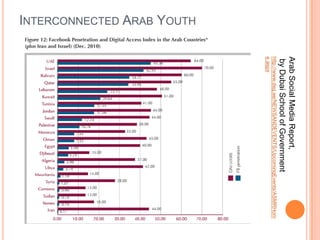
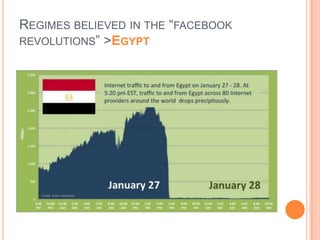
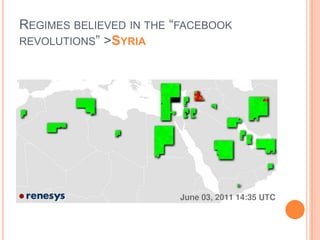
This document discusses the role of social media and new media in the Arab uprisings of 2011. It notes that new media played a key role in connecting protest movements, mobilizing masses through communication of rally points, and reinforcing the spread of uprisings across countries. Social media helped create a transnational public sphere where ideas and causes could spread more quickly. However, social media may also reinforce clashes of narratives rather than promote dialogue by aggregating people of similar views. The document concludes that Arab youth are interconnected globally but with local focus, empowered by new media, yet social media can also exacerbate divisions if not used to promote transparency and accountability.