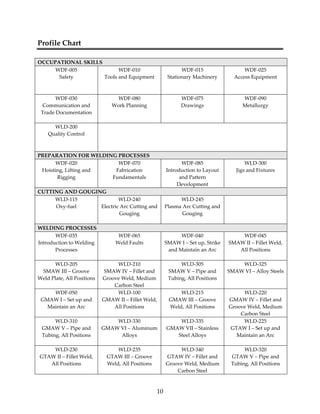
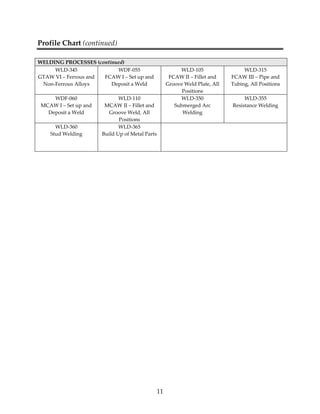
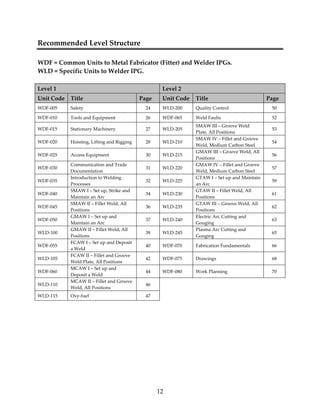
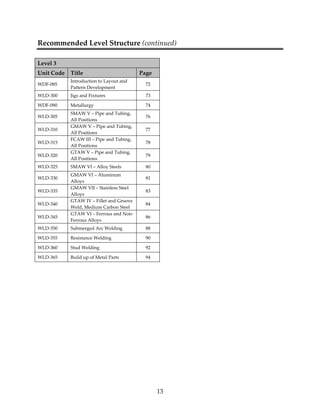
This document provides a summary of the Interprovincial Program Guide for the Welder trade in 3 sentences:
The document acknowledges contributions from various industry and instructional representatives across Canadian jurisdictions who participated in developing the national curriculum for the Welder occupation. It includes a user guide that explains how the program guide is structured and intended to be used, with units of training, outcomes and objectives but no prescribed delivery methods. The program guide also recognizes the guide as the national curriculum for the Welder trade and provides the table of contents that lists the units of training included at each of the three recommended levels for the program.