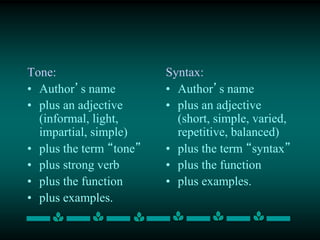
The document provides guidance on how to write a rhetorical analysis for an AP Lang & Comp essay. It defines rhetorical techniques as the effective use of words to persuade, and explains that a rhetorical analysis identifies and discusses how authors use specific techniques like ethos, logos, pathos, tone, diction, and syntax to create intended effects. The document advises analyzing the prompt, understanding the passage, selecting three techniques for analysis, and writing a thesis that identifies the effect and techniques. It also provides examples of analyzing and writing theses about diction, tone, and syntax.