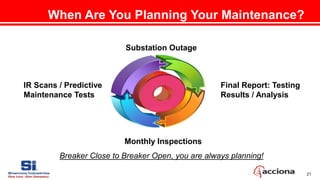
This document discusses planning for substation maintenance and reliability. It outlines key steps in the planning process including developing a robust maintenance plan, gathering data from inspections and tests, creating a detailed work scope, coordination between the owner and contractor during the proposal, pre-outage planning and outage stages, and reviewing test results after the outage. The goal is to plan maintenance properly to ensure safety, reliability and regulatory compliance while minimizing downtime.