The document summarizes assessment activities and initiatives at Middlesex Community College to improve student writing skills and success. It describes:
1) Revisions to pedagogy and curriculum to embed writing skills and student success behaviors through initiatives like writing coaches, vertical teaming, and an Accelerated Learning Program.
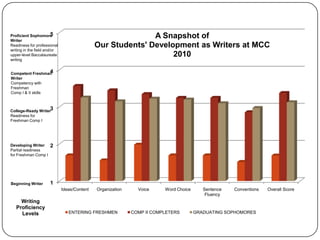
2) Assessment results of student writing from 2007 and 2010 that show percentages of students at adequate or above levels in areas like ideas, organization, and grammar.
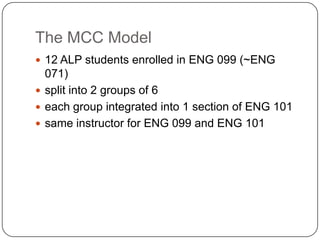
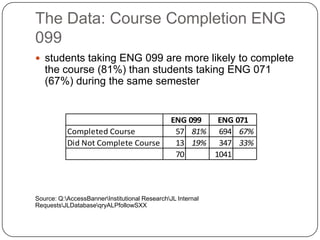
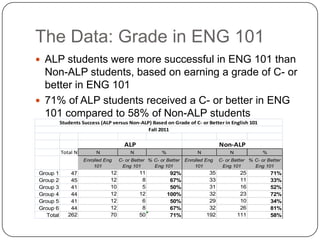
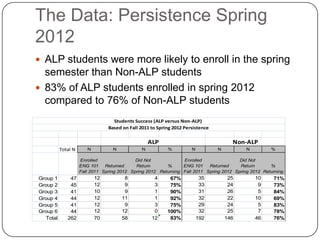
3) The Accelerated Learning Program which allows students to take English Composition I and a writing skills seminar concurrently, and data showing higher completion rates for students in this program compared to others.