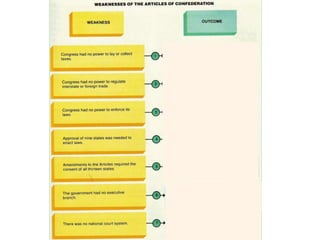
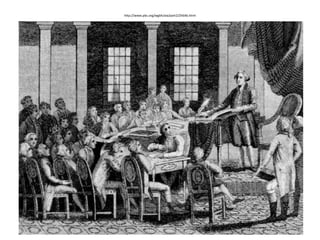
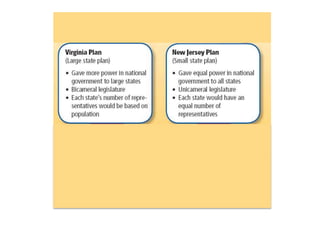
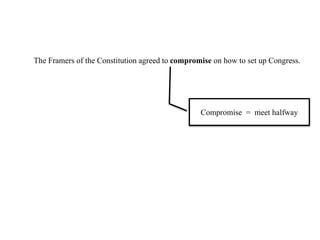
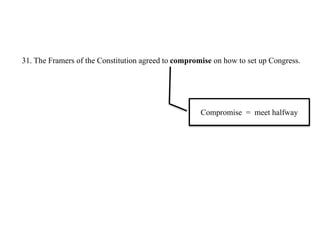
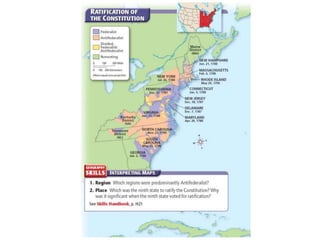
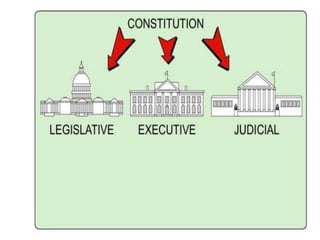
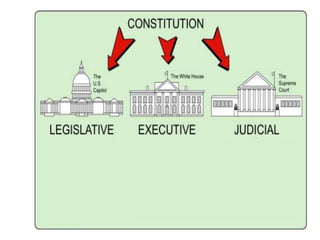
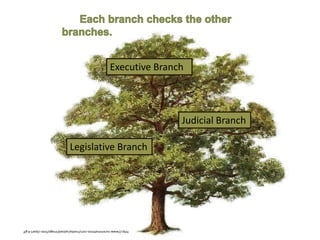
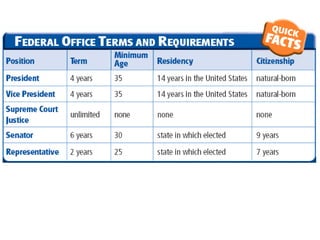
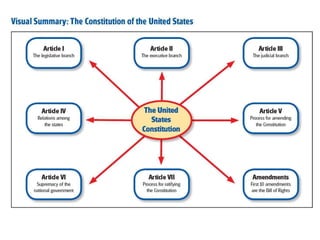
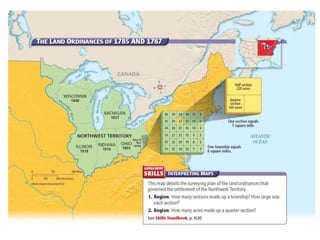
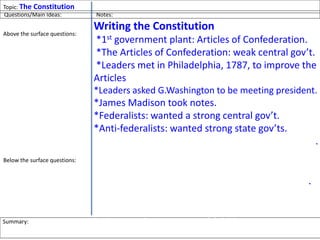
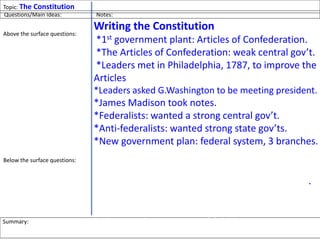
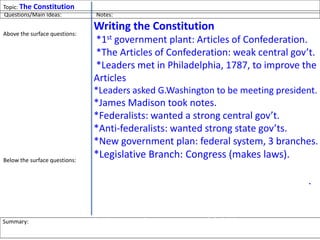
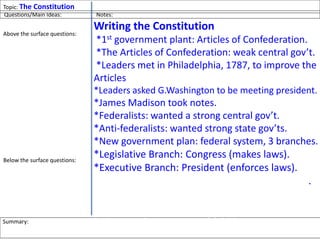
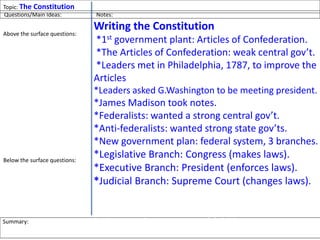
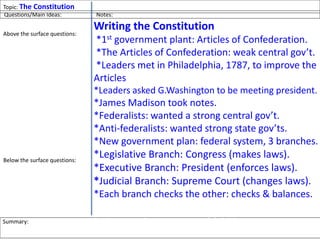
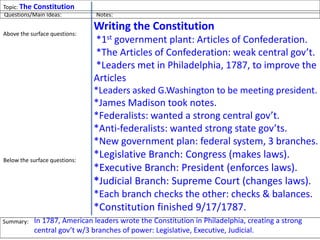
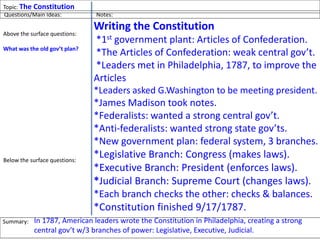
After declaring independence in 1776, the United States created a government plan called the Articles of Confederation, which was ultimately deemed ineffective due to its inability to collect taxes and provide strong governance. In 1787, delegates convened in Philadelphia to draft a new constitution, replacing the Articles with a stronger central government. This led to the establishment of the Constitution of the United States, addressing many issues faced under the previous system.