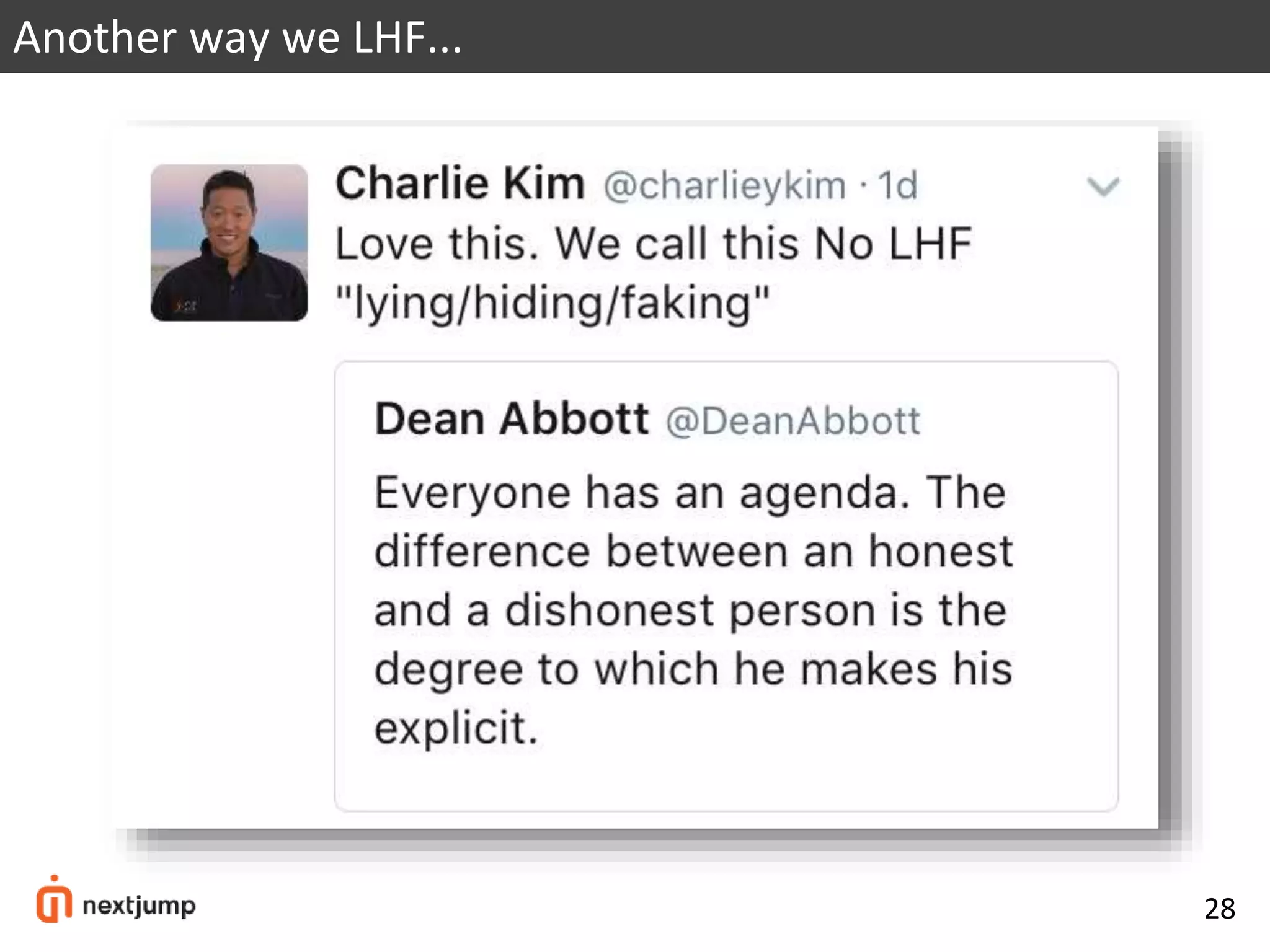
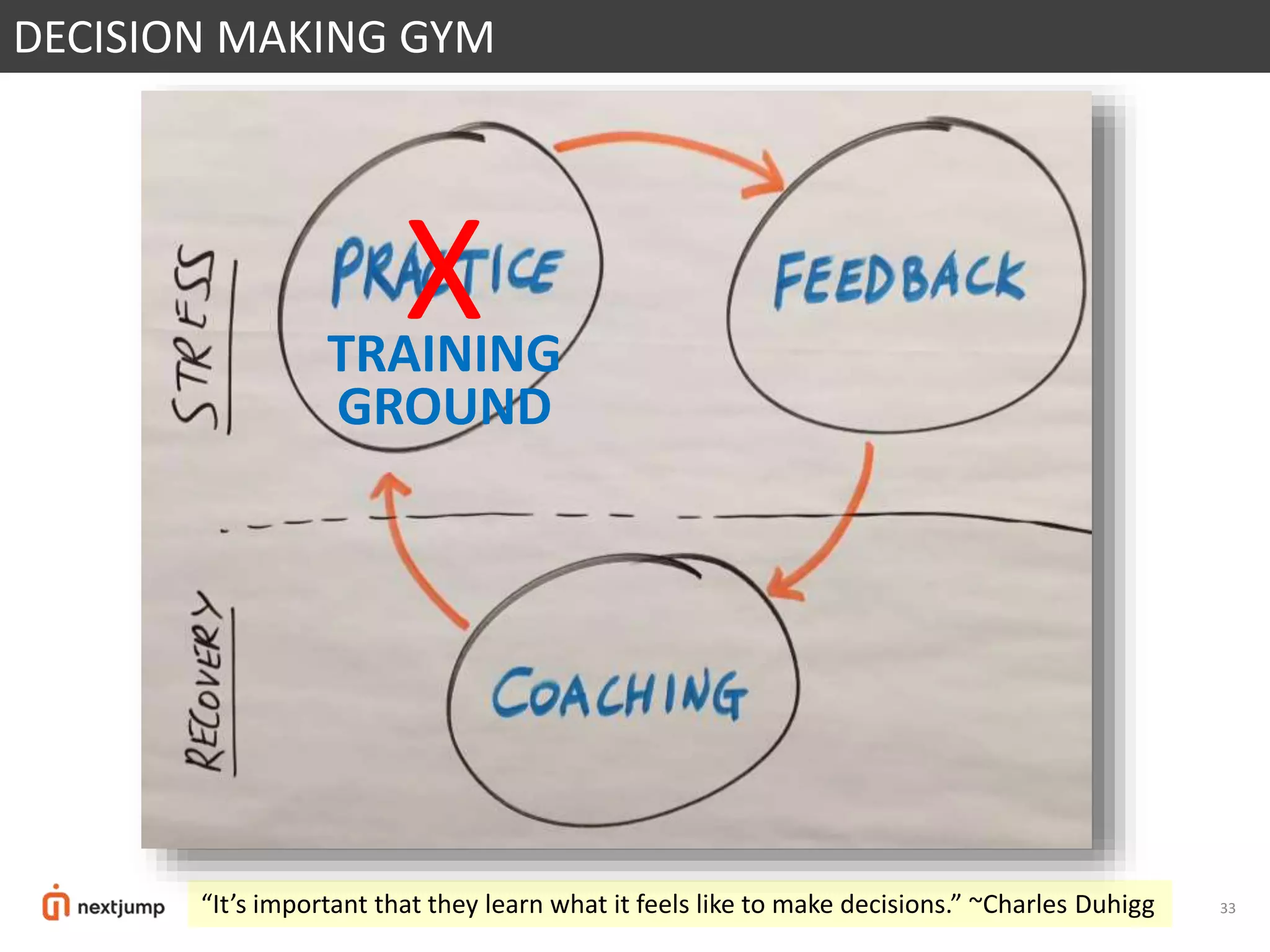
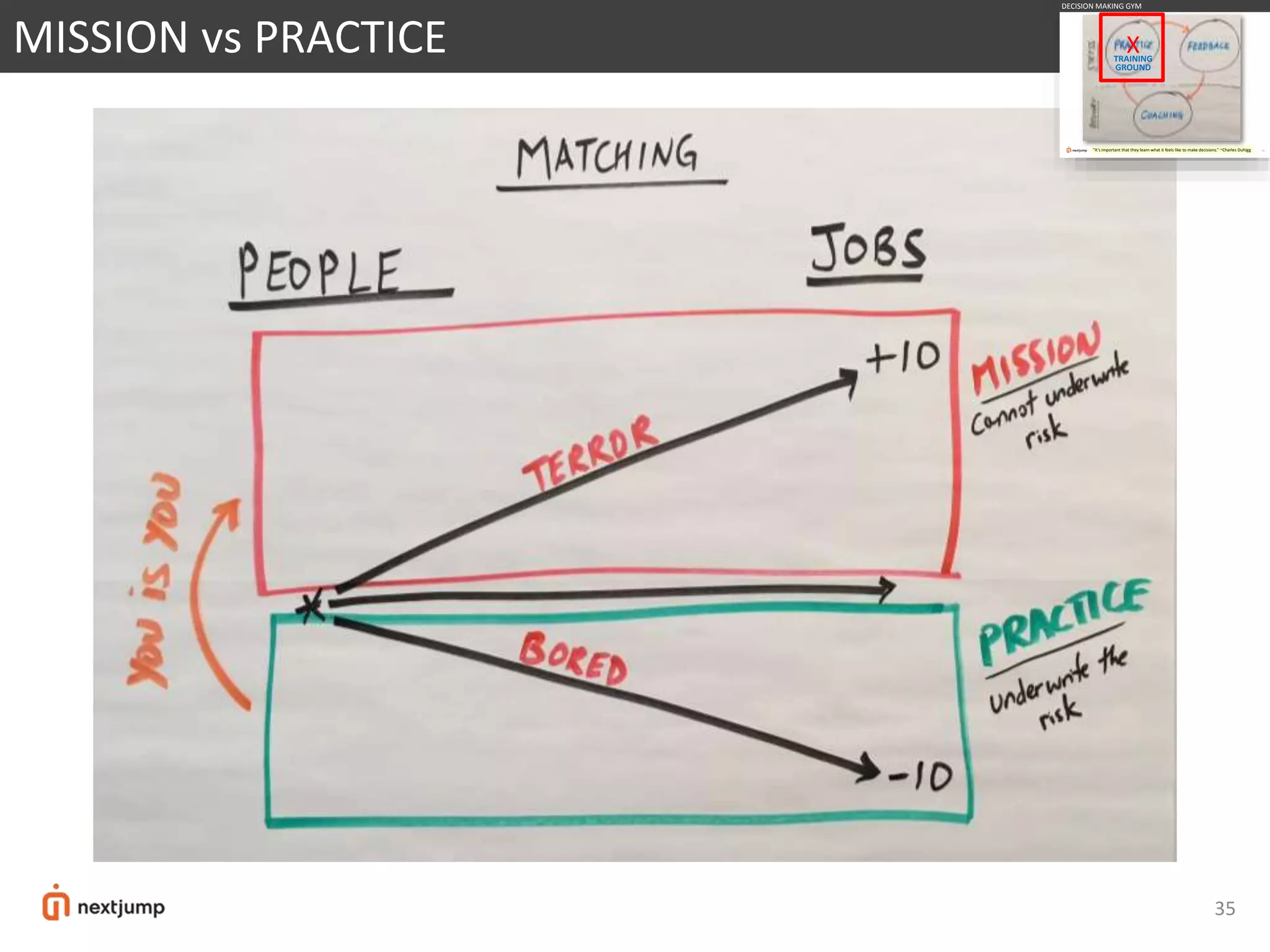
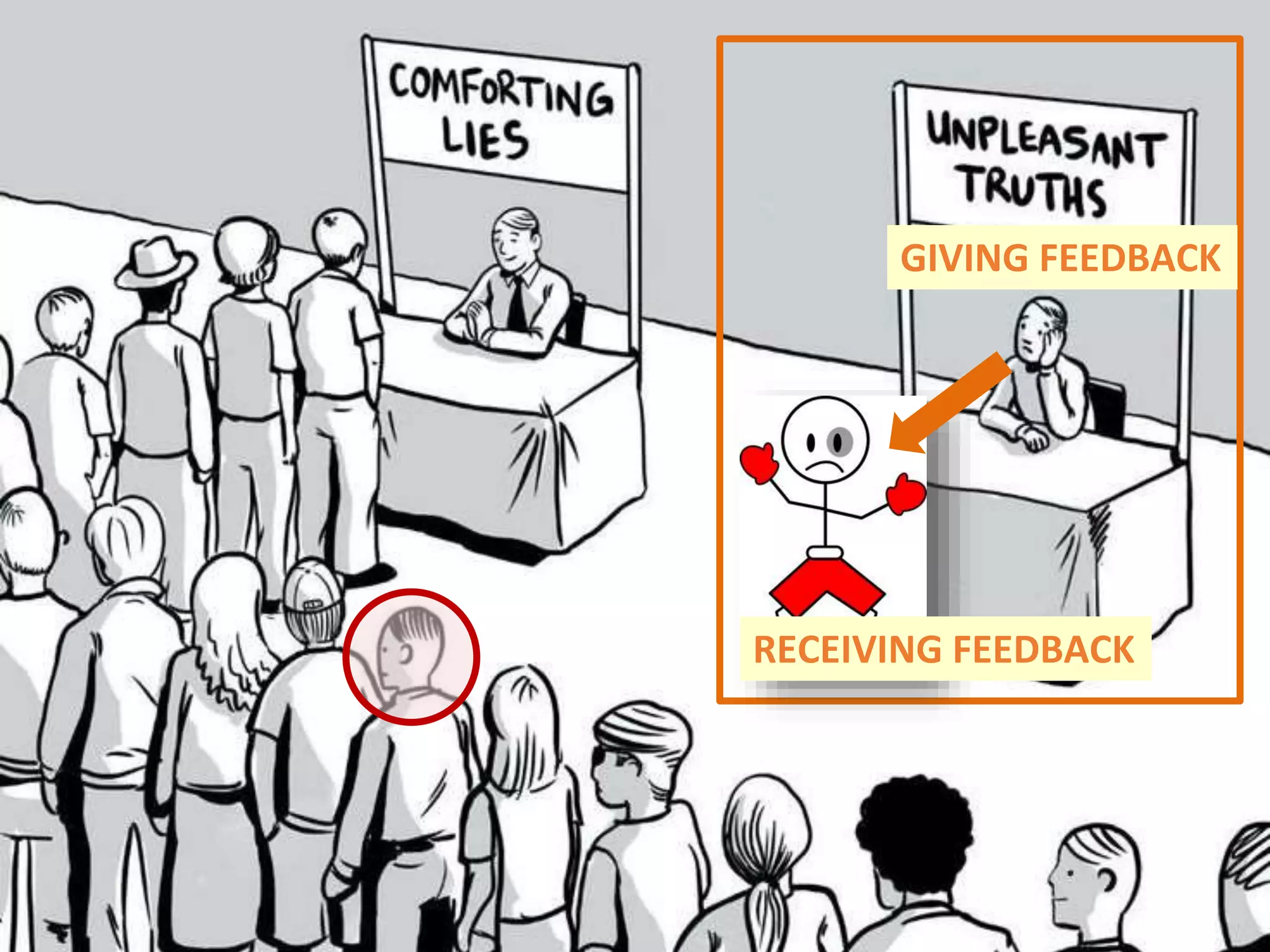
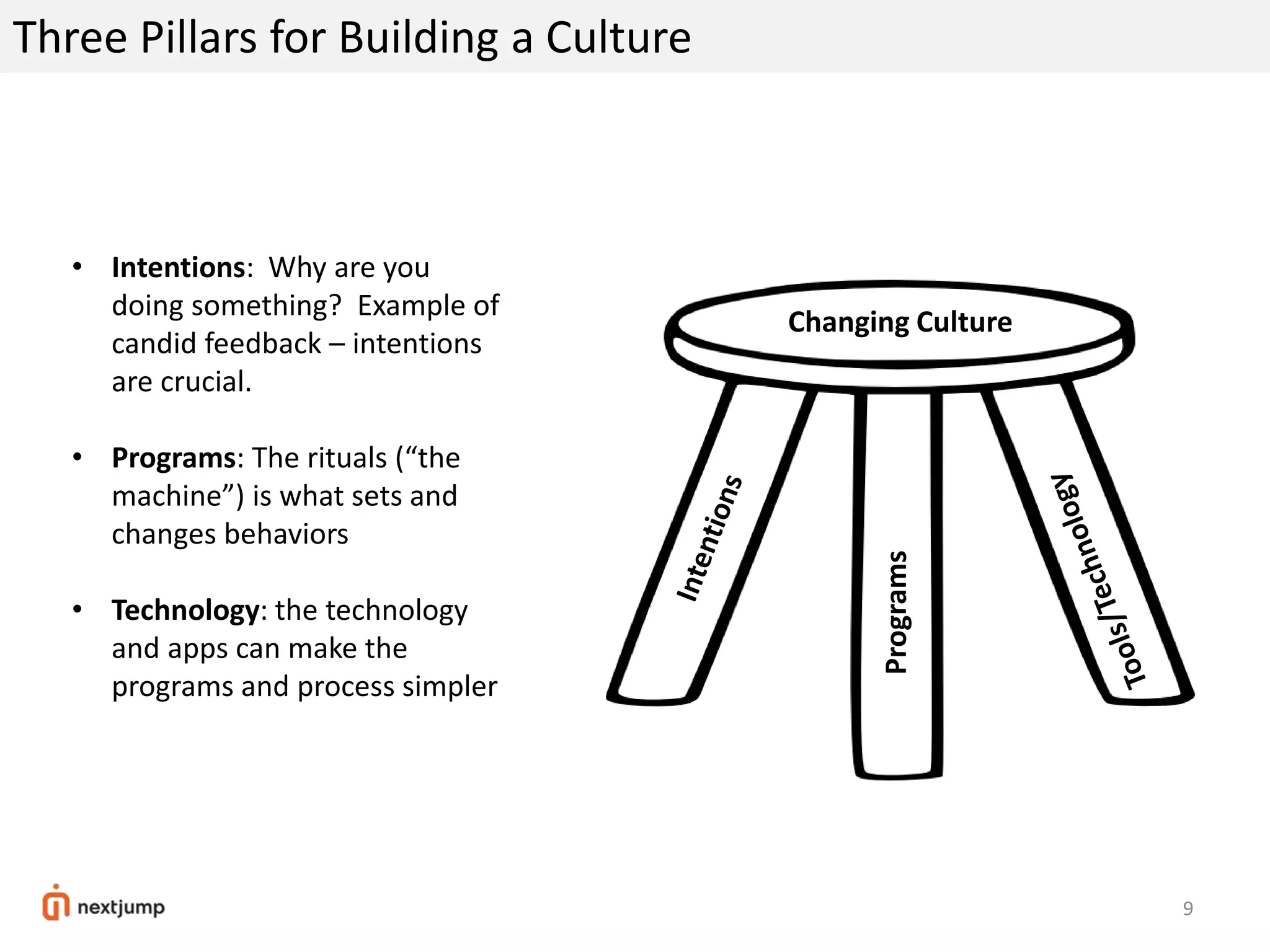
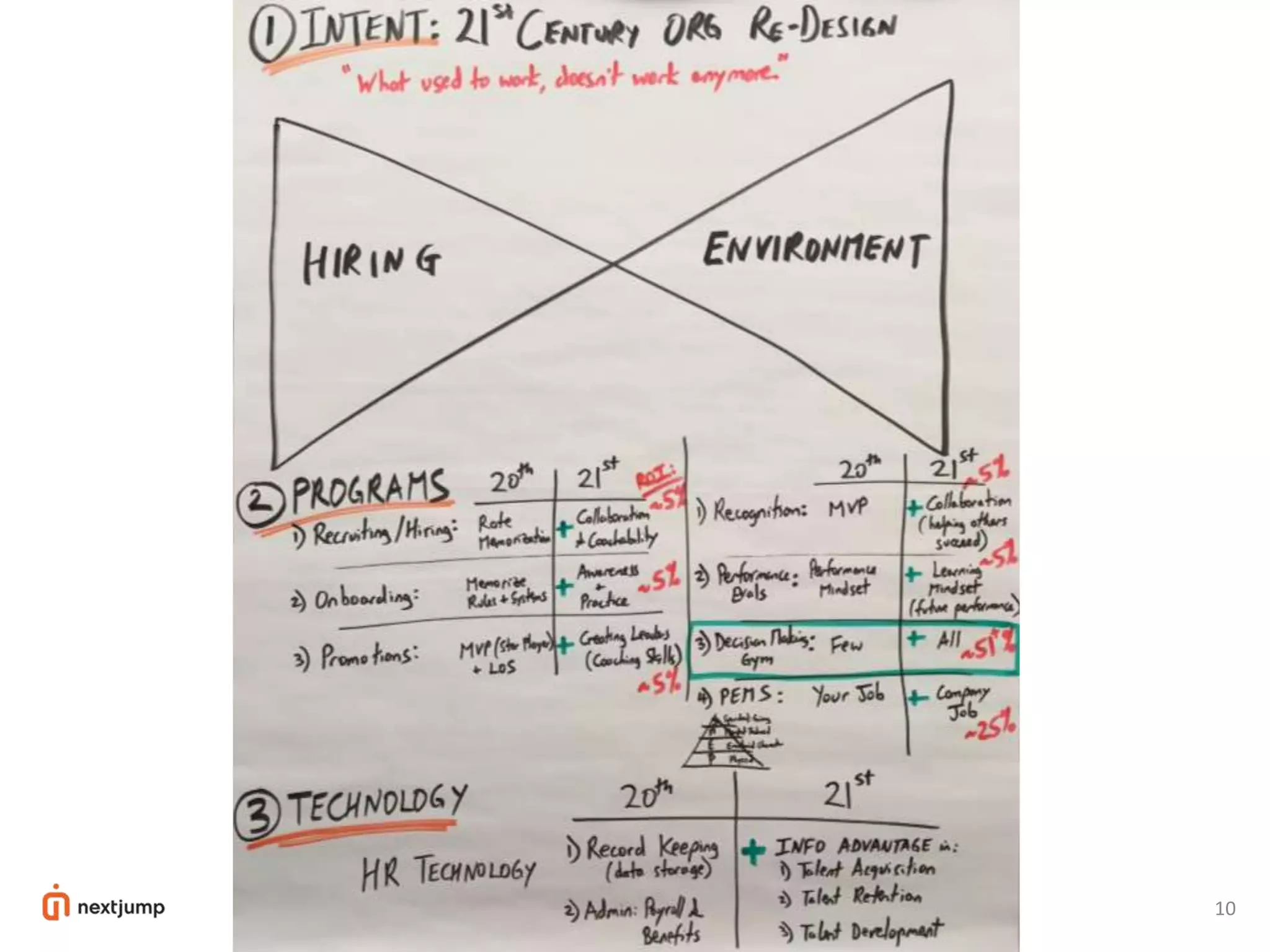
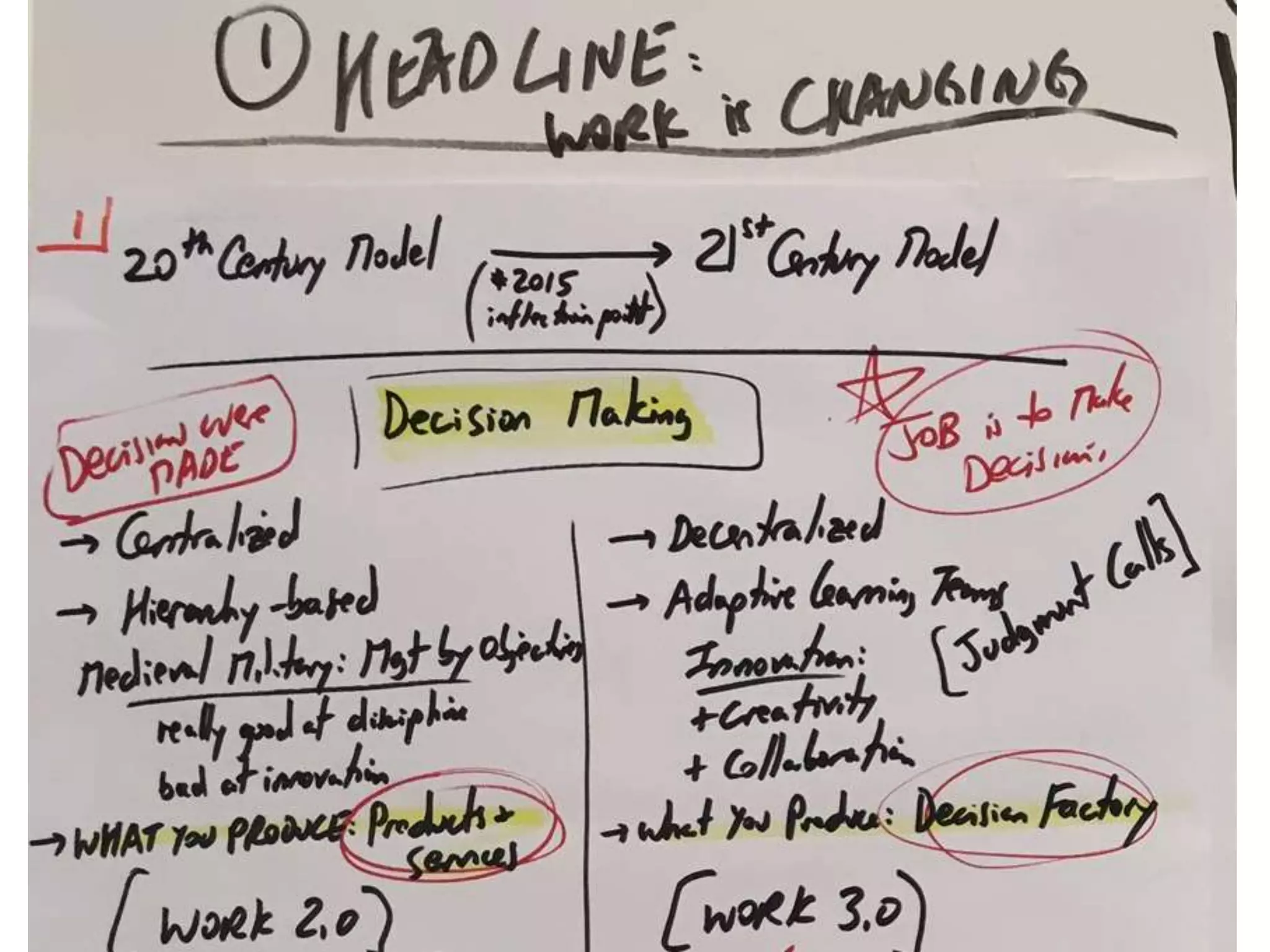
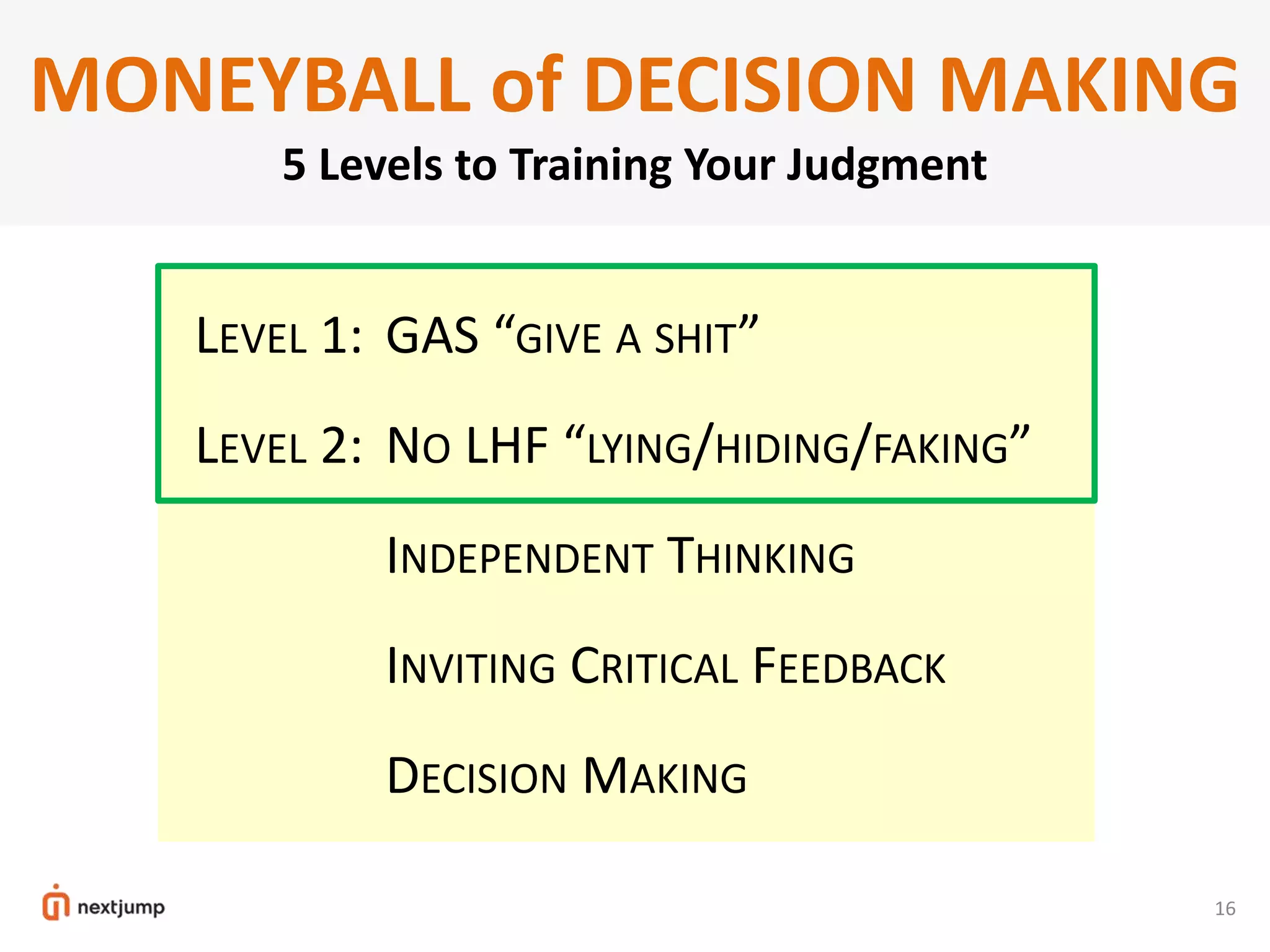
The document discusses organizational design for the 21st century. It argues that 20th century designs focused on centralized authority, but now continuous innovation is needed. Rapidly changing environments can lead to extinction if organizations cannot adapt. The three pillars for building an adaptive culture are intentions, programs, and technology. Decision making must shift from a top-down approach to empowering adaptive learning teams. A "decision making gym" is proposed to train judgment through receiving candid feedback from known groups and anonymously to build a culture of transparency, accuracy and reducing "lying, hiding and faking".





![6
CIA HEAD OF STRATEGY:
“The greatest challenge we are facing as a business, frankly, is
that our business environment is changing much more rapidly
than our ability to adapt. In nature, this sort of thing leads to
extinction.” [we need ADAPTIVE LEARNING TEAMS]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/charliek-171103175209/75/Work-3-0-21st-Century-Org-Re-Design-6-2048.jpg)


![12
EDUCATION 1.0
ISOLATION
FEAR
WORK 1.0
SUBJECTS
[SERVE THE KING]
WORK 2.0
FOLLOWERS
[ASSEMBLY LINE WORKERS]
WORK 3.0
DECISION MAKERS
[ADAPTIVE LEARNING TEAMS]
EDUCATION 2.0
COMPLIANCE
UNIFORMITY
EDUCATION 3.0
CREATIVITY
COLLABORATION
1750 KING FREDERICK THE GREAT 21ST CENTURY: INFO AGE1920 CUBBERLEY: FACTORY MODEL
ORIGINS of EDUCATION = ORIGINS of WORK](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/charliek-171103175209/75/Work-3-0-21st-Century-Org-Re-Design-12-2048.jpg)







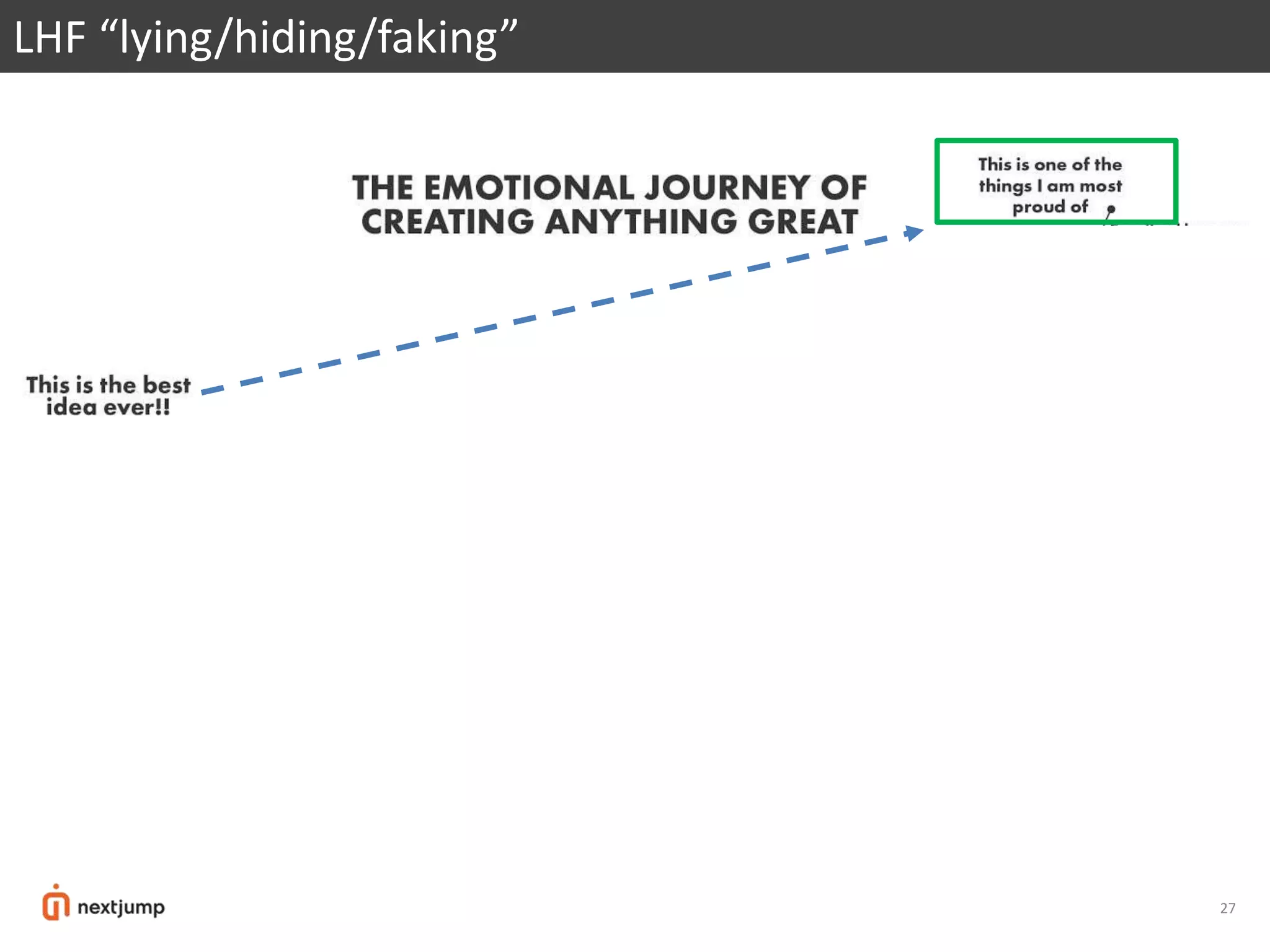
![WHAT is No LHF
TRUTH, AUTHENTICITY, LEAVING NOTHING UNSAID
FACTS, MY THINKING, MY ASSUMPTIONS, GUT/INTUITION, WHAT YOU’RE FEELING
[HIGHEST FORM OF TRANSPARENCY]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/charliek-171103175209/75/Work-3-0-21st-Century-Org-Re-Design-23-2048.jpg)