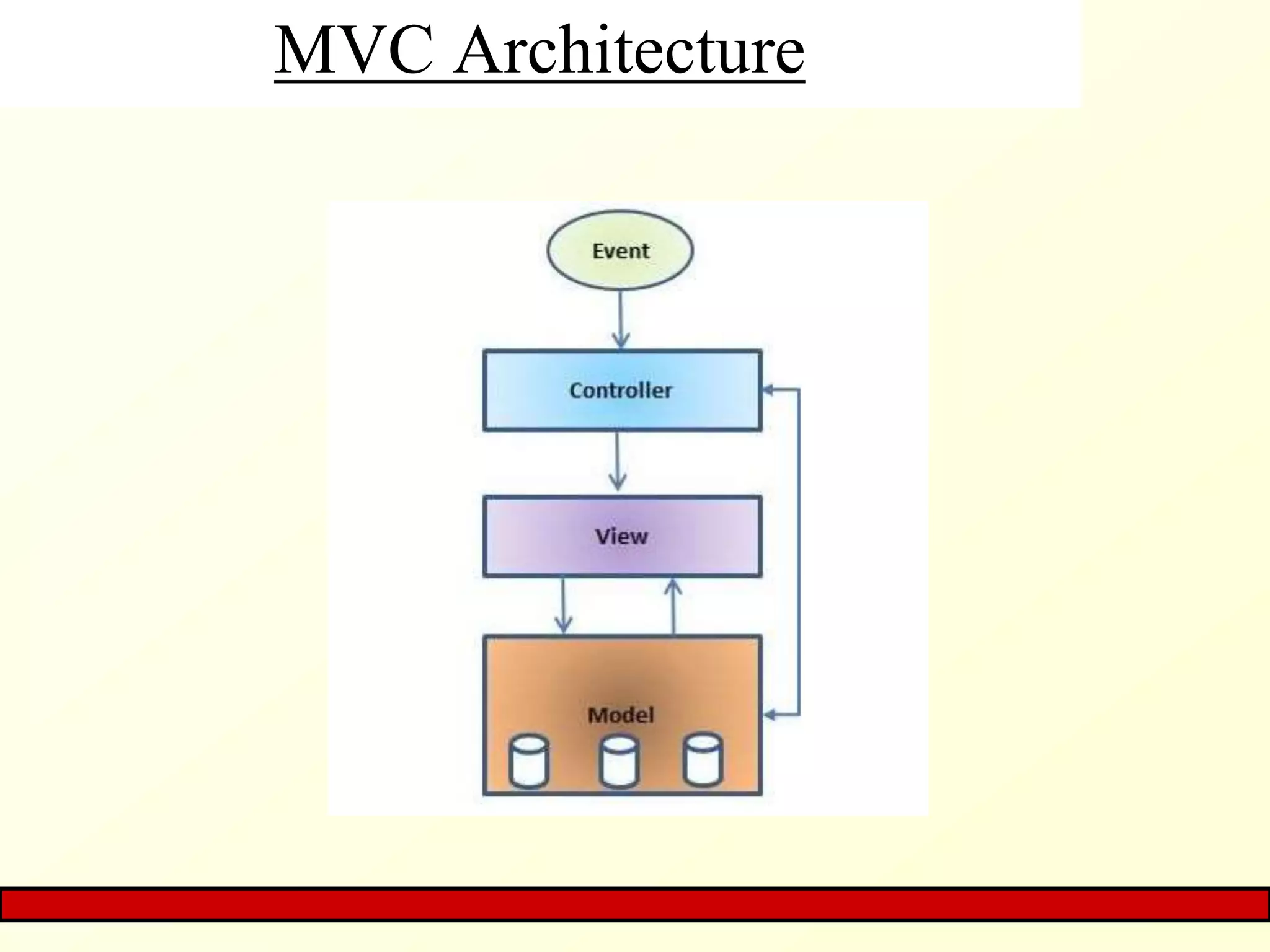
The document provides an overview of Java EE, focusing on its three-tier and MVC architecture, which simplifies server-side application development. It outlines Java EE container services, including deployment, inherent, vendor-specific, and API-based functionalities, as well as the MVC application's structure and benefits. The summary emphasizes the architecture's advantages, such as maintenance and testing, while noting the potential complexity of application development.