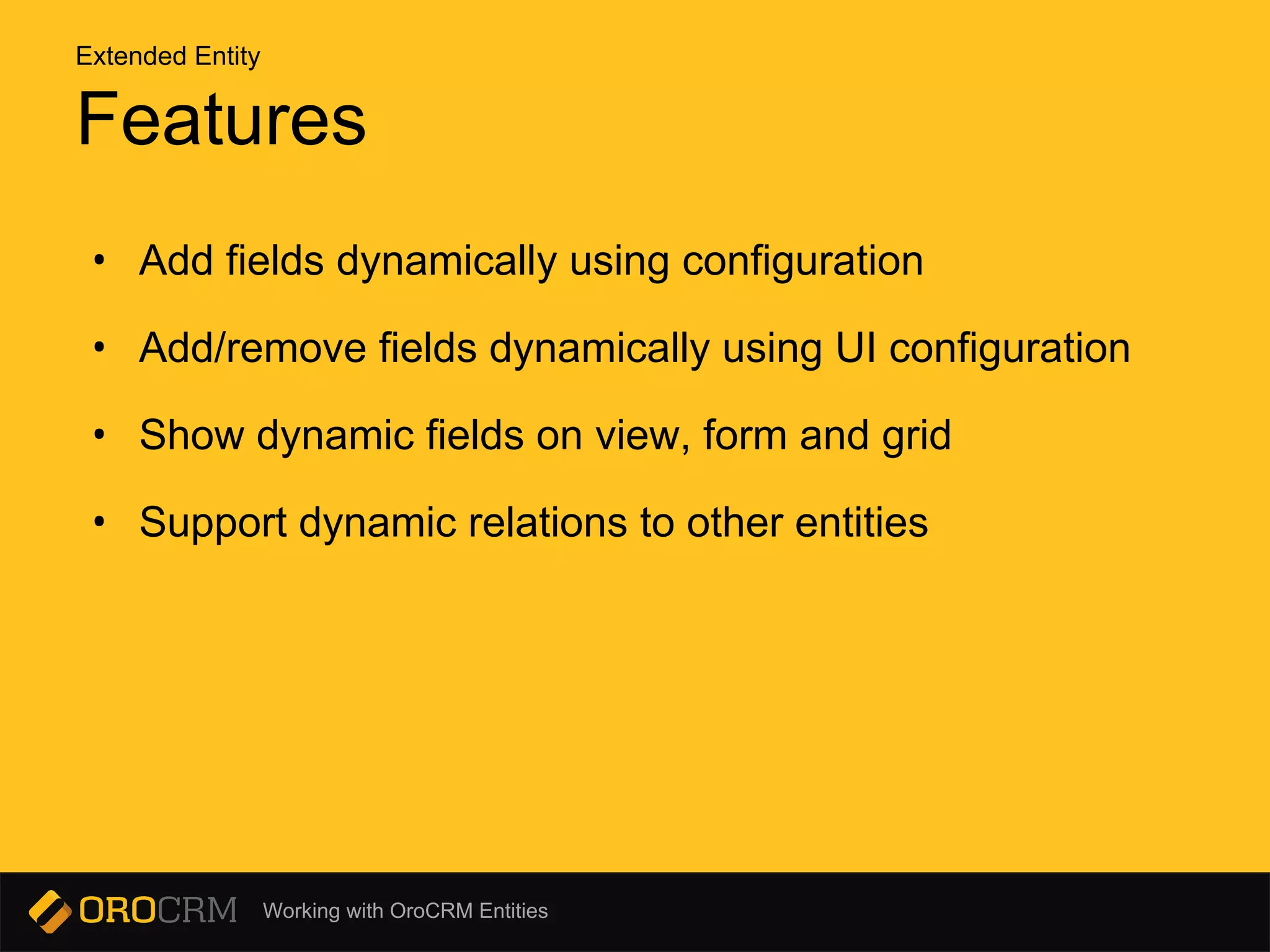
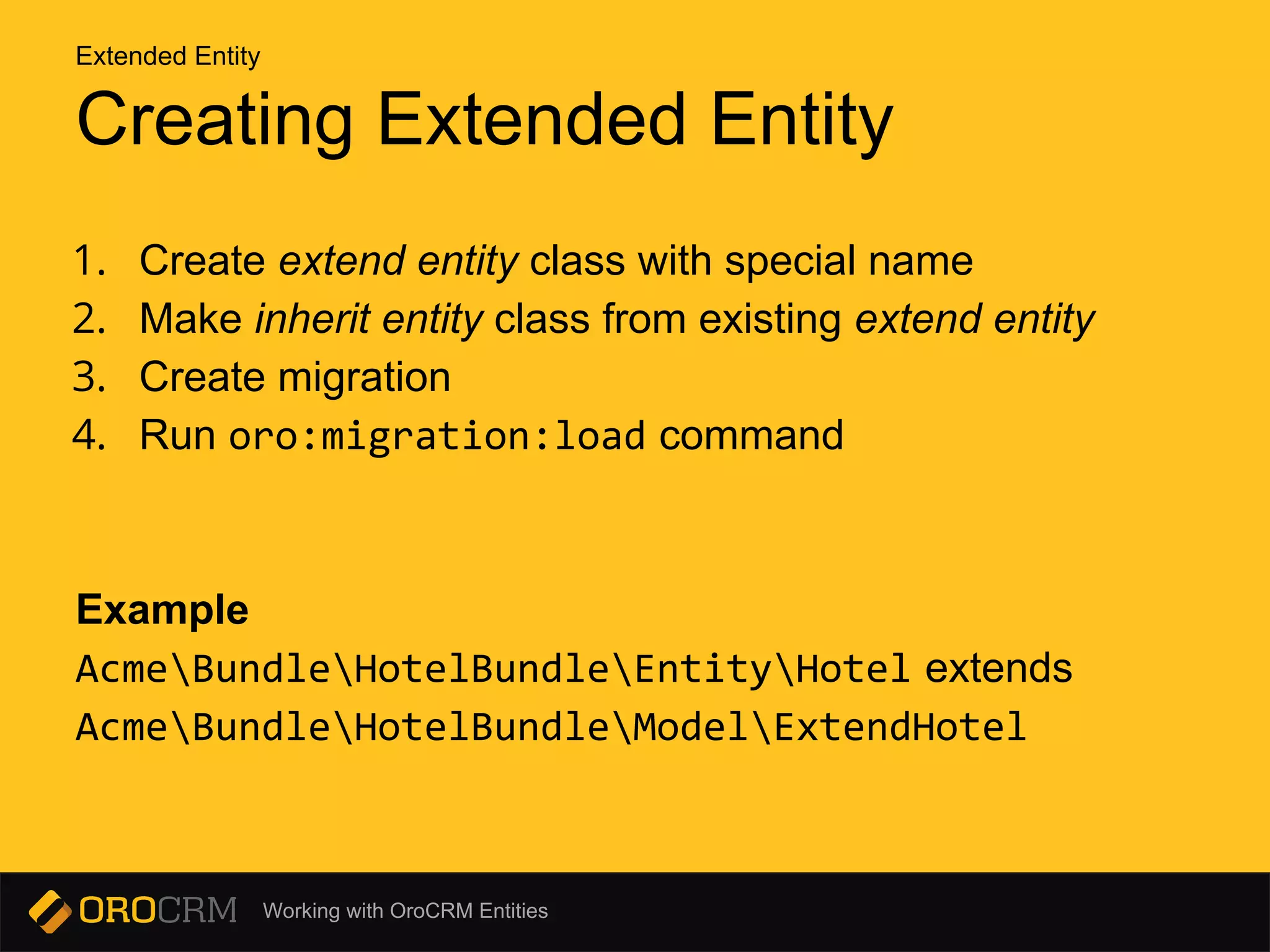
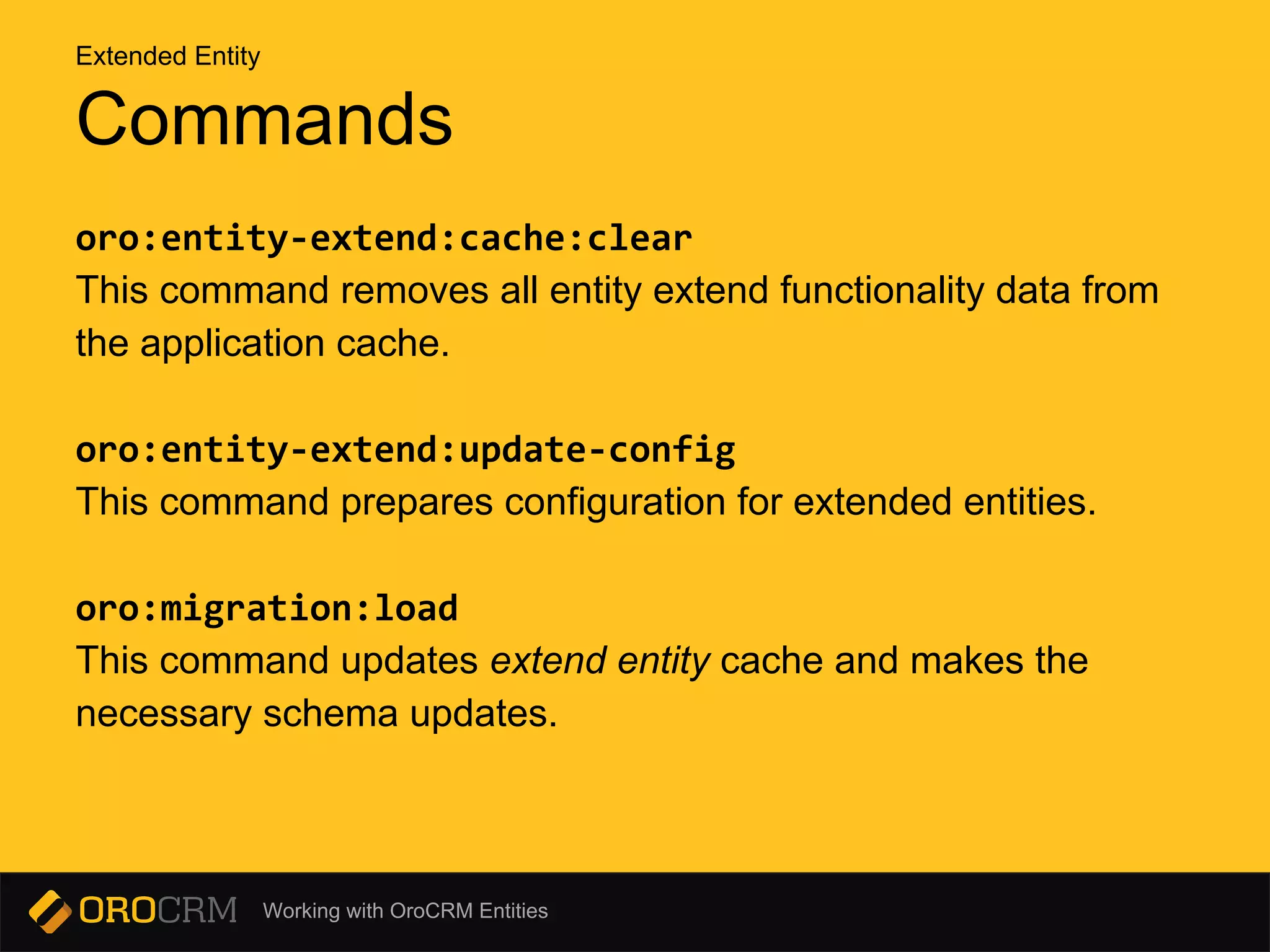
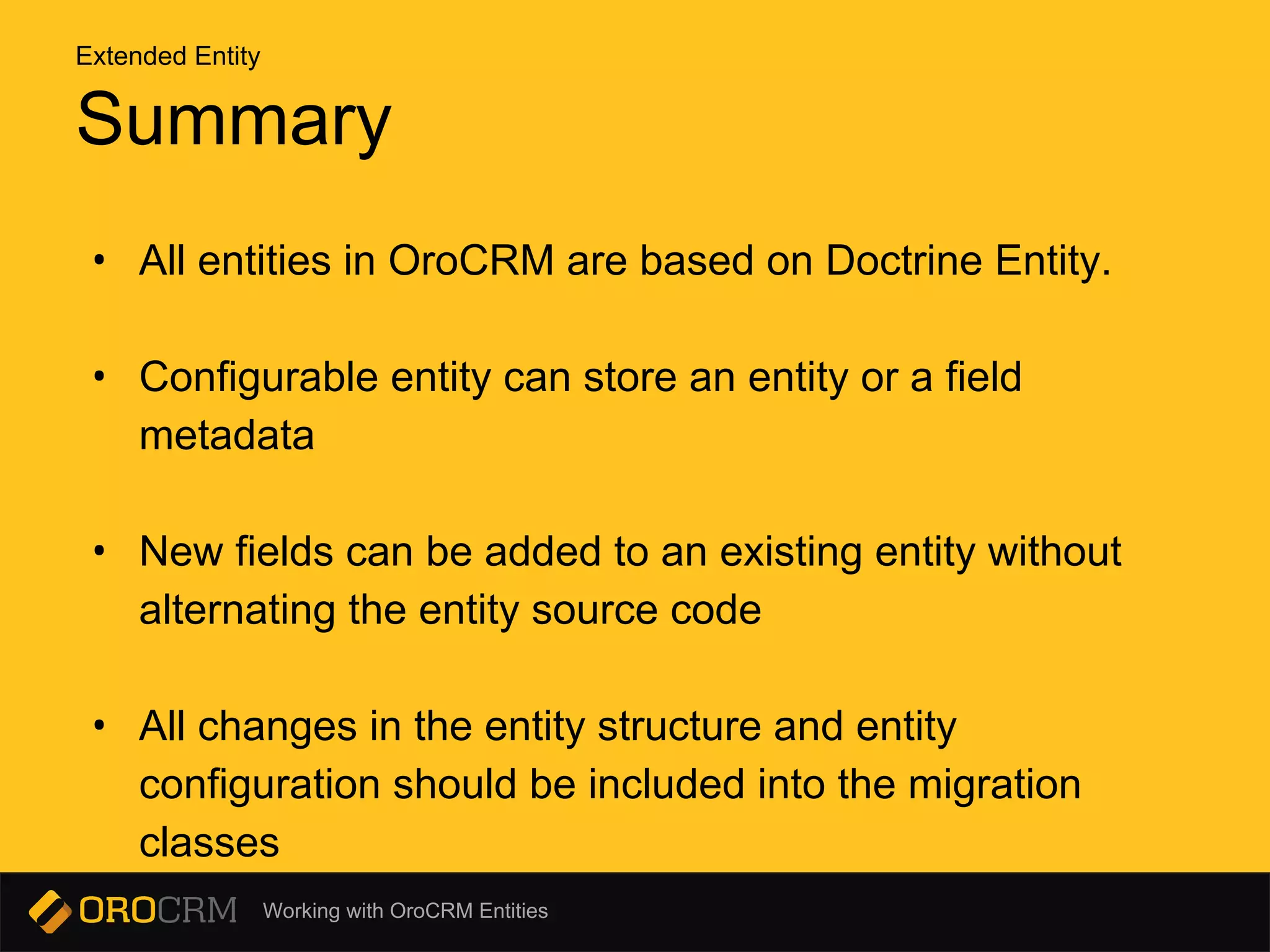
This document discusses different types of entities in OroCRM: doctrine entities, configurable entities, and extended entities. Doctrine entities are standard PHP objects that represent database tables. Configurable entities allow configuration of entities and fields through a configuration schema and provider service. Extended entities allow dynamically adding and removing fields to an existing entity through configuration or migrations without changing the source code. Commands like oro:migration:load are used to update the database schema and entity configurations.