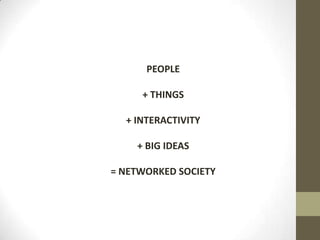
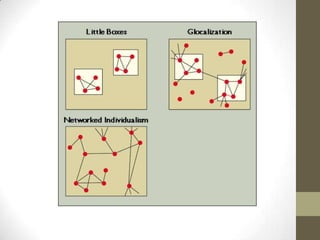
The document discusses the shift from hierarchical to networked societies as a result of increased digital communication technologies and social networks. It summarizes the key points made by Manuel Castells about the relationship between power, media, and communication in the network society. Specifically, it argues that (1) the media has become the social space where power is decided, (2) there has been a rise of mass self-communication through social media and blogs, and (3) mass media and communication networks are converging.