This document provides an in-depth guide on wp-cli, a command-line interface for managing WordPress installations. It discusses installation requirements, basic and advanced usage, remote command execution, and common troubleshooting issues. The document concludes by emphasizing wp-cli's effectiveness for managing WordPress tasks and encourages users to explore its capabilities.




![>> wp-cli: Inventory stuff
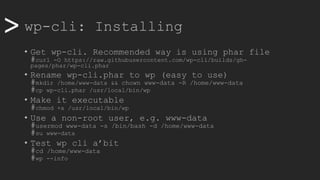
• #wp option --list
• #wp option get blogdescription
• #wp option update blogdescription "Here's to the Joker"
• #wp config list
• #wp checksum core
• #wp checksum plugin akismet
• #wp plugin list --status=inactive [active]
• #wp theme list --status=inactive [active]
• #wp post list (get [1..n])
• Let’s be lazy, make an alias (e.g.)
#alias wp-inactive='wp plugin list --status=inactive && wp theme list --
status=inactive'](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wcamp-wpcli-v1-191102092246/85/WordPress-CLI-in-depth-14-320.jpg)
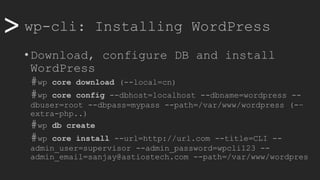
![>> wp-cli: Maintenance stuff
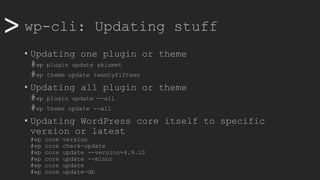
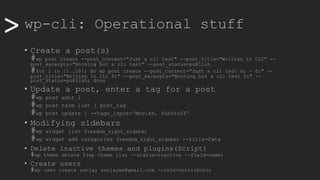
• Enter maintenance mode
#wp maintenance-mode activate [deactive]
• Search and replace
#wp search-replace "CLI" "Command Line Interface" wp_posts --dry-run
#wp search-replace "CLI" "Command Line Interface" wp_posts
• Backing up
#wp export
• Restoring (with a plugin)
#wp plugin install wordpress-importer && wp plugin activate
wordpress-importer
#wp import /home/www-data/wordcampsite1.wordpress.2019-10-31.000.xml
--authors=create](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wcamp-wpcli-v1-191102092246/85/WordPress-CLI-in-depth-18-320.jpg)
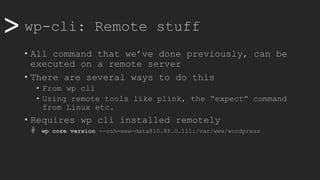
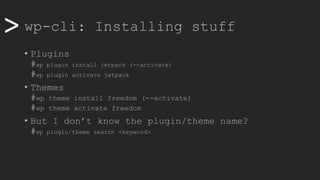
![>> wp-cli: Remote stuff
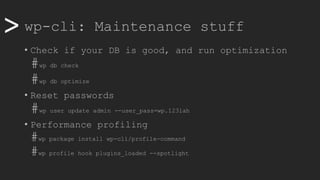
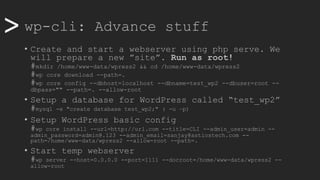
• Passwordless with SSH Keys (go back to root)
• Generate key on local machine
# /usr/bin/ssh-genkey
• Copy that key to remote machine and paste inside
# /usr/bin/ssh-copy-id www-data@10.88.0.111
• Create an alias for easy access, add to .yml file
@prod:
ssh: www-data@10.88.0.111
path: /var/www/wordpress
• Now, let’s update everything on remote using script
#!/bin/bash
myhost=$1
if [[ "$myhost" == "" ]]; then
echo "No host defined"
exit 1
else
wp core version --ssh=www-data@$myhost
wp plugin update --all --ssh=www-data@$myhost
wp theme update --all --ssh=www-data@$myhost
wp core update --ssh=www-data@$myhost
wp core update-db --ssh=www-data@$myhost
wp core version --ssh=www-data@$myhost
exit 0
fi](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wcamp-wpcli-v1-191102092246/85/WordPress-CLI-in-depth-22-320.jpg)