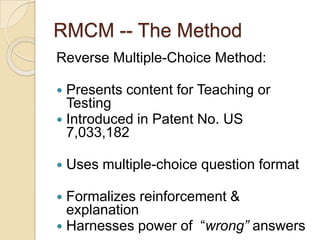
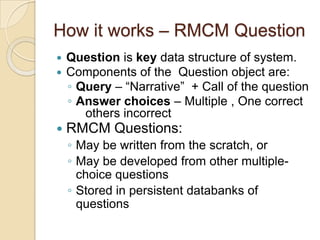
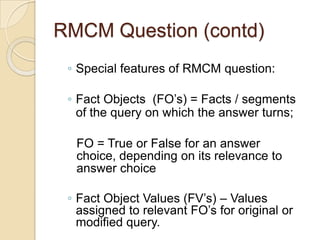
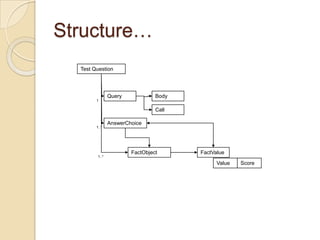
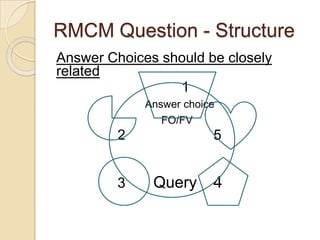
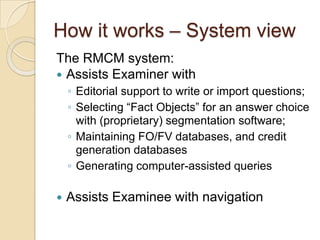
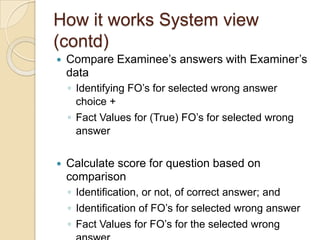
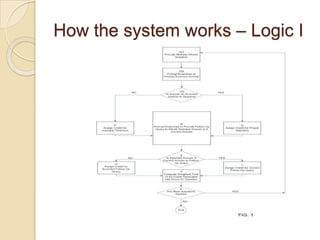
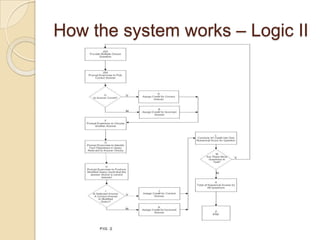
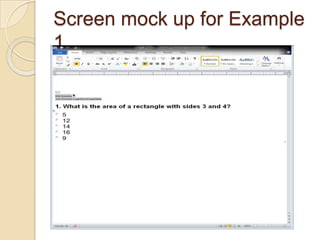
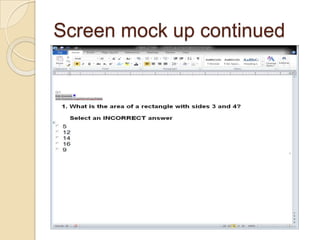
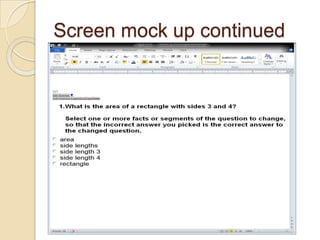
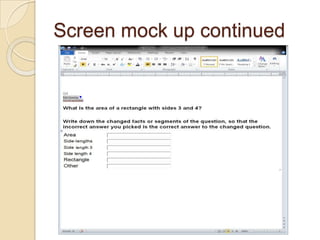
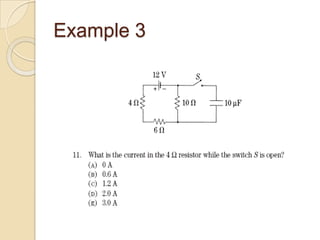
The Reverse Multiple-Choice Method (RMCM) presents content for teaching or testing using a multiple-choice question format. It formalizes reinforcement and explanation by requiring examinees to identify why answers are correct or incorrect, and modify incorrect answers by changing facts to make them correct. This forces analysis and comparison of concepts. RMCM aims to harness the power of "wrong" answers and be more efficient than open-ended questions while allowing automated scoring.